(Press-News.org) This comprehensive study focused on three key factors: distance, lighting and facial masking, and their impact on the ability of eyewitnesses to later correctly identify individuals they have seen. In the study, eyewitnesses were asked to identify perpetrators they had seen from various distances (5, 12.5 or 20 metres) and in different lighting conditions (daylight or deep twilight). The perpetrators were shown both with and without facial masking (sunglasses, hood, or both sunglasses and hood).
The key finding of the study is that distance plays a crucial role – the longer the distance, the harder it is to later identify a person correctly. Moreover, facial masking presents a challenge even in good lighting conditions and at close proximity. Compared to other facial masking methods, sunglasses had the most negative impact on identification accuracy.
– Facial masking has a significant effect on the ability of eyewitnesses to correctly identify a perpetrator. A distance of five meters in clear daylight already presents a substantial challenge for later identifying a perpetrator who was wearing sunglasses. When the distance is 20 metres and the lighting is low (deep twilight), it then becomes so difficult to later identify a perpetrator that facial masking has very little effect. If an eyewitness sees a perpetrator wearing sunglasses from a distance of 20 metres, our findings indicate that it is highly unlikely that the eyewitness would be able to correctly identify the perpetrator at a later time, says Thomas J. Nyman, Assistant Professor of Practice in Psychology at New York University Shanghai.
Julia Korkman, Professor of Practice in Legal Psychology at Åbo Akademi University, emphasises that with over 1300 participants aged from 5 to 90 years, the study is a unique example of citizen science. This makes the results robust and potentially applicable on a global scale.
– These results mean that we have a better starting point for assessing the value of eyewitness identification in relation to distance, lighting and facial masking, she says.
Article: “The masked villain: the effects of facial masking, distance, lighting, and eyewitness age on eyewitness identification accuracy” (Psychology, Crime & Law).
Link: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1068316X.2023.2242999
For more information, please contact:
Thomas J. Nyman
tn1175@nyu.edu
END
Could you correctly identify someone wearing sunglasses from a distance of 20 meters?
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Children with prediabetes and obesity may be more likely to progress to diabetes
2023-10-12
A new Journal of the Endocrine Society study highlights how to identify children at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and strategies for prevention, such as anti-obesity or anti-diabetes medication and lifestyle changes.
Prediabetes is a health condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes increases the risk of developing chronic kidney disease, heart disease and stroke. Around 5%-10% of adults with prediabetes develop diabetes each year.
Over the past three decades, there has been a sharp increase in the incidence and prevalence ...
Hostile sexism linked to less responsive parenting
2023-10-12
Fathers and mothers who believe that men should hold the power and authority in the family exhibit less responsive parenting behavior, according to a new article in Social Psychological and Personality Science. This research provides the first behavioral evidence demonstrating that hostile sexism is linked to less responsive parenting by both fathers and mothers.
Hostile sexism is characterized by beliefs that men should hold power and authority in society. Its harmful effects are well-established, especially in predicting harmful behavior toward women. However, this new research highlights its impact on parenting ...
Study: Struggling students who repeat third grade see improved achievement
2023-10-12
Washington, October 12, 2023—Third-grade retention can increase the reading and math scores of struggling students, with positive effects lasting into middle school, according to new research released today. The study, by NaYoung Hwang at the University of New Hampshire and Cory Koedel at the University of Missouri, was published today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
Video: Co-author NaYoung Hwang discusses findings and implications of the study
Despite mixed reviews among policymakers, researchers, ...
New center addresses global climate change impacts on water, other resources
2023-10-12
Jordan ranks second among countries with the lowest access to water and is expected to reach water insecurity by 2030. Within the country, the most water deprived communities live in the Northeast region of Mafraq’s Azraq Basin which is also home to approximately 120,000 resettled Syrian refugees who are dependent on water resources.
A new three-year program called the Global Center on Climate Change, Water, Energy, Food, and Health Systems, led by the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human ...
NIH research program All of Us establishes CU Anschutz-led Center aimed at better utilizing data
2023-10-12
AURORA, Colo. (October 12, 2023) – The National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program has awarded $30 million to the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and its partners to establish the Center for Linkage and Acquisition of Data (CLAD). The All of Us Research Program is a historic effort to enroll at least 1 million people who reflect the diversity of the United States. Providing researchers with the data will help drive new discoveries and advance precision medicine.
“This is ...
Team develops HydroBIM platform for design of hydropower hub buildings
2023-10-12
A research team has developed a platform based on building information modeling (BIM) technology for use in the design of hydropower hub buildings. The platform, called HydroBIM, combines BIM technology with geographic information systems, computer-aided engineering, internet of things, artificial intelligence, and other technologies. The HydroBIM platform provides a comprehensive approach to digital design, intelligent construction, and smart operation of hydropower engineering projects.
The work ...
Stronger lithium batteries may need ‘weaker’ solvation structure, researchers report
2023-10-12
Lithium batteries power our phones, computers, many of our cars and so much more — even the drill and weedwhacker. But as technology advances, can they keep up in their current format? No, but there is a way forward, according to a new review paper from researchers at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, by further developing the electrolytes that allow for energy storage and discharge.
The team published their work in Energy Materials and Devices on September 18, 2023.
“Lithium batteries ...
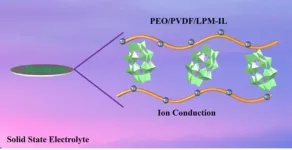
Polyoxometalates and ionic liquid enhance solid-state lithium-ion electrolyte performance
2023-10-12
Polyoxometalates (POMs) containing charged lithium ions combined with ionic liquids, increase the ion conductivity of a solid-state electrolyte membrane.
Solid-state lithium-ion batteries depend on the movement of ions (charged atoms) in the solid, rather than liquid, state to either charge or discharge the battery. These solid-state electrolytes are safer, more cost efficient and capable of higher energy densities than batteries that rely on liquid electrolyte solutions, but suffer from low ionic conductivity, or movement of ions, and poor thermal stability. A new composite ...
New study unveils stretchable high-resolution user-interactive synesthesia displays for visual–acoustic encryption
2023-10-12
The future of human-machine interfaces is on the cusp of a revolution with the unveiling of a groundbreaking technology - a stretchable high-resolution multicolor synesthesia display that generates synchronized sound and light as input/output sources. A research team, led by Professor Moon Kee Choi in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST, has succeeded in developing this cutting-edge display using transfer-printing techniques, propelling the field of multifunctional displays into new realms of possibility.
Traditionally, multifunctional ...
The advantage of digital-native brands setting up physical brand stores—and the challenge of preventing sales losses in existing channels
2023-10-12
Researchers from Erasmus School of Economics at Erasmus University Rotterdam, KU Leuven, Universität zu Lübeck, Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, and FoodLabs published a new Journal of Marketing article that investigates the multichannel impact of brand stores by digital-native FMCG brands.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Assessing the Multichannel Impact of Brand Store Entry by a Digital-Native Grocery Brand” and is authored ...