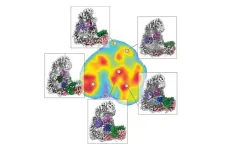
(Press-News.org) Skipping genetic counseling before or after taking a remote screening of inherited risk for ovarian or breast cancer does not increase distress, anxiety or depression, according to a study published Sept. 14 in JAMA Oncology.
“The accepted idea was that you needed genetic counseling before taking a genetic test,” said Dr. Elizabeth Swisher, a gynecologic oncologist at UW Medicine and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “But we’re finding out that many of these protocols actually represent barriers to testing.”
Swisher, the study’s lead author, said the clinical best practices were established more than two decades ago, before these tests became more widespread and available.
“Overall, it was a positive study,” Swisher said. “There were not any indications of emotional stress by leaving out counseling, either before or after the test was taken for those people with negative results.”
The findings emerged from a randomized clinical trial of 3,839 women enrolled between April 2017 and September 2020. The participants agreed to be tested for genetic markers of the two cancers. Some received pre-and post-test counseling, and some did not. Participants rated their distress and anxiety levels before and after testing. Everyone who had a positive finding of increased risk received post-test counseling. Women who did not have a finding of higher cancer risk could skip genetic counseling without increased distress, the study found.
This research was part of the three-year project called MAGENTA, shorthand for Making Genetic Testing Accessible. MAGENTA aimed to assess the impact of eliminating mandatory pre-test for everyone and post-test genetic counseling for patients for whom screening did not indicate a familial pathogenic variation.
Swisher compared the requirement for pre- and post-test counseling to what she witnessed as a medical student in the 1980s, when HIV testing was first offered during the AIDS epidemic.
“You’d get counseled, provide consent for testing and then you’d come back for the results,” she said. “In the end, you’d only see highly educated white men get tested.”
The more diverse populations who needed testing at that time were notably absent, she said. Today, HIV screening can be obtained at your local pharmacy or walk-in clinic. No counseling required.
Some people prefer to get the context provided during individualized counseling before undergoing a genetic test for cancer markers. But many people find it easier, cheaper and more convenient to skip counseling, the study findings showed.
“In this relatively low-risk testing, (skipping counseling) did not appear to cause harm,” Swisher noted, and it increased the portion of individuals who completed the testing.
Ultimately, Swisher said, she’d like to see all adults routinely undergo a comprehensive screening for genetic cancer risk, with individualized follow-up only in the case of a positive result, as with mammograms today.
Swisher is a deputy director of the Fred Hutch/University of Washington/Seattle Children’s Cancer Consortium.
END
Skipping counseling doesn't raise cancer gene test distress
Many people who underwent a cancer screening were content to pass up an accompanying consult, a UW Medicine-led study found.
2023-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nanoparticle vaccine candidate shows promise against emerging tick-borne virus in early studies
2023-09-21
Cleveland Clinic researchers have used nanoparticles to develop a potential vaccine candidate against Dabie Bandavirus, formerly known as Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV), a tick-borne virus that currently has no prevention, treatment or cure.
The patent-pending vaccine uses nanoparticles to carry the antigens that contain instructions for fighting off a virus. Nanoparticle vaccines are designed to effectively deliver antigens at a lower dose with fewer side effects for at-risk ...
University of Minnesota Medical School assistant professor, research team awarded $1 million grant to improve access to legal advocacy for rural and Indigenous communities
2023-09-21
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (09/21/2023) — Michele Statz, PhD, an assistant professor at the University of Minnesota Medical School, Duluth Campus and affiliated faculty with the University of Minnesota Law School’s Human Rights Center, and her research team have been awarded a $1 million grant from the National Science Foundation’s CIVIC Innovation Challenge to improve access to civil justice for rural and Indigenous communities in Alaska. The research team aims to develop a model that can be replicated in other communities across the country.
The “Bridging the Rural Justice Gap: Innovating & Scaling Up Civil Access to Justice in Alaska” ...
Scientists reveal intricate mechanisms cells use to build protein destruction signals
2023-09-21
Within the intricate molecular landscape inside of a cell, the orchestration of proteins demands precise control to avoid disease. While some proteins must be synthesised at specific times, others require timely breakdown and recycling. Protein degradation is a fundamental process that influences cellular activities such as the cell cycle, cell death, or immune response. At the core of this process lies the proteasome, a recycling hub in the cell. The proteasome degrades proteins if they carry a molecular tag formed by a chain of ubiquitin molecules. The task of attaching this tag falls to enzymes known as ubiquitin ligases.
