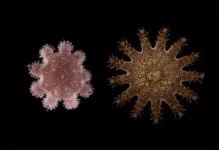
(Press-News.org) Research conducted by marine biologists from the University of Sydney has found juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish can withstand tremendous heatwaves well above levels that kill coral. These starfish then develop into carnivorous predators that devour reefs just as they begin to regrow.
Crown-of-thorns starfish are native to the Great Barrier Reef and found in the Indo-Pacific region, but they are classified as a species of concern because the damage large populations cause to coral is more significant than any other species. They fall behind only cyclones and bleaching events in their impact on coral mortality.
New findings suggest the species’ resilience to warming waters could exacerbate the ravaging effect climate change has on coral reefs.
The research is published in the journal Global Change Biology, led by Professor Maria Byrne from the School of Life and Environmental Sciences. She is also a member of the Marine Science Institute and Sydney Environment Institute.
Over the course of the experiment, juvenile crown-of-thorns displayed a surprisingly high heat tolerance, higher than that observed in their adult counterparts. This means that, even if the coral-eating adult stage declines in climate change-driven ocean warming scenarios, perhaps from a lack of their coral prey or from the heat, their herbivorous young can wait patiently for the opportune moment to grow into carnivores.
Coral bleaching and death can be triggered when waters warm by 1-3 degrees Celsius above the normal summer maximum, depending on how long the temperature lasts.
“We found juvenile crown of thorns starfish can tolerate almost three times the heat intensity that causes coral bleaching, using a model that measures temperature over time,” Professor Byrne said.
“This is an important finding that has implications for understanding the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems, especially the influence of understudied small cryptic species.
“Juveniles might well benefit from warming waters. The increase in the amount of their rubble habitat, generated by coral bleaching and mortality, allows their numbers to build over time.”
The crown-of-thorns starfish is nature’s ultimate coral predator, with a circle of life perfectly adapted to warming waters.
During outbreaks of their carnivorous adult phase, crown-of-thorns starfish dine pervasively on stony coral, leaving lifeless skeletons across the reef. These skeletons eventually become home to algae before crumbling. Bleaching induced coral mortality has a similar effect.
The remains of dead coral may provide the perfect habitat for the starfish’s tiny, algae-eating offspring. According to previous research by Professor Byrne, the juveniles can survive, and wait, for at least six years for the reef to come back to life, and given the opportunity as coral recovers these juveniles can grow into coral-eating predators and start the cycle again.
“The heat resistance and potential for the juveniles to gradually build-up in the reef infrastructure in coral rubble over years might be a phenomenon contributing to the initiation of adult crown-of-thorns starfish outbreaks,” said Matt Clements, PhD student and co-author of the study.
“Loss of natural predators due to overfishing and the build-up of nutrients in the water have been suspected to contribute to outbreaks of crown-of-thorns starfish. Now we have evidence that bleaching induced coral mortality could aid the seafloor-dwelling juveniles, leading to subsequent large waves of adults in reefs which exacerbate the ravages of climate change.”
The researchers also identified factors that contribute to the juveniles’ ability to survive in warming conditions. They include small size, which may reduce physiological requirements, and their ability to feed on a variety of food sources, despite preferring a diet of coralline algae.
END
Reef-devouring predator survives coral bleaching and feasts on the survivors
The crown-of-thorns starfish is nature’s ultimate coral predator that has a circle of life perfectly adapted to warming waters
2023-10-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does SARS-CoV-2 infection have urological effects?
2023-10-18
Research published in the Journal of Internal Medicine indicates that SARS-CoV-2 infection may worsen lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men.
The study included 17,986 men receiving medication for LUTS within the public healthcare system of Hong Kong in 2021–2022, half of whom had SARS-CoV-2 infection. The group with SARS-CoV-2 had significantly higher rates of retention of urine (4.55% versus 0.86%); blood in the urine (1.36% versus 0.41%); clinical urinary tract infection (4.31% versus 1.49%); bacteria in the urine (9.02% versus 1.97%); and addition of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which are drugs prescribed for enlarged prostate. (0.50% versus 0.02%). These urological ...
How did the initial COVID-19 wave affect mental health in the UK?
2023-10-18
New research published in Economic Inquiry reports substantial increases in psychological distress in the UK during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mental health effects were more pronounced for females; younger individuals; Black, Asian, and minority ethnic communities; and migrants. Also, people who had financial worries, loneliness, or were living in overcrowded dwellings experienced significantly worse mental health deterioration during the first wave.
