(Press-News.org) Executives from clinical stage artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company Insilico Medicine will present on the impact of AI on biotechnology at the Future Investment Initiative (FII) Conference in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine and Petrina Kamya, PhD, Head of AI Platforms and President of Insilico Medicine Canada will present on the topic “Will AI Rebuild Biotech?” on Oct. 26, 11:45am Arabic Standard Time. The event is available to be livestreamed.
The FII Conference brings together the world’s foremost CEOs, policymakers, investors, entrepreneurs, and young leaders shaping the future of international investment and the global economy. The theme for this year’s conference is The New Compass — helping investors navigate the direction of their companies and the global economy and develop strategies for the future.
In a difficult year for the biotech industry, Insilico Medicine has continued to advance its AI-designed therapeutics into the clinic. The company now has four drugs in clinical trials, including a lead drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Phase II trials that is the first AI-discovered and generative AI-designed molecule to meet this milestone. The company also has a novel QPCTL inhibitor for the treatment of advanced malignant tumors that has progressed to Phase I trials, and a novel USP1 inhibitor for the treatment of BRCA-mutated tumors that was recently licensed to Exelixis for $80m upfront and additional milestone and royalty payments. The Company’s novel drug for COVID-19 and related variants is also in Phase I trials.
In all, the company has 31 drugs for 29 targets in its pipeline, many in the cancer space, as well as in fibrosis, central nervous system diseases, immunity and aging-related diseases.
Insilico continues to develop its proprietary end-to-end Pharma.AI platform, which uses generative AI in biology, chemistry and clinical development to identify targets and disease hypotheses, design novel drug candidates, and predict the outcomes of clinical trials. This platform is supported by an AI-powered robotics laboratory that performs target discovery, compound screening, precision medicine generation and translational research. The Company continues to expand its global presence, with headquarters in New York City and Hong Kong, AI R&D teams in Abu Dhabi and Montreal, and labs in Shanghai and Suzhou.
About Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a global clinical stage biotechnology company powered by generative AI, is connecting biology, chemistry, and clinical trials analysis using next-generation AI systems. The company has developed AI platforms that utilize deep generative models, reinforcement learning, transformers, and other modern machine learning techniques for novel target discovery and the generation of novel molecular structures with desired properties. Insilico Medicine is developing breakthrough solutions to discover and develop innovative drugs for cancer, fibrosis, immunity, central nervous system diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and aging-related diseases. www.insilico.com
END
Insilico Medicine presents at Future Investment Initiative Conference in Riyadh
2023-10-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows promise for iNKT cell platform to treat cancer
2023-10-20
Allogeneic invariant natural killer T cells (allo-iNKTs) from a healthy donor have been shown to have therapeutic effects in treatment-resistant cancers and improve survival from COVID-19-related acute respiratory failure in previous studies. Unlike T cells, allo-iNKTs can be transferred from one person to another without causing graft-versus-host disease. But allo-iNKT cells rapidly become undetectable in the body after infusion, raising concerns over their rejection and disease relapse. Their functioning also varies from person to person.
Researchers from the School of Veterinary Medicine and Perelman School of Medicine hypothesized ...
Moving muscle fibers with magnets “programs” how they align within tissue
2023-10-20
Stimulating muscle fibers with magnets causes them to grow in the same direction, aligning muscle cells within tissue, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Boston University investigators report October 20 in the journal Device. The findings offer a simpler, less time-consuming way for medical researchers to program muscle cell alignment, which is strongly tied to healthy muscle function.
“The ability to make aligned muscle in a lab setting means that we can develop model tissues for understanding muscle in healthy and diseased states and for developing and testing new therapies ...
How cord-like aggregates of bacteria lead to tuberculosis infections
2023-10-20
The ability of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), a serious respiratory infection, to form snake-like cords was first noted nearly 80 years ago. In a study published October 20 in the journal Cell, investigators report the biophysical mechanisms by which these cords form and demonstrate how several generations of dividing bacteria hang together to create these structures that enable resistance to antibiotics.
