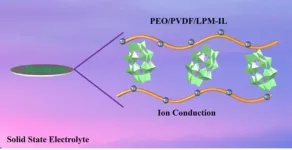
Polyoxometalates (POMs) containing charged lithium ions combined with ionic liquids, increase the ion conductivity of a solid-state electrolyte membrane.
Solid-state lithium-ion batteries depend on the movement of ions (charged atoms) in the solid, rather than liquid, state to either charge or discharge the battery. These solid-state electrolytes are safer, more cost efficient and capable of higher energy densities than batteries that rely on liquid electrolyte solutions, but suffer from low ionic conductivity, or movement of ions, and poor thermal stability. A new composite solid electrolyte (CSE) membrane was synthesized using lithium salts and an ionic liquid to improve the dissociation, and therefore conductivity, of charged lithium atoms in a solid-state electrolyte battery.
Polyoxometalates (POMs) are clusters of metal and oxygen atoms with properties that are determined by the well-defined structure of the POM atom cluster. Researchers from Northeast Normal University recently introduced a POM-based lithium salt, Li6P2Mo18O62 (LPM) into a solid-polymer electrolyte (SPE) made up of the polymer polyethylene oxide (PEO), an inexpensive and stable chain of many ethylene oxide subunits. PEO suffers from low ionic conductivity, and the addition of LPM salt alters the properties of the polymer and enhances ion movement. The research team also incorporated an ionic liquid (IL) to free lithium ions from LPM, further improving the conductivity of the composite electrolyte material.
The team published their results in the journal Polyoxometalates on September 28, 2023.
“Solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) are considered… the most promising candidates for next-generation energy storage devices due to their excellent thermal and electrochemical stability. Although SPEs have excellent flexibility and viscosity, they are severely limited due to their low ionic conductivity, poor mechanical strength and low thermal stability at room temperature. In contrast, inorganic solid electrolytes (ISEs) like LPM... usually have high ionic conductivity. By incorporating ISEs like LPM into SPEs to form composite polymer electrolytes, we leverage their respective properties… to achieve optimized mechanical properties and improve their ionic conductivity,” said Hong-Ying Zang, senior author of the paper and professor in the Key Laboratory of Polyoxometalate and Reticular Material Chemistry at Northeast Normal University in Changchun, China.
“Currently, inorganic electrolyte fillers include nanoparticles… and ionic-conductive inorganics. As a class of metal-oxygen clusters, the application of polyoxometalates in solid-state batteries is hampered by the difficulty of moving lithium ions. In this paper, we promote the dissociation of lithium ions from polyoxometalates with ILs… to impart LPM and IL composites (LPM-IL) with good electrical conductivity,” said Zang.
The team characterized the ion conductivity and mobility of the composite membrane by measuring the AC impedance, or the resistance of current flow in a circuit. The team found that electrolyte membranes containing the optimal concentration of LPM and IL demonstrated three times higher conductivity than membranes prepared without IL.
In a similar manner, the team determined that the conductivity of composite membranes generated with polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), a non-reactive thermoplastic filler material, in conjunction with PEO increased conductivity ten times compared to LPM-IL membranes synthesized without PVDF. The composite membrane also demonstrated good stability over 12 hours at a temperature of 80℃.
“The results of these experiments demonstrate that polyoxometalates can be used as inorganic solid electrolytes,” said Zang. IL effectively increased the dissociation of lithium ions from LPM and improved the ionic conductivity of the composite solid electrolyte membrane. The incorporation of PVDF also created a PEO-PVDF conductive network in the membrane that further promoted lithium ion movement, enhancing conductivity.
The research team believes their unique, PEO-based composite membrane containing PVDF, POM-based lithium salt and IL provides a practical means of increasing ionic conductivity in solid-state electrolytes for use in lithium-ion batteries. “Our next step is to improve the performance of polyoxometalates to create better solid-state lithium-ion batteries,” said Zang.
Other contributors include Qianqian Liu, Yunzuo Cui, Lijie Zhu, Dongming Cheng, Chen Wang, Siqi Lu, Bo Li and Xinyu Chen from the Key Laboratory of Polyoxometalate and Reticular Material Chemistry at the Ministry of Education at Northeast Normal University in Changchun, China.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22302102, 21871042, 21471028, 22073094), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities-Excellent Youth Team Program (2412023YQ001), the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (Grant No. 20200201083JC) and the Natural Science Foundation of Department of education of Jilin Province (JJKH20201169KJ).
##
About Polyoxometalates
Polyoxometalates is a peer-reviewed, international and interdisciplinary research journal that focuses on all aspects of polyoxometalates, featured in rapid review and fast publishing, sponsored by Tsinghua University and published by Tsinghua University Press. Submissions are solicited in all topical areas, ranging from basic aspects of the science of polyoxometalates to practical applications of such materials. Polyoxometalates offers readers an attractive mix of authoritative and comprehensive Reviews, original cutting-edge research in Communication and Full Paper formats, Comments, and Highlight.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END