Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology study shows promise for patients with muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
2023-10-05
(Press-News.org) The Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology today announced that the Alliance Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) determined that the phase III AMBASSADOR (A031501) trial met one of its dual primary endpoints of disease-free survival (DFS) for the adjuvant treatment of patients with localized muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma (MIUC) and locally advanced urothelial carcinoma. At a pre-specified interim analysis review, pembrolizumab demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in DFS versus observation in these patients after surgery. The trial will continue to evaluate its other dual primary endpoint of overall survival (OS). Detailed results from the trial will be presented at an upcoming scientific meeting and discussed with regulatory authorities.
“Patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after radical surgery are at high risk of disease recurrence and metastases. Pembrolizumab versus observation significantly reduced the risk of disease recurrence for these patients,” said Andrea B. Apolo, MD, study chair for the AMBASSADOR trial and Head of the Bladder Cancer Section of the Genitourinary Malignancies Branch and Director of the Bladder Cancer and Genitourinary Tumors Multidisciplinary Clinic in the Center for Cancer Research of the National Cancer Institute. “This is long awaited data in the bladder cancer community, and we are thrilled with the positive results of the AMBASSADOR study and what this means for our patients with bladder cancer.”
The safety profile of pembrolizumab in this trial was consistent with that observed in previously reported studies, and no new safety signals were identified.
"The AMBASSADOR trial provides critically important data to contextualize the role of adjuvant immune checkpoint blockade in the treatment of patients with muscle-invasive urothelial cancer once again demonstrating the clinical and scientific impact of the National Cancer Institute's National Clinical Trials Network Treatment Studies," noted Matthew Galsky, MD, Professor of Medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Associate Director for Translational Research at The Tisch Cancer Institute. Dr. Galsky is also Co-Chair of the Genitourinary Committee for the Alliance.
AMBASSADOR (A031501) is a randomized, open-label phase III trial evaluating pembrolizumab versus observation for the adjuvant treatment of localized MIUC and locally advanced urothelial carcinoma. The dual primary endpoints are OS and DFS, and secondary endpoints include OS and DFS in PD-L1 positive and negative patients. The trial enrolled 702 patients who were randomized to receive pembrolizumab (200 mg intravenously every three weeks for up to 18 cycles) or undergo observation.
“Cancer recurrence after surgery can be a devastating event for patients. In this study, pembrolizumab treatment led to a significant improvement in disease-free survival compared to observation, without any new safety signals,” said Jonathan Rosenberg, MD, Chief of Genitourinary Oncology Service in the Division of Solid Tumor Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and Co-Chair the Genitourinary Committee for the Alliance. “These results will help us further understand the role of immune checkpoint blockade in this patient population.”
It is estimated that approximately 82,290 people in the U.S. will be diagnosed with bladder cancer in 2023. Globally, there were approximately 573,000 new cases and 212,000 deaths from bladder cancer in 2020. Muscle-invasive bladder cancer is bladder cancer that has spread into the deep muscle of the bladder wall, and locally advanced urothelial cancer is cancer that begins in the urothelial cells and has spread from where it started to nearby tissue or lymph nodes. Despite surgery, up to 50% of patients with bladder cancer experience recurrence within 12 months.
AMBASSADOR is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, and is being led and conducted by the NCI funded Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology with participation from the NCI funded national clinical trials network (NCTN) as part of Merck’s collaboration with the NCI through a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA). To learn more about the AMBASSADOR trial, visit ClinicalTrials.gov.
# # #
Reference: Alliance A031501: Phase III randomized adjuvant study of pembrolizumab in muscle invasive and locally advanced urothelial carcinoma (AMBASSADOR) versus observation. A full description of this clinical trial can be found at https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03244384.
The Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology develops and conducts clinical trials with promising new cancer therapies, and utilizes the best science to develop optimal treatment and prevention strategies for cancer, as well as research methods to alleviate side effects of cancer and cancer treatments. The Alliance is part of the National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and serves as a research base for the NCI Community Research Oncology Program (NCORP). The Alliance comprises nearly 10,000 cancer specialists at hospitals, medical centers, and community clinics across the United States and Canada. To learn more, visit www.AllianceforClinicalTrialsinOncology.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-05
One treatment each of two psychedelic drugs lowered depression and anxiety and improved cognitive functioning in a sample of U.S. special operations forces veterans who sought care at a clinic in Mexico, according to a new analysis of the participants’ charts.
The treatment included a combination of ibogaine hydrochloride, derived from the West African shrub iboga, and 5-MeO-DMT, a psychedelic substance secreted by the Colorado River toad. Both are designated as Schedule I drugs under the U.S. Controlled Substances Act.
In addition to relieving symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), ...
