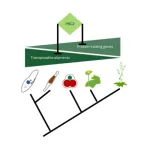
(Press-News.org) Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) was discovered decades ago in Drosophila, where it was found to be a key controller of developmental genes. Further analyses showed that PRC2 modifies chromatin and silences target gene expression. However, the ancestral function of PRC2 - as functioning primarily to control genes during development - was called into question when researchers discovered that PRC2 also plays a role in unicellular species, in which no development takes place. A first hint at PRC2’s original role came from studies in red algae, which found PRC2 left its methylation mark on transposons – jumping genes that move around the genome. Frederic Berger and his research group at the Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology (GMI) decided to follow this cue and, in an international collaboration with researchers at Freie Universität Berlin, University of Cambridge, Nantes University, the National Institute of Genetics (Japan) and Monash University, investigated how PRC2 acts in a range of eukaryotes.
To understand PRC2’s role in the ancestors of eukaryotes, the researchers studied the genomes of three widely distant lineages of eukaryotes: plants, SAR and ophistokonts, the lineage to which humans and fungi belong. All of these eukaryotes contain transposons, mobile genetic elements that can excise themselves from DNA and insert at novel locations – a potential threat to genome stability, hence why transposons have to be silenced. In mutant diatoms, bryophytes and red algae the removal of PRC2 activity caused the loss of silencing of transposable elements.
“These findings show that PRC2 represses transposable elements in these distant lineages, which defines this as a function that arose in the ancestor all three lineages. PRC2’s origin was likely to primarily defend the genome from invasion by transposons. This ancestral function is a profound change in paradigm”, says Frederic Berger, group leader at GMI and the study’s corresponding author.
Over the course of evolution, however, the function of PRC2 gradually shifted from repressing transposons to repressing protein-coding genes, its originally described role. In land plants, the researchers find “fossil TEs” to still be targets for PRC2, which then silences genes in the neighborhood. “In flowering plants, like Arabidopsis, which evolved more recently, remnants of TEs are still present and recruit PRC2 to silence nearby genes”, explains Tetsuya Hisanaga, a postdoctoral researcher in the Berger group and the study’s first author. “We hypothesize that in Arabidopsis, some TEs have been domesticated, becoming elements involved in modulating protein-coding genes.”
END
New origin story for key regulatory gene
PRC2 repressed jumping genes in ancestors of eukaryotes │ Study in Current Biology
2023-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ultrathin films achieve record hydrogen-nitrogen separation
2023-09-21
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of materials that contain nano-sized pores. These pores give MOFs record-breaking internal surface areas, which make them extremely versatile for a number of applications: separating petrochemicals and gases, mimicking DNA, producing hydrogen, and removing heavy metals, fluoride anions, and even gold from water are just a few examples.
In the gas-separation domain, MOFs are particularly interesting for separating hydrogen from nitrogen, which is crucial for clean energy production, fuel cell efficiency, ammonia synthesis, and various ...
Getting ready for bed controlled by specific brain wiring in mice
2023-09-21
The team, led by Imperial College London researchers, uncovered the wiring in mouse brains that leads them to begin nesting in preparation for sleep. Published today in Nature Neuroscience, the study reveals that preparing properly for sleep is likely a hard-wired survival feature – one often neglected or overridden by humans.
We all need to sleep, but since we are unconscious when we do so, it makes sense to fall asleep in a safe and warm place. For some animals this is especially important, as a burrow or nest provides a haven from ...
Mutation-specific peptide vaccine against midline gliomas used in patients for the first time
2023-09-21
Tumor vaccines can help the body fight cancer. These vaccines alert the patient's immune system to proteins that are carrying cancer-typical alterations. Physicians and cancer researchers from Heidelberg and Mannheim have now treated adult patients with advanced midline gliomas, difficult-to-treat brain tumors, with a peptide vaccine for the first time. The vaccine mimicked a mutational change in a histone protein typical of this type of cancer. The vaccine proved to be safe and induced the desired immune responses directed ...
This parasitic plant convinces hosts to grow into its own flesh—it’s also an extreme example of genome shrinkage
2023-09-21
If you happen to come across plants of the Balanophoraceae family in a corner of a forest, you might easily mistake them for fungi growing around tree roots. Their mushroom-like structures are actually inflorescences, composed of minute flowers.
But unlike some other parasitic plants that extend an haustorium into host tissue to steal nutrients, Balanophora induces the vascular system of their host plant to grow into a tuber, forming a unique underground organ with mixed host-parasite tissue. This ...
Mutations in 11 genes associated with aggressive prostate cancer identified in new research
2023-09-21
An international research team led by scientists in the Center for Genetic Epidemiology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center has singled out mutations in 11 genes that are associated with aggressive forms of prostate cancer. These findings come from the largest-scale prostate cancer study ever exploring the exome — that is, the key sections of the genetic code that contain the instructions to make proteins. The scientists analyzed samples from about 17,500 prostate cancer ...
Dinosaur feathers reveal traces of ancient proteins
2023-09-21
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) in Ireland have discovered X-ray evidence of proteins in fossil feathers that sheds new light on feather evolution.
Previous studies suggested that ancient feathers had a different composition to the feathers of birds today. The new research, however, reveals that the protein composition of modern-day feathers was also present in the feathers of dinosaurs and early birds, confirming that the chemistry of feathers originated much earlier than previously thought.
The research, published today in Nature Ecology and Evolution, was led by palaeontologists ...
Researchers develop first method to study microRNA activity in single cells
2023-09-21
MicroRNAs are small molecules that regulate gene activity by binding to and destroying RNAs produced by the genes. More than 60% of all human genes are estimated to be regulated by microRNAs, therefore it is not surprising that these small molecules are involved in many biological processes including diseases such as cancer. To discover the function of a microRNA, it is necessary to find out exactly which RNAs are targeted by it. While such methods exist, they require a lot of material typically in order of millions of cells, to ...
Nanoparticles made from plant viruses could be farmers’ new ally in pest control
2023-09-21
A new form of agricultural pest control could one day take root—one that treats crop infestations deep under the ground in a targeted manner with less pesticide.
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed nanoparticles, fashioned from plant viruses, that can deliver pesticide molecules to soil depths that were previously unreachable. This advance could potentially help farmers effectively combat parasitic nematodes that plague the root zones of crops, all while minimizing costs, pesticide use and environmental toxicity.
Controlling infestations caused by root-damaging nematodes has long been a challenge in agriculture. One reason is that the types of pesticides ...
Social vs. language role: researchers question function of two brain areas
2023-09-21
A research team led by Prof. LIN Nan from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences found that during sentence processing, the neural activity of two canonical language areas, i.e., the left ventral temporoparietal junction (vTPJ) and the lateral anterior temporal lobe (lATL), is associated with social-semantic working memory rather than language processing per se.
The study was published in Nature Human Behaviour on Sept. 21.
Language and social cognition are two deeply interrelated abilities of the human species, but have traditionally been studied ...
Inauguration ceremony of carbon future
2023-09-21
On September 17th, 2023, Carbon Future, an international interdisciplinary journal sponsored by Tsinghua University, has been officially inaugurated.
Carbon Future is an open access, peer-reviewed and international interdisciplinary journal that reports carbon-related materials and processes, including carbon materials, catalysis, energy conversion and storage, as well as low carbon emission process and engineering. The journal is published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, and publicly released on SciOpen, an internationally digital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] New origin story for key regulatory genePRC2 repressed jumping genes in ancestors of eukaryotes │ Study in Current Biology