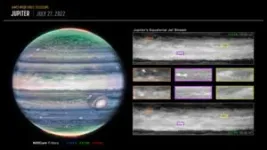
(Press-News.org) NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has discovered a new, never-before-seen feature in Jupiter’s atmosphere. The high-speed jet stream, which spans more than 3,000 miles (4,800 kilometers) wide, sits over Jupiter’s equator above the main cloud decks. The discovery of this jet is giving insights into how the layers of Jupiter’s famously turbulent atmosphere interact with each other, and how Webb is uniquely capable of tracking those features.
“This is something that totally surprised us,” said Ricardo Hueso of the University of the Basque Country in Bilbao, Spain, lead author on the paper describing the findings. “What we have always seen as blurred hazes in Jupiter’s atmosphere now appear as crisp features that we can track along with the planet’s fast rotation.”
The research team analyzed data from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) captured in July 2022. The Early Release Science program – jointly led by Imke de Pater from the University of California, Berkeley and Thierry Fouchet from the Observatory of Paris – was designed to take images of Jupiter 10 hours apart, or one Jupiter day, in four different filters, each uniquely able to detect changes in small features at different altitudes of Jupiter’s atmosphere.
“Even though various ground-based telescopes, spacecraft like NASA’s Juno and Cassini, and NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have observed the Jovian system’s changing weather patterns, Webb has already provided new findings on Jupiter’s rings, satellites, and its atmosphere,” de Pater noted.
While Jupiter is different from Earth in many ways – Jupiter is a gas giant, Earth is a rocky, temperate world – both planets have layered atmospheres. Infrared, visible, radio, and ultraviolet light wavelengths observed by these other missions detect the lower, deeper layers of the planet’s atmosphere – where gigantic storms and ammonia ice clouds reside.
On the other hand, Webb’s look farther into the near-infrared than before is sensitive to the higher-altitude layers of the atmosphere, around 15-30 miles (25-50 kilometers) above Jupiter’s cloud tops. In near-infrared imaging, high-altitude hazes typically appear blurry, with enhanced brightness over the equatorial region. With Webb, finer details are resolved within the bright hazy band.
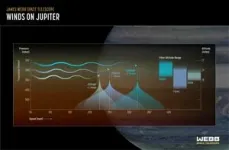
The newly discovered jet stream travels at about 320 miles per hour (515 kilometers per hour), twice the sustained winds of a Category 5 hurricane here on Earth. It is located around 25 miles (40 kilometers) above the clouds, in Jupiter’s lower stratosphere.
By comparing the winds observed by Webb at high altitudes, to the winds observed at deeper layers from Hubble, the team could measure how fast the winds change with altitude and generate wind shears.
While Webb’s exquisite resolution and wavelength coverage allowed for the detection of small cloud features used to track the jet, the complementary observations from Hubble taken one day after the Webb observations were also crucial to determine the base state of Jupiter’s equatorial atmosphere and observe the development of convective storms in Jupiter’s equator not connected to the jet.
“We knew the different wavelengths of Webb and Hubble would reveal the three-dimensional structure of storm clouds, but we were also able to use the timing of the data to see how rapidly storms develop,” added team member Michael Wong of the University of California, Berkeley, who led the associated Hubble observations.
The researchers are looking forward to additional observations of Jupiter with Webb to determine if the jet’s speed and altitude change over time.
“Jupiter has a complicated but repeatable pattern of winds and temperatures in its equatorial stratosphere, high above the winds in the clouds and hazes measured at these wavelengths,” explained team member Leigh Fletcher of the University of Leicester in the United Kingdom. “If the strength of this new jet is connected to this oscillating stratospheric pattern, we might expect the jet to vary considerably over the next 2 to 4 years – it’ll be really exciting to test this theory in the years to come.”
“It’s amazing to me that, after years of tracking Jupiter’s clouds and winds from numerous observatories, we still have more to learn about Jupiter, and features like this jet can remain hidden from view until these new NIRCam images were taken in 2022,” continued Fletcher.
The researchers’ results were recently published in Nature Astronomy.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
END
NASA's Webb discovers new feature in Jupiter’s atmosphere
Narrow jet stream near Jupiter's equator has winds traveling 320 miles per hour
2023-10-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson research highlights: ESMO 2023 special edition
2023-10-19
ABSTRACTS: LBA71, 1088MO, 95MO, LBA48, 1082O, 1085O, LBA34, 243MO
MADRID ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights provides a glimpse into recent basic, translational and clinical cancer research from MD Anderson experts.
This special edition features upcoming oral presentations by MD Anderson researchers at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress focused on clinical advances across a variety of cancer types. Highlights include a combination strategy for EGFR-mutant metastatic lung cancer, updated results for a Phase ...