The study used data from the UKHLS, also known as Understanding Society, which is a household panel dataset that captures, among other things, information from adults about their economic and social circumstances, ...
Heat-tolerant predatory sea stars will likely be a threat to coral during climate change
2023-10-18
Population outbreaks of the crown-of-thorns sea star (COTS), a predator of coral, can cause widespread coral mortality. COTS are herbivorous as juveniles but then switch to coral consumption as they grow to adulthood. When researchers exposed juvenile COTS to heat stress scenarios at time and temperature durations designed to reflect conditions that cause coral bleaching and mortality, juveniles exhibited tolerance to heatwave conditions well above levels that kill coral.
The findings, which are published in Global Change Biology, indicate that juvenile COTS are likely to persist as major coral predators in reefs already vulnerable to the effects of climate change.
“This ...
Does COVID-19 affect Alzheimer’s disease risk?
2023-10-18
The various neurological symptoms that patients with COVID-19 have experienced suggest that viral infections may increase the risk of neurodegeneration, which could in turn contribute to the development of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). A review in the Journal of Neurochemistry highlights the potential mechanistic links between COVID-19 and AD.
The authors note that age is the largest contributing factor to AD and COVID-19, and both appear to enhance the effects of the other, with potentially synergistic effects on neurodegeneration.
“I believe over the next several ...
Can planting multiple crops in the same plot improve agricultural production and sustainability?
2023-10-18
Agricultural management has typically focused on increasing yields, but there is an increasing need for sustainable food production that limits negative impacts on the environment. A new study published in Grassland Research provides insights into the potential benefits of diversifying agricultural practices, revealing how different mixtures of plant species can improve production, quality, and conservation.
For the study, investigators planted multiple species in different grassland plots, manipulating plant species richness from one to six species spanning three functional groups ...
New method may accurately identify body fluids at crime scenes
2023-10-18
Identifying different types of body fluids can help forensic experts reconstruct a crime scene, but it’s difficult to do so. In a study published in Electrophoresis, researchers developed a method using two different types of RNA—called microRNA (miRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA)—to determine five common body fluids.
Compared with previously reported single mRNA or miRNA assays, the combination of several mRNAs and miRNAs showed significant advantages for labeling human body fluids.
“Our findings indicate that this combined mRNA and miRNA system may provide a scientific ...
You don’t lose if you snooze
2023-10-18
It is often claimed that using the snooze button can have negative effects on sleep and cognitive processes, but there has been no direct evidence to this effect. New research from the Department of Psychology at Stockholm University shows that snoozing may actually support the waking process for regular snoozers.
It's common to want to stay in bed, potentially even go back to sleep, when the alarm goes off in the morning. The snooze button has been a function in alarm clocks and cell phones for decades and is ...
Do humans get lazier when robots help with tasks?
2023-10-18
Now that improvements in technology mean that some robots work alongside humans, there is evidence that those humans have learned to see them as team-mates — and teamwork can have negative as well as positive effects on people’s performance. People sometimes relax, letting their colleagues do the work instead. This is called ‘social loafing’, and it’s common where people know their contribution won’t be noticed or they’ve acclimatized to another team member’s high performance. Scientists at the Technical University of Berlin investigated whether humans social loaf when they work with robots.
“Teamwork ...
Using AI to develop hydrogen fuel cell catalysts more efficiently and economically
2023-10-18
Proton exchange membrane hydrogen fuel cells (PEMFCs) used in hydrogen vehicles use expensive platinum catalysts to facilitate the oxygen reduction reaction at the anode. There are a vast number of elemental combinations and compositions that need to be explored to develop more efficient and cost-effective catalyst materials than platinum, and researchers are still doing a lot of trial and error in the lab.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok Jin Yoon) announced that Dr. Donghun ...
Enhancing the safety and efficacy of drone flights in polar regions
2023-10-18
Collecting accurate weather data in remote and challenging environments like the polar regions and mountains can be extremely difficult. These areas often lack the infrastructure and resources needed for traditional weather stations, and the harsh weather conditions can make it dangerous for humans to access and maintain these stations.
Drones can navigate these challenging terrains, gather data, and transmit it to researchers, making them an indispensable tool for addressing these data gaps. Unfortunately, in-cloud flights still pose a challenge, with icing from supercooled cloud droplets that can damage vital drone components, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] Reef-devouring predator survives coral bleaching and feasts on the survivorsThe crown-of-thorns starfish is nature’s ultimate coral predator that has a circle of life perfectly adapted to warming waters