(Press-News.org) The Buck Institute for Research on Aging and Phenome Health are joining forces in the quest to understand the biology of aging. Phenome Health, a Seattle-based nonprofit research organization led by CEO Lee Hood, MD, PhD, uses a data-driven approach to health and disease that integrates diverse types of biological big data. The new Center for Phenomic Health at the Buck will be co-led by Dr. Hood, who joins the Buck as Chief Innovation Officer and Distinguished Professor, and Eric Verdin, MD, Buck President and CEO.
Dr. Hood is a world-renowned scientist whose technology (automated DNA sequencing) paved the way for the Human Genome Project. He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the National Academy of Medicine. Of the more than 6,000 scientists worldwide who belong to one or more of these academies, Dr. Hood is one of only 20 people elected to all three. Dr. Hood has co-founded 17 biotech companies and the Institute of Systems Biology. His many national and international awards include the Lasker Prize, the Kyoto Prize, and the National Medal of Science. His most recent book, coauthored with long-time collaborator Dr. Nathan Price, is titled The Age of Scientific Wellness: Why the Future of Medicine is Personalized, Predictive, Data-Rich, and in Your Hands. Dr. Hood will continue to run his laboratory at the Institute for Systems Biology which he co-founded in 2000.
“I am delighted to welcome Dr. Hood to the Buck family as our Chief Innovation Officer and Distinguished Professor. The opportunity to form a Center with Lee Hood and his Phenome Health team will be transformational for the Buck,” said Dr. Verdin. “We believe combining the novel computational and human characterization engine of Phenome Health with the Buck’s expertise in geroscience, the biology of aging, has the power to redefine how we age and treat—or prevent altogether—the chronic diseases of aging.”
Phenome Health’s platform combines whole-genome sequencing with phenomic data, including social determinants of health, electronic health records, self-tracking data from wearables and self-assessments, cognitive and psychiatric brain assessments, and clinical samples of the blood, saliva, and microbiome. Using next-generation AI, the team integrates these data to understand the biology of aging, its associated diseases and interventions targeting the aging process. The Center will be the nexus for these two distinguished research partners to advance healthspan for everyone. “I could not be more delighted to enter into this partnership with the Buck,” said Dr. Hood. “The Center is uniquely positioned to translate data into understanding healthy aging, ushering in scientific wellness and ultimately extending each individual’s healthspan.”
About Phenome Health:
Phenome Health is a nonprofit research organization committed to delivering scientific innovation and enacting social change. By taking a data-driven approach to better understanding human health and biology, Phenome Health tackles some of the biggest challenges facing medicine and healthcare today aimed at increasing longevity, detecting disease, and optimizing wellness and prevention. It has assembled an ecosystem of partners and resources to employ a powerful approach to personalized population health. Phenome Health boasts a unique team of biotechnology, health, clinical, psychology, and computational technology experts across the United States. https://phenomehealth.org/
About the Buck Institute:
The Buck’s success will ultimately change healthcare. The Buck Institute for Research on Aging aims to end the threat of age-related diseases for this and future generations by bringing together the most capable and passionate scientists from a broad range of disciplines to identify and impede the ways in which we age. An independent, nonprofit institution, its goal is to increase human healthspan, or the healthy years of life. Globally recognized as the pioneer and leader in efforts to target aging, the number one risk factor for serious chronic diseases including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, cancer, macular degeneration, atherosclerosis (heart attack and stroke), and type 2 diabetes, the Buck wants to help people live better longer. https://www.buckinstitute.org/
END
The Buck Institute and Phenome Health announce major strategic partnership
Famed Scientist Lee Hood will co-direct the Center for Phenomic Health at the Buck-
2023-09-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Revolutionary breakthrough: human stomach micro-physiological system unveiled
2023-09-27
A groundbreaking development in biomedical engineering has led to the creation of a human stomach micro-physiological system (hsMPS), representing a significant leap forward in understanding and treating various gastrointestinal diseases, including stomach cancer. The research team, led by Professor Tae-Eun Park from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Seong-Ho Kong from Seoul National University Hospital, has successfully developed a biomimetic chip that combines organoid and organ-on-a-chip technologies to simulate the complex defense mechanisms of the human gastric mucosa.
Organoids, which mimic human organs using stem cells, have ...
ORNL launches Center for AI Security Research to study AI’s impacts on society, security
2023-09-27
The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory announced the establishment of its Center for AI Security Research, or CAISER, to address threats already present as governments and industries around the world adopt artificial intelligence and take advantage of the benefits it promises in data processing, operational efficiencies and decision-making.
In partnership with federal agencies such as the Air Force Research Laboratory’s Information Directorate and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate ...
