(Press-News.org) A team of New York University computer scientists has created a neural network that can explain how it reaches its predictions. The work reveals what accounts for the functionality of neural networks—the engines that drive artificial intelligence and machine learning—thereby illuminating a process that has largely been concealed from users.
The breakthrough centers on a specific usage of neural networks that has become popular in recent years—tackling challenging biological questions. Among these are examinations of the intricacies of RNA splicing—the focal point of the study—which plays a role in transferring information from DNA to functional RNA and protein products.
“Many neural networks are black boxes—these algorithms cannot explain how they work, raising concerns about their trustworthiness and stifling progress into understanding the underlying biological processes of genome encoding,” says Oded Regev, a computer science professor at NYU’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author of the paper, which appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. “By harnessing a new approach that improves both the quantity and the quality of the data for machine-learning training, we designed an interpretable neural network that can accurately predict complex outcomes and explain how it arrives at its predictions.”
Regev and the paper’s other authors, Susan Liao, a faculty fellow at the Courant Institute, and Mukund Sudarshan, a Courant doctoral student at the time of the study, created a neural network based on what is already known about RNA splicing.
Specifically, they developed a model—the data-driven equivalent of a high-powered microscope—that allows scientists to trace and quantify the RNA splicing process, from input sequence to output splicing prediction.
“Using an ‘interpretable-by-design’ approach, we’ve developed a neural network model that provides insights into RNA splicing—a fundamental process in the transfer of genomic information,” notes Regev. “Our model revealed that a small, hairpin-like structure in RNA can decrease splicing.”
The researchers confirmed the insights their model provides through a series of experiments. These results showed a match with the model’s discovery: Whenever the RNA molecule folded into a hairpin configuration, splicing was halted, and the moment the researchers disrupted this hairpin structure, splicing was restored.
The research was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation (MCB-2226731), the Simons Foundation, the Life Sciences Research Foundation, an Additional Ventures Career Development Award, and a PhRMA Fellowship.
END
Researchers create a neural network for genomics—one that explains how it achieves accurate predictions
Breakthrough offers new insights into what lies behind machine learning
2023-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Astronomers discover first step toward planet formation
2023-10-06
Astronomers have gotten very good at spotting the signs of planet formation around stars. But for a complete understanding of planet formation, we also need to study examples where planet formation has not yet started. Looking for something and not finding it can be even more difficult than finding it sometimes, but new detailed observations of the young star DG Taurus show that it has a smooth protoplanetary disk without signs of planet formation. This successful non-detection of planet formation may indicate ...
Faster growth of the placenta is linked to increased risk of preeclampsia
2023-10-06
Research sheds light on how genetics influences the growth of the placenta and reveals a link to increased risk of disease in the mother.
The placenta is an organ which grows in the womb alongside the foetus, which is attached to it by the umbilical cord. It is the only organ that contain tissue from both mother and child. The placenta provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing foetus and removes waste as the baby develops. A poorly functioning placenta is associated with pregnancy complications, and later risk of disease in the child.
Despite its key role, little is yet known ...
Integrated chronic care in Africa can improve outcomes and save money
2023-10-06
Across Africa about two million premature deaths each year are caused by the effects of diabetes and hypertension.
In contrast, most people living with HIV are in regular care and virally suppressed, and HIV mortality rates have fallen five-fold since their peak of 2 million deaths annually in the early 2000s to less than 500,000 in 2022.
Dr Josephine Birungi, a co-author and Graduate Researcher-Public Health at La Trobe University, said that the similarities in chronic disease management of HIV and other chronic conditions should make integrated clinics beneficial.
“The only difference is the medicine they take. We’re seeing ...
ObesityWeek® features hundreds of innovative scientific abstracts
2023-10-06
ROCKVILLE, Md.— Neary 240 scientific abstracts covering a variety of topics such as anti-obesity medications, body mass index and pediatric obesity will be featured at the 41st Annual Meeting of The Obesity Society’s (TOS) at ObesityWeek® 2023. This in-person event will take place Oct. 14–17, 2023 at the Kay Bailey Hutchison Convention Center in Dallas, Texas.