2023-10-05
HOUSTON – (Oct. 5, 2023) – An interdisciplinary team of Rice University scientists has won a $1.9 million National Science Foundation grant for research on materials that could serve as the basis for next-generation energy-efficient computing devices.
The team ⎯ led by Kaiyuan Yang and including co-investigators Ramamoorthy Ramesh, Yimo Han, Douglas Natelson, Shengxi Huang and Lane Martin ⎯ will focus on multiferroics, materials with distinctive electric and magnetic properties that carry “transformative technological potential,” ...
2023-10-05
AMES, Iowa – The foundation of a house remains, the basement ripped open and exposed, with the rest of the house blown away. A brick-veneered bank building partially caved in. A collapsed high school gym. Gravestones knocked over. Debris piercing a building.
Partha Sarkar kept hitting next, scrolling through the photo evidence of the destruction he gathered and assessed the day after an EF5 tornado ripped through Parkersburg on May 25, 2008.
Then Sarkar, professor and interim chair of aerospace engineering at Iowa State University, opened a photo showing a house ...
2023-10-05
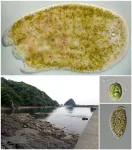
Acoels have been found to host a wide diversity of symbiotic, photosynthetic microalgae.
Animals and plants need energy. Some animals get energy by eating other animals, and many plants harvest the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis. However, in the ocean, there exists a remarkable group of small, worm-like animals called acoels that do both—some acoels form relationships (symbiosis) with single-celled, photosynthetic microalgae.
A study by Assistant Professor Kevin Wakeman and his undergraduate student, Siratee Riewluang, at Hokkaido University, Japan, has shed some light on the biodiversity underpinning symbiotic relationships between acoels and microalgae. ...
2023-10-05
Bumblebees have a remarkably successful method for fighting off Asian hornets, new research shows.
When attacked, buff-tailed bumblebees drop to the ground – taking the hornets down with them. This either causes the hornet to lose its grip, or the bee raises its sting and tussles until the hornet gives up.
University of Exeter scientists witnessed over 120 such attacks, and were stunned to find that bumblebees fought off the hornets every time.
Despite this, they found bumblebee colonies had reduced growth rates in ...
2023-10-05
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) has conceived of and launched a new artificial intelligence (AI) fellowship in just two months — record speed — to support leaders in Congress as they craft legislation, in particular policies related to emerging opportunities and challenges with AI. Capitol Hill’s surging interest in AI policy follows the public release of ChatGPT and other generative AI tools.
The STPF Rapid Response Cohort in AI operates under the AAAS Science & Technology Policy Fellowships (STPF) program and is part of the 51st class of 276 scientists and engineers placed across ...
2023-10-05
A new paper in Molecular Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, for the first time provides a comprehensive set of genomic resources for pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, that researchers believe will be integral for protecting these threatened mammals.
Pangolins, which are found in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, are the only mammals covered in scales. They are trafficked at record numbers for their meat and supposed medicinal properties. The animals are also at risk due to widespread deforestation of their native habitats. Pangolins are made up of eight surviving species ...
2023-10-05
Eating more plant-based meals is better for our health and better for the planet. But cultural preferences are significant barriers to reducing meat consumption - especially for men, who are underrepresented among vegans and vegetarians. Studies have found that eating meat is associated with masculinity, and that gender stereotypes label plant-based diets as suitable for women but not men. So is it possible to change the perception of plant-based food with marketing, and convince men to eat more of it?
“Men might be less inclined to consume vegan food due to the need to perform gender,” said Alma Scholz, lead author of a new study published in Frontiers in Communication. ...
2023-10-05
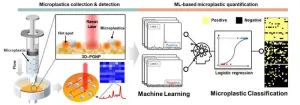
A research team led by Dr. Ho Sang Jung of the Department of Nano-Bio Convergence at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, in collaboration with the KOTITI Testing & Research Institute, has developed the world's first technology to rapidly and highly sensitively detect microplastics(MPs) in the field, which are well known to cause human and genetic toxicity through environmental pollution and the food chain.
The on-site applicable MPs detection technology developed ...
2023-10-05
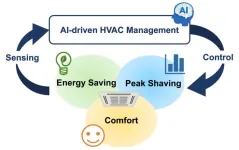
Osaka, Japan – As organizations work to reduce their energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, one area that remains to be optimized is indoor heating and cooling. In fact, HVAC – which stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning – represents, on average, about 40% of a building’s total energy use. Methods that conserve electricity while still providing a comfortable indoor environment for workers could make a significant difference in the fight against climate change.
Now, researchers from Osaka University have demonstrated significant energy savings through the application of a new, AI-driven algorithm ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology study shows promise for patients with muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma