(Press-News.org) Washington, October 12, 2023—Third-grade retention can increase the reading and math scores of struggling students, with positive effects lasting into middle school, according to new research released today. The study, by NaYoung Hwang at the University of New Hampshire and Cory Koedel at the University of Missouri, was published today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
Video: Co-author NaYoung Hwang discusses findings and implications of the study
Despite mixed reviews among policymakers, researchers, and educators, grade retention policies are on the rise in the United States. Currently, 25 states and the District of Columbia require or allow school districts to retain students who are not proficient in reading at the end of third grade, although in recent years some states have begun to revisit or rescind their policies.
For their study, Hwang and Koedel examined Indiana’s test-based retention policy, using statewide data on third graders through seventh graders from 2011–12 to 2016–17. The authors found large increases in students’ reading and math scores for up to five years after the retention event. There was also no evidence of third grade retention resulting in disciplinary or attendance problems. Moreover, the positive effects were consistent regardless student gender, race/ethnicity, or family income level.
“Our findings show that repeating third grade can substantially improve educational outcomes without causing certain behavioral issues,” said NaYoung Hwang, an assistant professor of education at the University of New Hampshire. “Our results corroborate an emerging theme in the grade-retention literature that timing greatly affects how grade retention impacts student outcomes.”
Prior research has found that the impact of grade retention on students is more positive—although not entirely positive—when it occurs in early grades, with most of the negative impacts found when retention happens in the sixth grade or higher. Previous studies have also found some evidence that retention can have a harmful impact on the suspension rates of boys and Black and Hispanic students, who are at a higher baseline risk of disciplinary action.
“There are concerns about possible negative impacts of retention on students, especially those most at risk, and it’s important that researchers continue to examine how these policies affect students of different backgrounds, grade levels, and geographic regions,” said Hwang.
Hwang and Koedel stressed that the academic and socio-emotional support provided to these students by their schools is crucial to their success.
“It’s important that scholars, educators, and policymakers continue to assess and highlight best practices for supporting the success of these students, and that states and districts learn from one another,” Hwang said.
The authors noted their study does not examine the longer run effects of grade retention, including outcomes in high school, or the effects on other non-academic outcomes, such as self-esteem, peer relationships, or confidence.
Study citation: Hwang, N. & Koedel, C. (2023). Helping or hurting: The effects of retention in the third grade on student outcomes. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis. Prepublished October 12, 2023. http://doi.org/10.3102/01623737231197639
###
About AERA
The American Educational Research Association (AERA) is the largest national interdisciplinary research association devoted to the scientific study of education and learning. Founded in 1916, AERA advances knowledge about education, encourages scholarly inquiry related to education, and promotes the use of research to improve education and serve the public good. Find AERA on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram.
END
Study: Struggling students who repeat third grade see improved achievement
Researchers found no evidence that retention caused disciplinary or attendance problems
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New center addresses global climate change impacts on water, other resources
2023-10-12
Jordan ranks second among countries with the lowest access to water and is expected to reach water insecurity by 2030. Within the country, the most water deprived communities live in the Northeast region of Mafraq’s Azraq Basin which is also home to approximately 120,000 resettled Syrian refugees who are dependent on water resources.
A new three-year program called the Global Center on Climate Change, Water, Energy, Food, and Health Systems, led by the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human ...
NIH research program All of Us establishes CU Anschutz-led Center aimed at better utilizing data
2023-10-12
AURORA, Colo. (October 12, 2023) – The National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program has awarded $30 million to the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and its partners to establish the Center for Linkage and Acquisition of Data (CLAD). The All of Us Research Program is a historic effort to enroll at least 1 million people who reflect the diversity of the United States. Providing researchers with the data will help drive new discoveries and advance precision medicine.
“This is ...
Team develops HydroBIM platform for design of hydropower hub buildings
2023-10-12
A research team has developed a platform based on building information modeling (BIM) technology for use in the design of hydropower hub buildings. The platform, called HydroBIM, combines BIM technology with geographic information systems, computer-aided engineering, internet of things, artificial intelligence, and other technologies. The HydroBIM platform provides a comprehensive approach to digital design, intelligent construction, and smart operation of hydropower engineering projects.
