Letting go of an extra weight to control sleeping sickness
2023-10-12
(Press-News.org)
Letting go of an extra weight to control sleeping sickness
A new study led by Luísa Figueiredo, group leader at the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes (iMM; Portugal), and published today in the scientific journal Nature Microbiology* found a new strategy by the host to cope with Trypanosoma brucei infection. Trypanosoma brucei is the parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans, and nagana in cattle, which remain a public health concern and a major economic burden in Sub-Saharan Africa. Understanding the response of the infected organism during disease progression paves the way for the development of new treatment strategies.
Upon the bite of an infected tsetse fly, the parasites colonise intersticial spaces in the mammalian hosts, leading to death if the infection is left untreated. “Some years ago, our laboratory found that the parasite that causes sleeping sickness, Trypanosoma brucei, accumulates in disproportionately high numbers in the adipose tissue. We found this very intriguing, and directed our research to the understanding of how adipose tissue colonisation affects disease progression”, introduces Luísa Figueiredo, leader of the lab where the study was carried out. “The accumulation of the parasites in these tissues is accompanied by weight loss. Now, we found that the weight loss is largely due to the loss of adipose tissue by lipolysis, a metabolic process that breaks triacylglycerols into their constituent molecules, including free fatty acids”, continues Luísa Figueiredo. The loss of adipose tissue can occur due to many different signals. “We found that in this case, the lipolysis is in large part induced by the host immune response to the infection”, says Henrique Machado, first author of the study, explaining: “We infected immunocompromised mice and mice with impaired lipolysis, and saw that, in both cases, there is less loss of body weight despite having higher number of parasites”.
Then, the authors set out to understand if the lipolysis contributes to the progression of the disease. “We saw that the loss of adipose tissue through lipolysis prolongs the life of the infected mice. This, adding to the fact that the lipolysis exerts a control on the number of parasites, indicates that this response has a protective effect, somehow. Interestingly, we discovered that this protective effect is due to the release of the free fatty acids, during lipolysis, that are toxic for the parasites and lead to parasite death”, explains Luísa Figueiredo, saying: “It’s as if the host body sacrifices itself, by losing fat mass, to kill the parasites”.
These findings can open a completely new line of treatments for sleeping sickness and nagana targeting the infection in the adipose tissue, since the relevance of this tissue was previously unknown.
*Henrique Machado, Peter Hofer, Rudolf Zechner, Terry K. Smith, Luísa M. Figueiredo. 2023. Adipocyte lipolysis protects the host against Trypanosoma brucei infection. Nature Microbiology. DOI: 10.1038/s41564-023-01496-7.
This work was developed at iMM in collaboration with the University of Graz, Austria, the BioTechMed-Graz, Austria, and the University of St Andrews, United Kingdom. This work was supported by the European Research Council, the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, the Austrian Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung, and the Foundation Loius Jeantet.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-12
Physicists have shown that simulating models of hypothetical time travel can solve experimental problems that appear impossible to solve using standard physics.
If gamblers, investors and quantum experimentalists could bend the arrow of time, their advantage would be significantly higher, leading to significantly better outcomes.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge have shown that by manipulating entanglement – a feature of quantum theory that causes particles to be intrinsically linked – they can simulate what could happen if one could travel backwards in time. So that gamblers, investors and ...
2023-10-12
Recent paleontological explorations in the Tatacoa Desert in Colombia led to the recovery of the most complete skeleton of a "saber-toothed marsupial” discovered in northern South America. The specimen belongs to the species Anachlysictis gracilis, which is part of a group of extinct predatory mammals known as sparassodonts, that lived in South America during the Cenozoic, after the extinction of the dinosaurs.
This species lived approximately 13 million years ago in the area known among paleontologists as ‘La Venta’, in the current La Tatacoa desert, a tropical dry forest that “at that time was a tropical rainforest, similar to the current Amazon,” said ...
2023-10-12
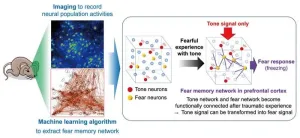
Okazaki, Japan – Scientists have long speculated about the physical changes that occur in the brain when a new memory is formed. Now, research from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) has shed light on this intriguing neurological mystery.
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, The research team has succeeded in detecting the brain neuronal networks involved in trauma memory by using a novel method that combines optical and machine-learning-based approaches, capturing the complex changes that occur during memory formation and uncovering the mechanisms by which trauma memories ...
2023-10-12
This comprehensive study focused on three key factors: distance, lighting and facial masking, and their impact on the ability of eyewitnesses to later correctly identify individuals they have seen. In the study, eyewitnesses were asked to identify perpetrators they had seen from various distances (5, 12.5 or 20 metres) and in different lighting conditions (daylight or deep twilight). The perpetrators were shown both with and without facial masking (sunglasses, hood, or both sunglasses and hood).
The key finding of the study is that distance plays a crucial role – the longer the distance, the harder it is ...
2023-10-12
A new Journal of the Endocrine Society study highlights how to identify children at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and strategies for prevention, such as anti-obesity or anti-diabetes medication and lifestyle changes.
Prediabetes is a health condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes increases the risk of developing chronic kidney disease, heart disease and stroke. Around 5%-10% of adults with prediabetes develop diabetes each year.
Over the past three decades, there has been a sharp increase in the incidence and prevalence ...
2023-10-12
Fathers and mothers who believe that men should hold the power and authority in the family exhibit less responsive parenting behavior, according to a new article in Social Psychological and Personality Science. This research provides the first behavioral evidence demonstrating that hostile sexism is linked to less responsive parenting by both fathers and mothers.
Hostile sexism is characterized by beliefs that men should hold power and authority in society. Its harmful effects are well-established, especially in predicting harmful behavior toward women. However, this new research highlights its impact on parenting ...
2023-10-12
Washington, October 12, 2023—Third-grade retention can increase the reading and math scores of struggling students, with positive effects lasting into middle school, according to new research released today. The study, by NaYoung Hwang at the University of New Hampshire and Cory Koedel at the University of Missouri, was published today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
Video: Co-author NaYoung Hwang discusses findings and implications of the study
Despite mixed reviews among policymakers, researchers, ...
2023-10-12
Jordan ranks second among countries with the lowest access to water and is expected to reach water insecurity by 2030. Within the country, the most water deprived communities live in the Northeast region of Mafraq’s Azraq Basin which is also home to approximately 120,000 resettled Syrian refugees who are dependent on water resources.
A new three-year program called the Global Center on Climate Change, Water, Energy, Food, and Health Systems, led by the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human ...
2023-10-12
AURORA, Colo. (October 12, 2023) – The National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program has awarded $30 million to the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and its partners to establish the Center for Linkage and Acquisition of Data (CLAD). The All of Us Research Program is a historic effort to enroll at least 1 million people who reflect the diversity of the United States. Providing researchers with the data will help drive new discoveries and advance precision medicine.
“This is ...
2023-10-12
A research team has developed a platform based on building information modeling (BIM) technology for use in the design of hydropower hub buildings. The platform, called HydroBIM, combines BIM technology with geographic information systems, computer-aided engineering, internet of things, artificial intelligence, and other technologies. The HydroBIM platform provides a comprehensive approach to digital design, intelligent construction, and smart operation of hydropower engineering projects.
The work ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Letting go of an extra weight to control sleeping sickness