Extreme weight loss: Star sheds unexpected amounts of mass just before going supernova
2023-09-27
Cambridge, Mass. — A newly discovered nearby supernova whose star ejected up to a full solar mass of material in the year prior to its explosion is challenging the standard theory of stellar evolution. The new observations are giving astronomers insight into what happens in the final year prior to a star’s death and explosion.
SN 2023ixf is a new Type II supernova discovered in May 2023 by amateur astronomer Kōichi Itagaki of Yamagata, Japan shortly after its progenitor, or origin star, ...
Target: BP™ intitiative helps more than 8.6 million Americans with hypertension improve heart health
2023-09-27
DALLAS, September 27, 2023 — The American Heart Association and American Medical Association (AMA) nationally recognized 1,709 health care organizations (HCOs) — 400 more than in 2022 — for their efforts to prioritize control of their patients’ blood pressure (BP), a leading preventable risk factor for heart disease, stroke and premature death.
According to the 2022 American Heart Association Statistical Update, nearly half of U.S. adults — 121.5 million ...
Tiny CRISPR tool could help shred viruses
2023-09-27
HOUSTON – (Sept. 27, 2023) Small and precise: These are the ideal characteristics for CRISPR systems, the Nobel-prize winning technology used to edit nucleic acids like RNA and DNA.
Rice University scientists have described in detail the three-dimensional structure of one of the smallest known CRISPR-Cas13 systems used to shred or modify RNA and employed their findings to further engineer the tool to improve its precision. According to a study published in Nature Communications, the molecule works differently than other proteins in the same family.
“There are different types of CRISPR systems, and the one ...
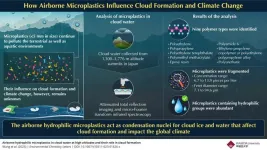
Plastic cloud: New study analyzes airborne microplastics in clouds
2023-09-27
Plastic particles less than 5 mm in size are called “microplastics.” These tiny bits of plastic are often found in industrial effluents, or form from the degradation of bulkier plastic waste. Research shows that large amounts of microplastics are ingested or inhaled by humans and animals alike and have been detected in multiple organs such as lung, heart, blood, placenta, and feces. Ten million tons of these plastic bits end up in the ocean, released with the ocean spray, and find their way into the atmosphere. This implies that microplastics may have become an essential component of clouds, ...
Winners of the ASTRO-Sumitomo Pharma-Pfizer Alliance new combination therapy challenge announced
2023-09-27
ARLINGTON, Va., September 27, 2023 — The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) today announced the three winning research proposals for the 2022 ASTRO-Myovant Sciences (now known as Sumitomo Pharma)-Pfizer Alliance New Combination (Relugolix-Radiation) Therapy Challenge. The Challenge aims to identify research that addresses ways prostate cancer treatments can be improved with the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor antagonist relugolix in patients who received radiation therapy.
The Challenge invited researchers to propose the study of relugolix in different scenarios: ...
New evidence for sub-network specializations within the Default Mode Network and the Special Role of Facial Movements in Brain Activation and Self-Perception
2023-09-27
Recent advancements in neuroscience have unveiled new insights into the neural processes responsible for self-referential cognition. This research has brought particular attention to a critical neural network known as the Default Mode Network (DMN), comprising brain regions such as the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), posterior cingulate cortex, temporoparietal junction (TPJ), and both lateral and medial temporal lobes.
Central to self-related processing, is the information associated with one’s ...
Ultrasound enables gene delivery throughout the brain
2023-09-27
HOUSTON – (Sept. 27, 2023) – Rice University researchers tested the safety and feasibility of gene delivery to multiple brain regions using a noninvasive, ultrasound-based technique in rodents, and their findings suggest that the efficiency of gene delivery improves within each targeted site when more sites are opened.
Shirin Nouraein, a doctoral student working in the lab of Rice bioengineer Jerzy Szablowski, is the lead author on the study recently published in the journal Gene Therapy.
The paper, “Acoustically Targeted Noninvasive Gene Therapy in Large Brain Volumes,” ...
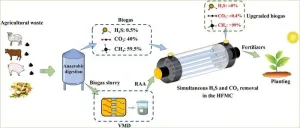
Elevating biogas upgrading performance on renewable aqueous ammonia solution via a novel “membrane method”
2023-09-27
Biogas is usually produced by anaerobic digestion of organic waste such as animal manures and straw wastes, which is a typical green renewable energy and can be used as a fuel for power generation and heat production. China has owned large scale of biogas production, with an annual output of about 15 billion m3 biogas, and the biogas development and utilization provide a new choice for coping with the energy crisis. Factually, biogas contains about 60% CH4 and about ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] The Buck Institute and Phenome Health announce major strategic partnershipFamed Scientist Lee Hood will co-direct the Center for Phenomic Health at the Buck-