The work ...
Stronger lithium batteries may need ‘weaker’ solvation structure, researchers report
2023-10-12
Lithium batteries power our phones, computers, many of our cars and so much more — even the drill and weedwhacker. But as technology advances, can they keep up in their current format? No, but there is a way forward, according to a new review paper from researchers at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, by further developing the electrolytes that allow for energy storage and discharge.
The team published their work in Energy Materials and Devices on September 18, 2023.
“Lithium batteries ...
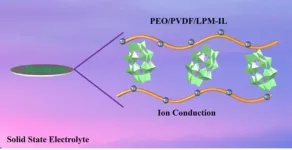
Polyoxometalates and ionic liquid enhance solid-state lithium-ion electrolyte performance
2023-10-12
Polyoxometalates (POMs) containing charged lithium ions combined with ionic liquids, increase the ion conductivity of a solid-state electrolyte membrane.
Solid-state lithium-ion batteries depend on the movement of ions (charged atoms) in the solid, rather than liquid, state to either charge or discharge the battery. These solid-state electrolytes are safer, more cost efficient and capable of higher energy densities than batteries that rely on liquid electrolyte solutions, but suffer from low ionic conductivity, or movement of ions, and poor thermal stability. A new composite ...
New study unveils stretchable high-resolution user-interactive synesthesia displays for visual–acoustic encryption
2023-10-12
The future of human-machine interfaces is on the cusp of a revolution with the unveiling of a groundbreaking technology - a stretchable high-resolution multicolor synesthesia display that generates synchronized sound and light as input/output sources. A research team, led by Professor Moon Kee Choi in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST, has succeeded in developing this cutting-edge display using transfer-printing techniques, propelling the field of multifunctional displays into new realms of possibility.
Traditionally, multifunctional ...
The advantage of digital-native brands setting up physical brand stores—and the challenge of preventing sales losses in existing channels
2023-10-12
Researchers from Erasmus School of Economics at Erasmus University Rotterdam, KU Leuven, Universität zu Lübeck, Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, and FoodLabs published a new Journal of Marketing article that investigates the multichannel impact of brand stores by digital-native FMCG brands.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Assessing the Multichannel Impact of Brand Store Entry by a Digital-Native Grocery Brand” and is authored ...
Extreme habitats: Microbial life in Old Faithful Geyser
2023-10-12
Contributed by Arianna Soldati, GSA Science Communication Fellow
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: An eruption of Old Faithful Geyser in Yellowstone National Park is a sight to behold. Indeed, millions of tourists flock to the park each year to see it. Hot water and steam are ejected in the air to a height of 100–180 feet approximately every 90 minutes. Many adjectives come to mind to describe it: powerful, mesmerizing, unique, otherworldly . . . homey? Not so much. Yet new research by Lisa M. Keller, published on PNAS Nexus earlier this year and to be presented on Sunday at the Geological Society of America’s GSA Connects 2023 meeting, shows that for ...
Inferring wildfire intensity from quartz luminescence
2023-10-12
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: On 8 June 2020, the Mangum Fire ignited 16 miles north of the North Rim of Grand Canyon National Park. By the time it was mostly contained, about a month later, the fire had burned over 70,000 acres of land.
April Phinney, a M.Sc. candidate at Utah State University, immediately started drafting a burn intensity map based on remote sensing data. Six months later, she set boots on the burned ground and started collecting soil samples, hoping they would contain quartz grains. This research ...
Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas awards grants to four TTUHSC Researchers
2023-10-12
The Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) recently awarded grants to four researchers from the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC). Combined, the grants will provide nearly $2.3 million that TTUHSC will use to conduct a pair of two-year pilot studies, acquire a state-of-the-art piece of laboratory equipment known as a cell sorter, and administer a colorectal cancer screening and prevention program.
Three of the recipients are from the TTUHSC School of Medicine, including Hongjun (Henry) Liang, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Cell Physiology and Molecular Biophysics; Min Kang, Pharm.D., a professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] Study: Struggling students who repeat third grade see improved achievementResearchers found no evidence that retention caused disciplinary or attendance problems