To excel at engineering design, generative AI must learn to innovate, study finds
2023-10-19
ChatGPT and other deep generative models are proving to be uncanny mimics. These AI supermodels can churn out poems, finish symphonies, and create new videos and images by automatically learning from millions of examples of previous works. These enormously powerful and versatile tools excel at generating new content that resembles everything they’ve seen before.
But as MIT engineers say in a new study, similarity isn’t enough if you want to truly innovate in engineering tasks.
“Deep generative models (DGMs) are ...
Startup workers flee for bigger, more established companies during pandemic
2023-10-19
October 19, 2023
Startup workers flee for bigger, more established companies during pandemic
Findings reveal vulnerability of early-stage firms in downturns
Toronto - The world may have felt like it had stopped in the pandemic’s first weeks. But a “flight to safety” was underway at a popular digital job platform catering to the startup sector.
Digging into the data for nearly 180,000 users from AngelList Talent (now called Wellfound), the biggest online recruitment platform for private and entrepreneurial companies, researchers have found that U.S. job hunters turned away from smaller, early-stage companies in favour of positions at bigger, more established firms.
Just ...
Research repository arXiv receives $10M for upgrades
2023-10-19
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell Tech has announced a total of more than $10 million in gifts and grants from the Simons Foundation and the National Science Foundation, respectively, to support arXiv, a free distribution service and open-access archive for scholarly articles.
The funding will allow the growing repository with more than 2 million articles to migrate to the cloud and modernize its code to ensure reliability, fault tolerance and accessibility for researchers.
“I am deeply grateful for this tremendous support from both the Simons Foundation ...
Electrons are quick-change artists in molten salts, chemists show
2023-10-19
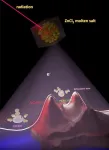
In a finding that helps elucidate how molten salts in advanced nuclear reactors might behave, scientists have shown how electrons interacting with the ions of the molten salt can form three states with different properties. Understanding these states can help predict the impact of radiation on the performance of salt-fueled reactors.
The researchers, from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Iowa, computationally simulated the introduction of an excess electron into molten zinc chloride salt to see what would happen.
They found three possible scenarios. In one, the electron becomes part of a molecular radical that ...
Communities of color experienced fear and mistrust of institutions during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-10-19
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A study led by researchers in the School of Medicine at the University of California, Riverside, has found that in communities of color in Inland Southern California, historical, cultural, and social traumas induce fear and mistrust in public health and medical, scientific, and governmental institutions, which, in turn, influence these communities’ hesitation to get tested and vaccinated for COVID-19.
The study, published in Culture, Medicine, and Psychiatry, underscores the need for community-based health interventions that consider structural and social determinants of health ...
Nail salon and other small beauty service workers face significant daily health challenges
2023-10-19
The beauty service microbusiness industry in the United States — such as the small, independently-owned nail salons found across the country — is huge, with more than $62 billion in annual sales.
However, most of the workers who provide these highly sought services are Asian female immigrants who earn very low wages. These workers face numerous workplace health challenges stemming from the chemicals they use, repetitive movements with handheld tools and awkward body posturing.
They also are reluctant to bring attention to these conditions due to factors such as possible immigration-related trauma, lack of English proficiency, ...
Pandemic prevention consortium announces new leadership team
2023-10-19
Recognizing the many milestones it has reached in recent months, Strategies to Prevent Spillover, or STOP Spillover, a project funded by the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) and led by Tufts University, has announced that the interim leadership team that was put in place in March 2023 will take on a permanent role for the next two years of the project.
Hellen Amuguni, an associate professor in the Department of Infectious Disease and Global Health at Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine, is the new project director. The co-deputy directors are Felicia Nutter, director of the International Veterinary ...
mRNA delivered by extracellular vesicles induces immunotherapy response in glioblastoma
2023-10-19
HOUSTON ― A team of researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center has developed a new method for using extracellular vesicles to enhance responses to immunotherapy in glioblastoma, potentially opening the door for wider use of engineered messenger RNA (mRNA) for cancer therapy. The study was published today in Nature Communications.
Earlier this year, a team of researchers led by Betty Kim, M.D., Ph.D., and Wen Jiang, M.D., Ph.D.,developed a novel method for loading mRNA into extracellular vesicles, small structures created by cells to transport biomolecules and nucleic acids within ...
Point-of-care technology initiative awarded $8.9 million renewal
2023-10-19
UMass Chan and UMass Lowell’s point-of-care technology initiative awarded $8.9 million renewal
UMass Chan Medical School and UMass Lowell have received an $8.9 million award from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for renewed support of their initiative to advance the development of home-based and point-of-care health technologies. The program aims to jumpstart new tools to address heart, lung, blood and sleep disorders, especially in underserved populations.
The Center for Advancing Point of Care Technologies ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
[Press-News.org] NASA's Webb discovers new feature in Jupiter’s atmosphereNarrow jet stream near Jupiter's equator has winds traveling 320 miles per hour