(Press-News.org) One treatment each of two psychedelic drugs lowered depression and anxiety and improved cognitive functioning in a sample of U.S. special operations forces veterans who sought care at a clinic in Mexico, according to a new analysis of the participants’ charts.
The treatment included a combination of ibogaine hydrochloride, derived from the West African shrub iboga, and 5-MeO-DMT, a psychedelic substance secreted by the Colorado River toad. Both are designated as Schedule I drugs under the U.S. Controlled Substances Act.
In addition to relieving symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), the combined treatment also alleviated cognitive impairment linked to traumatic brain injury – which stood out to researchers from The Ohio State University who led the chart-review analysis. Many special operations forces veterans seeking treatment for complex psychiatric symptoms do not respond to more traditional therapies.
“What sets this group apart from some other veterans and civilians is that often, they are exposed to repeated traumatic events as a routine part of their jobs. This build-up of exposure to these difficulties seems to produce a cluster of challenges that include traumatic brain injury, which we know in and of itself predisposes people to mental health problems,” said lead author Alan Davis, associate professor and director of the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education (CPDRE) in Ohio State’s College of Social Work.
“So the fact that we saw that there were improvements in cognitive functioning linked to brain injury were probably the most striking results, because that’s something we didn’t predict and it’s very new and novel in terms of how psychedelics might help in so many different domains.”
The study is published in the American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse.
Most of the veterans attending the clinic retreat program had been on active duty after 9/11 and reported seeking care for memory problems, brain injury, depression, anxiety, PTSD, sleep problems, anger and fatigue. Head injuries were reported by 86% of attendees, most of whom attributed memory problems, irritability, disordered sleep and ringing in the ears to those long-ago head traumas.
Eighty-six veterans completed pre-treatment questionnaires assessing a range of mental health symptoms as well as satisfaction with life, anger levels and suicidality. Each attendee received a single oral ibogaine hydrochloride dose and, on a separate day, at least three incremental inhalation doses adding up to 50 milligrams of 5-MeO-DMT, also commonly called Five or Bufo. Preparation and reflection sessions preceded and followed each treatment.
Overall, participants reported large improvements in self-reported PTSD symptoms, depression, anxiety, insomnia severity and anger, as well as a significant increase in satisfaction with life, from pre-treatment to the one-month follow-up, and sustained benefits at the three- and six-month follow-ups. Additional reported improvements that continued for six months included reductions in disability and post-concussive symptoms, and very large increases in psychological flexibility and cognitive functioning.
Davis said the improved cognitive functioning warrants more research into whether better thinking results from lowered mental health symptoms or biological changes to signaling in the brain, or a mixture of both types of effects. And they noted that changes to psychological flexibility – one’s capacity to act in ways that are consistent with their values regardless of whatever internal or external experience they might have – have been found in previous research to be connected to insightful and mystical psychedelic experiences.
“I think we’re seeing a similar picture emerging here where the more one is psychologically flexible, the more likely it is that one’s mental health symptoms will be reduced or ameliorated,” Davis said.
Most attendees also reported moderate to strong desirable changes across a range of attitudes, behaviors and relationships. One month after treatment, almost half reported the psychedelic experience was the most spiritually significant (48.6%) or psychologically insightful (42.9%) of their lives, and 17.1% called it the most difficult or challenging experience in their life.
Davis and colleagues took a conservative approach to analyzing outcome data, building in an assumption that attendees who didn’t complete all of the follow-up surveys may not have gotten the relief they had hoped for from the treatment. But they said finding that a population of veterans with complicated trauma histories can benefit from psychedelic therapy supports the importance of continuing to test psychedelic-assisted therapies in U.S. clinical trials.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy is currently being studied at Ohio State for the treatment of PTSD among military veterans.
This work was funded by Veterans Exploring Treatment Solutions. The authors are also supported by the Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research at Johns Hopkins University, the CPDRE, the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
Co-authors of the study include Yitong Xin and Nathan Sepeda of Ohio State and Lynnette Averill of Baylor College of Medicine and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs.
#
Contact: Alan Davis, Davis.5996@osu.edu
Written by Emily Caldwell, Caldwell.151@osu.edu; 614-292-8152
END
HOUSTON – (Oct. 5, 2023) – An interdisciplinary team of Rice University scientists has won a $1.9 million National Science Foundation grant for research on materials that could serve as the basis for next-generation energy-efficient computing devices.