Innovative scientific research results will be presented in both oral and poster formats. These communications provide notable exposure and recognition for studies and authors, and represent cutting-edge research in obesity prevention and ...
Colombian National Cancer Institute signs MOU with BGI Genomics to combat cancer
2023-10-06
On October 2, 2023, BGI Genomics signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Colombian National Cancer Institute (INC or Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia). This collaboration, which aims to foster research and further develop cutting-edge solutions based on genetic sequencing for early diagnosis of cervical and colorectal cancer, reflects a shared dedication to enhancing health outcomes in the region.
The MoU was formally inked at INC facilities by Dr. Carolina Wiesner, INC Director, and Mr. Rainer Perez, alternate legal representative of BGI Genomics in Colombia. Mr. Marco Antonio Rincón, Latin America Business Director, BGI Genomics, notes: ...
Ginger pigment molecules found in fossil frogs
2023-10-06
UCC palaeontologists discover molecular evidence of phaeomelanin, the pigment that produces ginger colouration.
“This will paint a more accurate picture of ancient animal colour.”
Phaeomelanin is now toxic to animals – discovery may be first step in understand its evolution.
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) have found the first molecular evidence of phaeomelanin, the pigment that produces ginger colouration, in the fossil record.
The new study reports ...
Scientists discover ‘long colds’ may exist, as well as long Covid
2023-10-06
A new study from Queen Mary University of London, published in The Lancet’s EClinicalMedicine, has found that people may experience long-term symptoms —or ‘long colds’—after acute respiratory infections that test negative for COVID-19.
Some of the most common symptoms of the ‘long cold’ included coughing, stomach pain, and diarrhea more than 4 weeks after the initial infection. While the severity of an illness appears to be a key driver of risk of long-term symptoms, ...
Our sense of smell changes the colors we see, show scientists
2023-10-06
Our five senses bombard us with environmental input 24/7. One way our brain makes sense of this abundance of information is by combining information from two or more senses, such as between smells and the smoothness of textures, pitch, color, and musical dimensions. This sensory integration also causes us to associate higher temperatures with warmer colors, lower sound pitches with less elevated positions, and colors with the flavor of particular foods – for example, the taste of oranges with the color of the same name.
Now, a study in Frontiers in Psychology has shown experimentally that such unconscious 'crossmodal' ...
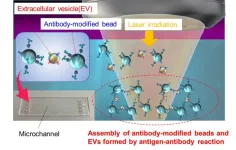
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles
2023-10-06
Osaka, Japan - Can particles as minuscule as viruses be detected accurately within a mere 5 minutes? Osaka Metropolitan University scientists say yes, with their innovative method for ultrafast and ultrasensitive quantitative measurement of biological nanoparticles, opening doors for early diagnosis of a broad range of diseases.
Nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs) including exosomes, with diameters of 50–150 nm, play essential roles in intercellular communication and have garnered attention as biomarkers for various diseases and drug delivery capsules. Consequently, the rapid and sensitive detection of nanoscale EVs from trace samples is ...
Fathers’ parental leave might protect men against alcohol-related morbidity
2023-10-06
Men who have been on parental leave have a significantly reduced risk of being hospitalized due to alcohol consumption. This is shown by a study published in Addiction from researchers at the Department of Public Health Sciences, Stockholm University.
The aim of the study was to assess whether fathers’ parental leave influences alcohol-related morbidity and mortality. In order to try to find out if that is the case, the researchers have investigated the effects of parental leave policy that was implemented in Sweden in 1995. The policy encouraged fathers to use parental leave by reserving 30 days of leave for their use alone and resulted in the proportion ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
[Press-News.org] Researchers create a neural network for genomics—one that explains how it achieves accurate predictionsBreakthrough offers new insights into what lies behind machine learning