“Our work clearly showed that cord formation is important for infection and why this highly ordered architecture might be important for pathogenesis,” says senior author Vivek Thacker (@DrVivekThacker), who ...
Wobbly gel mat trains muscle cells to work together
2023-10-20
There’s no doubt that exercise does a body good, including strengthening and toning our muscles. But how exactly does exercise make this happen?
As we run and lift and stretch, our muscles experience chemical signals from surrounding cells, as well as mechanical forces from jostling against tissues. Some physiologists wonder: Is it the body’s natural chemical stimulants or the physical forces of repeated motion — or some mix of the two — that ultimately drive our muscles to grow? The answer could be the key to identifying therapies to help people recover from muscle ...
Specialty palliative care and symptom severity and control in adolescents and young adults with cancer
2023-10-20
About The Study: In this study of 5,435 adolescents and young adults with cancer, those reporting moderate or severe symptoms through a screening program were more likely to subsequently receive specialty palliative care. These findings suggest that specialty palliative care was associated with a subsequent decrease in pain severity but did not affect other symptoms. New interventions targeting other symptoms during treatment and particularly at the end of life are needed.
Authors: Sumit Gupta, M.D., Ph.D., of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Noninvasive bioelectronic treatment of postcesarean pain
2023-10-20
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial of 134 individuals who underwent a cesarean delivery, use of a high-frequency electrical stimulation device as part of a multimodal analgesia protocol decreased opioid use in the immediate postoperative period and opioids prescribed at discharge. These findings suggest that the use of this device may be a helpful adjunct to decrease opioid use without compromising pain control after cesarean delivery.
Authors: Jennifer L. Grasch, M.D., of the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Does suspending kids from school harm their grades and health?
2023-10-20
Being suspended from school or sent to the office is tied to a big drop in grade point average (GPA), especially for Black and Latinx children, according to UC San Francisco researchers.
Their study, publishing Oct. 20, 2023, in JAMA Network Open, analyzed the school records of 16,849 students in grades 6 through 10 in a large urban school district in California from 2014 to 2017. Black students who had an “exclusionary school discipline” (ESD) event – being removed from a classroom or suspended ...
What do new moms and roaches have in common?
2023-10-20
Researchers are studying the dramatic physical transformation that some insects undergo to give birth to live young.
This includes suppressing their immune systems to accommodate babies, which is something some insects and people have in common. Understanding how these systems work can help improve treatments for fibromyalgia and other immune disorders.
Biologists at the University of Cincinnati were part of an international team examining the complex structural and physiological changes that take place in Hawaii’s beetle-mimic cockroaches, which give birth to live young.
“It’s ...
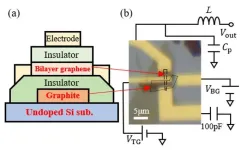
Researchers demonstrate a high-speed electrical readout method for graphene nanodevices
2023-10-20
The 'wonder material' graphene is well-known for its high electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and flexibility. Stacking two layers of graphene with atomic layer thickness produces bilayer graphene, which possesses excellent electrical, mechanical, and optical properties. As such, bilayer graphene has attracted significant attention and is being utilized in a host of next-generation devices, including quantum computers.
But complicating their application in quantum computing comes in the form of gaining accurate measurements of the quantum bit states. Most research has primarily used low-frequency electronics to overcome this. However, ...
PFAS remain a concern for hormone health, scientists conclude
2023-10-20
20 October 2023, Brussels, Belgium – At this critical junction for EU chemicals legislation, the independent scientific voice took centre stage at the 5th Annual Forum on Endocrine Disruptors. Together with an impressive number of concerned stakeholders, they called for the immediate adoption implementation of better EU legislation. While a restriction on per-and polyfluoroalkaline substances (PFAS) is ongoing, it risks being watered down by the massive volume of industry submissions to the public consultation. In addition, the European Commission’s legislative ...