The team ⎯ led by Kaiyuan Yang and including co-investigators Ramamoorthy Ramesh, Yimo Han, Douglas Natelson, Shengxi Huang and Lane Martin ⎯ will focus on multiferroics, materials with distinctive electric and magnetic properties that carry “transformative technological potential,” ...
AMES, Iowa – The foundation of a house remains, the basement ripped open and exposed, with the rest of the house blown away. A brick-veneered bank building partially caved in. A collapsed high school gym. Gravestones knocked over. Debris piercing a building.
Partha Sarkar kept hitting next, scrolling through the photo evidence of the destruction he gathered and assessed the day after an EF5 tornado ripped through Parkersburg on May 25, 2008.
Then Sarkar, professor and interim chair of aerospace engineering at Iowa State University, opened a photo showing a house ...
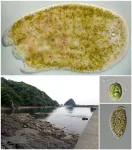
Acoels have been found to host a wide diversity of symbiotic, photosynthetic microalgae.
Animals and plants need energy. Some animals get energy by eating other animals, and many plants harvest the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis. However, in the ocean, there exists a remarkable group of small, worm-like animals called acoels that do both—some acoels form relationships (symbiosis) with single-celled, photosynthetic microalgae.
A study by Assistant Professor Kevin Wakeman and his undergraduate student, Siratee Riewluang, at Hokkaido University, Japan, has shed some light on the biodiversity underpinning symbiotic relationships between acoels and microalgae. ...
Bumblebees have a remarkably successful method for fighting off Asian hornets, new research shows.
When attacked, buff-tailed bumblebees drop to the ground – taking the hornets down with them. This either causes the hornet to lose its grip, or the bee raises its sting and tussles until the hornet gives up.
University of Exeter scientists witnessed over 120 such attacks, and were stunned to find that bumblebees fought off the hornets every time.
Despite this, they found bumblebee colonies had reduced growth rates in ...
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) has conceived of and launched a new artificial intelligence (AI) fellowship in just two months — record speed — to support leaders in Congress as they craft legislation, in particular policies related to emerging opportunities and challenges with AI. Capitol Hill’s surging interest in AI policy follows the public release of ChatGPT and other generative AI tools.
The STPF Rapid Response Cohort in AI operates under the AAAS Science & Technology Policy Fellowships (STPF) program and is part of the 51st class of 276 scientists and engineers placed across ...
A new paper in Molecular Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, for the first time provides a comprehensive set of genomic resources for pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, that researchers believe will be integral for protecting these threatened mammals.
Pangolins, which are found in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, are the only mammals covered in scales. They are trafficked at record numbers for their meat and supposed medicinal properties. The animals are also at risk due to widespread deforestation of their native habitats. Pangolins are made up of eight surviving species ...
Eating more plant-based meals is better for our health and better for the planet. But cultural preferences are significant barriers to reducing meat consumption - especially for men, who are underrepresented among vegans and vegetarians. Studies have found that eating meat is associated with masculinity, and that gender stereotypes label plant-based diets as suitable for women but not men. So is it possible to change the perception of plant-based food with marketing, and convince men to eat more of it?
“Men might be less inclined to consume vegan food due to the need to perform gender,” said Alma Scholz, lead author of a new study published in Frontiers in Communication. ...
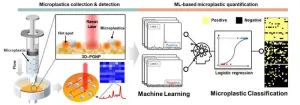
A research team led by Dr. Ho Sang Jung of the Department of Nano-Bio Convergence at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, in collaboration with the KOTITI Testing & Research Institute, has developed the world's first technology to rapidly and highly sensitively detect microplastics(MPs) in the field, which are well known to cause human and genetic toxicity through environmental pollution and the food chain.
The on-site applicable MPs detection technology developed ...
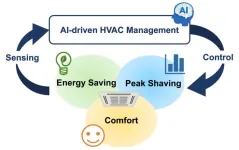
Osaka, Japan – As organizations work to reduce their energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, one area that remains to be optimized is indoor heating and cooling. In fact, HVAC – which stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning – represents, on average, about 40% of a building’s total energy use. Methods that conserve electricity while still providing a comfortable indoor environment for workers could make a significant difference in the fight against climate change.
Now, researchers from Osaka University have demonstrated significant energy savings through the application of a new, AI-driven algorithm ...
A new study conducted by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center suggests that enhanced infection prevention and control (IPC) measures implemented to address the COVID-19 pandemic contributed to a significant decrease in many healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and a reduction in respiratory viral infections (RVIs). The findings, published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC), provide some of the first evidence that strict pandemic-related IPC interventions reduced HAI rates among vulnerable patient populations.
“Previous, large-scale ...