(Press-News.org) About The Study: This randomized trial in 25 adult medical-surgical intensive care units (ICUs) in Canada found that the transition from standard-volume to small-volume tubes for blood collection in the ICU may reduce red blood cell transfusion without impacting biospecimen sufficiency for laboratory analysis.
Authors: Deborah M. Siegal, M.D., M.Sc., of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.20820)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.20820?guestAccessKey=16456b47-2e38-45c0-8e90-9e720f7f3dc4&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=101223
END
Small-volume blood collection tubes to reduce transfusions in intensive care
JAMA
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The burden of lung cancer in women compared with men in the US
2023-10-12
About The Study: Based on high-quality population-based data, this study found that the higher lung cancer incidence in women than in men has not only continued in individuals younger than 50 years but also now extends to middle-aged adults as younger women with a high risk of the disease enter older age. Reasons for this shift are unclear because the prevalence and intensity of smoking are not higher in younger women compared with men except for a slightly elevated prevalence among those born in the 1960s.
Authors: Ahmedin Jemal, D.V.M., Ph.D., of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Race and ethnicity and primary language in emergency department triage
2023-10-12
About The Study: In this study of 249,000 visits to seven academic and community hospital emergency departments, patients who identified as Black, Hispanic, and Other race and ethnicity were assigned less acute Emergency Severity Index scores than their white peers despite having received more involved physician workups, suggesting some degree of mistriage. Clinical decision support systems might reduce these disparities but would require careful calibration to avoid replicating bias.
Authors: Joshua W. Joseph, M.D., M.S., ...
Big blood savings: large trial in JAMA shows taking less blood for lab testing reduces transfusions in intensive care
2023-10-12
A world-first clinical trial published in JAMA could provide an easy way to save tens of thousands of units of blood every year in Canada and much more worldwide. The trial, which involved more than 27,000 patients in 25 adult intensive care units (ICUs) across Canada, showed that taking less blood for lab tests using “small-volume” tubes reduced the need for almost one blood transfusion for every 10 patients.
Most hospitals use standard tubes that automatically draw four to six milliliters (ml) of blood, but a typical laboratory test requires less than 0.5 ml of blood, meaning the rest (more ...
We can respond to verbal stimuli while sleeping
2023-10-12
Sleep is generally defined as a period during which the body and mind are at rest—as if disconnected from the world. However, a new study led by Delphine Oudiette, Isabelle Arnulf, and Lionel Naccache at Paris Brain Institute shows that the frontier between wakefulness and sleep is much more porous than it seems.
The researchers have shown that ordinary sleepers can pick up verbal information transmitted by a human voice and respond to it by contracting their facial muscles. This astonishing ability occurs intermittently during almost all stages of sleep—like windows of connection with the outside world were temporarily opened on this occasion.
These new findings ...
Flagship individuals can boost conservation
2023-10-12
“Flagship” individual animals like Cecil the lion or Freya the walrus can boost conservation, new research suggests.
Much-loved species like pandas and polar bears are widely used in conservation campaigns.
However, a new study argues that individual animals or plants can also be used as flagships, with enormous potential to raise awareness and mobilise public support.
The recent outcry over the felling of the “Sycamore Gap” tree in the UK demonstrates the power of individual plants or animals in public opinion.
“Flagship individuals typically share some common characteristics,” ...
Letting go of an extra weight to control sleeping sickness
2023-10-12
Letting go of an extra weight to control sleeping sickness
A new study led by Luísa Figueiredo, group leader at the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes (iMM; Portugal), and published today in the scientific journal Nature Microbiology* found a new strategy by the host to cope with Trypanosoma brucei infection. Trypanosoma brucei is the parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans, and nagana in cattle, which remain a public health ...
Simulations of ‘backwards time travel’ can improve scientific experiments
2023-10-12
Physicists have shown that simulating models of hypothetical time travel can solve experimental problems that appear impossible to solve using standard physics.
If gamblers, investors and quantum experimentalists could bend the arrow of time, their advantage would be significantly higher, leading to significantly better outcomes.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge have shown that by manipulating entanglement – a feature of quantum theory that causes particles to be intrinsically linked – they can simulate what could happen if one could travel backwards in time. So that gamblers, investors and ...
Extraordinary fossil find reveals details about the weight and diet of extinct saber-toothed marsupial
2023-10-12
Recent paleontological explorations in the Tatacoa Desert in Colombia led to the recovery of the most complete skeleton of a "saber-toothed marsupial” discovered in northern South America. The specimen belongs to the species Anachlysictis gracilis, which is part of a group of extinct predatory mammals known as sparassodonts, that lived in South America during the Cenozoic, after the extinction of the dinosaurs.
This species lived approximately 13 million years ago in the area known among paleontologists as ‘La Venta’, in the current La Tatacoa desert, a tropical dry forest that “at that time was a tropical rainforest, similar to the current Amazon,” said ...
Traumatic memories can rewire the brain
2023-10-12
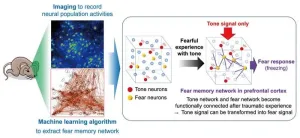
Okazaki, Japan – Scientists have long speculated about the physical changes that occur in the brain when a new memory is formed. Now, research from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) has shed light on this intriguing neurological mystery.
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, The research team has succeeded in detecting the brain neuronal networks involved in trauma memory by using a novel method that combines optical and machine-learning-based approaches, capturing the complex changes that occur during memory formation and uncovering the mechanisms by which trauma memories ...
Could you correctly identify someone wearing sunglasses from a distance of 20 meters?
2023-10-12
This comprehensive study focused on three key factors: distance, lighting and facial masking, and their impact on the ability of eyewitnesses to later correctly identify individuals they have seen. In the study, eyewitnesses were asked to identify perpetrators they had seen from various distances (5, 12.5 or 20 metres) and in different lighting conditions (daylight or deep twilight). The perpetrators were shown both with and without facial masking (sunglasses, hood, or both sunglasses and hood).
The key finding of the study is that distance plays a crucial role – the longer the distance, the harder it is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Small-volume blood collection tubes to reduce transfusions in intensive careJAMA