(Press-News.org) Okazaki, Japan – Scientists have long speculated about the physical changes that occur in the brain when a new memory is formed. Now, research from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) has shed light on this intriguing neurological mystery.
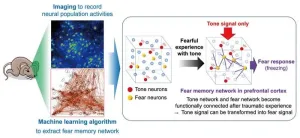
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, The research team has succeeded in detecting the brain neuronal networks involved in trauma memory by using a novel method that combines optical and machine-learning-based approaches, capturing the complex changes that occur during memory formation and uncovering the mechanisms by which trauma memories are created.
Animals learn to adapt to changing environments for survival. Associative learning, which includes classical conditioning, is one of the simplest types of learning and has been studied intensively over the past century. During the last two decades, technical developments in molecular, genetic, and optogenetic methods have made it possible to identify brain regions and specific populations of neurons that control the formation and retrieval of new associative memories. For instance, the dorsal part of the medial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) is critical for the retrieval of associative fear memory in rodents. However, the way in which the neurons in this region encode and retrieve associative memory is not well understood, which the research team aimed to address.
“The dmPFC shows specific neural activation and synchrony during fear-memory retrieval and evoked fear responses, such as freezing and heart rate deceleration,” explains lead author Masakazu Agetsuma. “Artificial silencing of the dmPFC in mice suppressed fear responses, indicating that this region is required to recall associative fear-memory. Because it is connected with brain systems implicated in learning and associated psychiatric diseases, we wanted to explore how changes in the dmPFC specifically regulate new associative memory information.”
The research team used longitudinal two-photon imaging and various computational neuroscience techniques to determine how neural activity changes in the mouse prefrontal cortex after learning in a fear-conditioning paradigm. Prefrontal neurons behave in a highly complex manner, and each neuron responds to various sensory and motor events. To address this complexity, the research team developed a new analytical method based on the ‘elastic net,’ a machine-learning algorithm, to identify which specific neurons encode fear memory. They further analyzed the spatial arrangement and functional connectivity of the neurons using graphical modeling.
“We successfully detected a neural population that encodes fear memory,” says Agetsuma. “Our analyses showed us that fear conditioning induced the formation of a fear-memory neural network with ‘hub’ neurons that functionally connected the memory neurons.”
Importantly, the researchers uncovered direct evidence that associative memory formation was accompanied by a novel associative connection between originally distinct networks, i.e., the conditioned stimulus (CS, e.g., tone) network and the unconditioned stimulus (US, e.g., fearful experience) network. “We propose that this newly discovered connection might facilitate information processing by triggering a fear response (CR) to a CS (i.e., a neural network for CS-to-CR transformation).”
Memories have long been thought to be formed by the enhancement of neural connections, which are strengthened by the repeated activation of groups of neurons. The findings of the present study, which were based on both real-life observations and model-based analysis, support this. Furthermore, the study demonstrates how combined methods (optics and machine learning) can be used to visualize the dynamics of neural networks in great detail. These techniques could be used to uncover additional information about the neurological changes associated with learning and memory.
###
The article, “Activity-dependent organization of prefrontal hub-networks for associative learning and signal transformation” was published in Nature Communications at DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-41547-5
END
Traumatic memories can rewire the brain
Researchers from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences find neural correlates of fear-based learning in mice
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Could you correctly identify someone wearing sunglasses from a distance of 20 meters?
2023-10-12
This comprehensive study focused on three key factors: distance, lighting and facial masking, and their impact on the ability of eyewitnesses to later correctly identify individuals they have seen. In the study, eyewitnesses were asked to identify perpetrators they had seen from various distances (5, 12.5 or 20 metres) and in different lighting conditions (daylight or deep twilight). The perpetrators were shown both with and without facial masking (sunglasses, hood, or both sunglasses and hood).
The key finding of the study is that distance plays a crucial role – the longer the distance, the harder it is ...
Children with prediabetes and obesity may be more likely to progress to diabetes
2023-10-12
A new Journal of the Endocrine Society study highlights how to identify children at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and strategies for prevention, such as anti-obesity or anti-diabetes medication and lifestyle changes.