This process, known ...
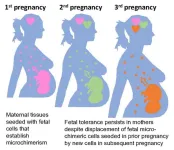
Moms’ ability to ‘remember’ prior pregnancies suggests new strategies for preventing complications
2023-09-21
Scientists have known for decades that pregnancy requires a mother’s body to adjust so that her immune system does not attack the growing fetus as if it were a hostile foreign invader. Yet despite learning a great deal more about the immunology of pregnancy in recent years, a new study shows that the cellular crosstalk between a mother and her offspring is even more complex and long-lasting than expected.
The study was published online Sept. 21, 2023, in the journal Science by a research team led by Sing Sing Way, MD, PhD, Division of Infectious Diseases at Cincinnati Children’s and the Center ...
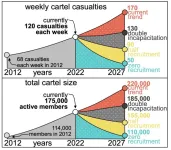
Curbing violence in Mexico: Disrupting cartel recruitment holds the key, a new study finds
2023-09-21
Not through courts and not through prisons. The only way to reduce violence in Mexico is to cut off recruitment. Increasing incapacitation instead leads to both more homicides and cartel members, researcher Rafael Prieto-Curiel from the Complexity Science Hub and colleagues show in a study in Science.
In 2021, approximately 34,000 people died from intentional homicides in Mexico – the equivalent of nearly 27 victims per 100,000 population. This ranks Mexico among the least peaceful countries worldwide.
FIFTH LARGEST EMPLOYER
In order to be able to address this violence ...
Rewiring tumor mitochondria enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and fight cancer
2023-09-21
Immunotherapy, which uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer, is an effective treatment option, yet many patients do not respond to it. Thus, cancer researchers are seeking new ways to optimize immunotherapy so that it is more effective for more people. Now, Salk Institute scientists have found that manipulating an early step in energy production in mitochondria—the cell’s powerhouses—reduces melanoma tumor growth and enhances the immune response in mice.
The study, published in Science on September 21, ...
Two studies indicate CO2 on Europa’s surface originated from within the moon’s internal ocean
2023-09-21
A pair of independent studies, using recent James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observations of carbon dioxide (CO2) ice on Jupiter’s moon Europa, indicate the CO2 originates from a source within the icy body’s subsurface ocean. The findings from both research groups provide new insights into the poorly known composition of Europa’s internal ocean. Beneath a crust of solid water ice, Jupiter’s moon Europa is thought to have a subsurface ocean of salty liquid water. Because of this, Europa is a prime target in the search for life elsewhere in the Solar System. Assessing this deep ...
Global study reveals extensive impact of metal mining contamination on rivers and floodplains, suggesting need for new safeguards to address spike in demand for ‘green’ minerals
2023-09-21
A groundbreaking study, published today in Science, has provided new insights into the extensive impact of metal mining contamination on rivers and floodplains across the world, with an estimated 23 million people believed to be affected by potentially dangerous concentrations of toxic waste.
Led by Professors Mark Macklin and Chris Thomas, Directors of the Lincoln Centre for Water and Planetary Health at the University of Lincoln, UK – working with Dr Amogh Mudbhatkal from the University’s Department of Geography – the study offers a comprehensive understanding of the environmental and health challenges associated with metal mining activities.
Using ...
Regeneration across complete spinal cord injuries reverses paralysis
2023-09-21
When the spinal cords of mice and humans are partially damaged, the initial paralysis is followed by the extensive, spontaneous recovery of motor function. However, after a complete spinal cord injury, this natural repair of the spinal cord doesn’t occur and there is no recovery. Meaningful recovery after severe injuries requires strategies that promote the regeneration of nerve fibers, but the requisite conditions for these strategies to successfully restore motor function have remained elusive.
“Five years ago, we demonstrated that nerve fibers can be regenerated across anatomically complete spinal cord ...
The dance of organ positioning: a tango of three proteins
2023-09-21
In order to keep track of their environment, cells use cilia, antenna-like structures that can sense a variety of stimuli, including the flow of fluids outside the cell. Genetic defects that cause cilia to malfunction and lose their sensory abilities can result in disorders known as “ciliopathies”, including polycystic kidney diseases; but they can also disrupt the correct asymmetric positioning of internal organs during embryonic development – what is known as “organ laterality”.
An example of such asymmetry is the heart, which is typically ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Skipping counseling doesn't raise cancer gene test distressMany people who underwent a cancer screening were content to pass up an accompanying consult, a UW Medicine-led study found.