Prediabetes is a health condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes increases the risk of developing chronic kidney disease, heart disease and stroke. Around 5%-10% of adults with prediabetes develop diabetes each year.
Over the past three decades, there has been a sharp increase in the incidence and prevalence ...
Hostile sexism linked to less responsive parenting
2023-10-12
Fathers and mothers who believe that men should hold the power and authority in the family exhibit less responsive parenting behavior, according to a new article in Social Psychological and Personality Science. This research provides the first behavioral evidence demonstrating that hostile sexism is linked to less responsive parenting by both fathers and mothers.
Hostile sexism is characterized by beliefs that men should hold power and authority in society. Its harmful effects are well-established, especially in predicting harmful behavior toward women. However, this new research highlights its impact on parenting ...
Study: Struggling students who repeat third grade see improved achievement
2023-10-12
Washington, October 12, 2023—Third-grade retention can increase the reading and math scores of struggling students, with positive effects lasting into middle school, according to new research released today. The study, by NaYoung Hwang at the University of New Hampshire and Cory Koedel at the University of Missouri, was published today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
Video: Co-author NaYoung Hwang discusses findings and implications of the study
Despite mixed reviews among policymakers, researchers, ...
New center addresses global climate change impacts on water, other resources
2023-10-12
Jordan ranks second among countries with the lowest access to water and is expected to reach water insecurity by 2030. Within the country, the most water deprived communities live in the Northeast region of Mafraq’s Azraq Basin which is also home to approximately 120,000 resettled Syrian refugees who are dependent on water resources.
A new three-year program called the Global Center on Climate Change, Water, Energy, Food, and Health Systems, led by the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human ...
NIH research program All of Us establishes CU Anschutz-led Center aimed at better utilizing data
2023-10-12
AURORA, Colo. (October 12, 2023) – The National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program has awarded $30 million to the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and its partners to establish the Center for Linkage and Acquisition of Data (CLAD). The All of Us Research Program is a historic effort to enroll at least 1 million people who reflect the diversity of the United States. Providing researchers with the data will help drive new discoveries and advance precision medicine.
“This is ...
Team develops HydroBIM platform for design of hydropower hub buildings
2023-10-12
A research team has developed a platform based on building information modeling (BIM) technology for use in the design of hydropower hub buildings. The platform, called HydroBIM, combines BIM technology with geographic information systems, computer-aided engineering, internet of things, artificial intelligence, and other technologies. The HydroBIM platform provides a comprehensive approach to digital design, intelligent construction, and smart operation of hydropower engineering projects.
The work ...
Stronger lithium batteries may need ‘weaker’ solvation structure, researchers report
2023-10-12
Lithium batteries power our phones, computers, many of our cars and so much more — even the drill and weedwhacker. But as technology advances, can they keep up in their current format? No, but there is a way forward, according to a new review paper from researchers at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, by further developing the electrolytes that allow for energy storage and discharge.
The team published their work in Energy Materials and Devices on September 18, 2023.
“Lithium batteries ...
Polyoxometalates and ionic liquid enhance solid-state lithium-ion electrolyte performance
2023-10-12
Polyoxometalates (POMs) containing charged lithium ions combined with ionic liquids, increase the ion conductivity of a solid-state electrolyte membrane.
Solid-state lithium-ion batteries depend on the movement of ions (charged atoms) in the solid, rather than liquid, state to either charge or discharge the battery. These solid-state electrolytes are safer, more cost efficient and capable of higher energy densities than batteries that rely on liquid electrolyte solutions, but suffer from low ionic conductivity, or movement of ions, and poor thermal stability. A new composite ...
New study unveils stretchable high-resolution user-interactive synesthesia displays for visual–acoustic encryption
2023-10-12
The future of human-machine interfaces is on the cusp of a revolution with the unveiling of a groundbreaking technology - a stretchable high-resolution multicolor synesthesia display that generates synchronized sound and light as input/output sources. A research team, led by Professor Moon Kee Choi in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST, has succeeded in developing this cutting-edge display using transfer-printing techniques, propelling the field of multifunctional displays into new realms of possibility.
Traditionally, multifunctional ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
[Press-News.org] Traumatic memories can rewire the brainResearchers from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences find neural correlates of fear-based learning in mice