(Press-News.org) Older adults who live in disadvantaged communities are less likely to attend cardiac rehabilitation after common heart procedures, a Michigan Medicine-led study finds.
The study aimed to calculate how many Medicare beneficiaries attended cardiac rehabilitation, a medically supervised program exercise and education program, after coronary revascularization between mid-2016 and 2018.
Patient communities were categorized using the Distressed Community Index, which analyzes economic well-being and social determinants of health, such as educational disparities and poverty rate, of United States zip codes.
Only 26% of patients from distressed communities use cardiac rehab, compared to 46% of patients from areas deemed prosperous. Any patient who attended cardiac rehab, no matter where they lived, had a reduced risk of death, hospitalization and heart attack, according to results published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
“Addressing barriers to participation in cardiac rehabilitation in distressed communities may improve outcomes for these patients and reduce longstanding disparities in such outcomes,” said first author Michael P. Thompson, Ph.D., assistant professor of cardiac surgery at University of Michigan Medical School.
“While some individuals who face geographic barriers to participation may benefit from transportation services or virtual options for cardiac rehab, there is a critical need to address socioeconomic barriers that prevent so many patients from attending this lifesaving therapy.”
Additional authors include, Hechuan Hou, Francis D. Pagani, M.D., Ph.D., Robert B. Hawkins, M.D., Devraj Sukul, M.D., and Donald S. Likosky, Ph.D., all of University of Michigan, James W. Stewart II, M.D., of Yale School of Medicine, and Steven J. Keteyian, Ph.D., of Henry Ford Health.
This study was funded as part of a career development award Thompson received from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ, Grant no. 1K01HS027830).
Paper cited: “Relationship Between Community-Level Distress and Cardiac Rehabilitation Participation, Facility Access, and Clinical Outcomes After Inpatient Coronary Revascularization,” Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.123.010148
END
Older adults from distressed communities attend less cardiac rehab after heart procedures
Researchers say reducing barriers must be prioritized
2023-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Finding the genes that help kingfishers dive without hurting their brains
2023-10-24
If you’ve ever belly-flopped into a pool, then you know: water can be surprisingly hard if you hit it at the wrong angle. But many species of kingfishers dive headfirst into water to catch their fishy prey. In a new scientific study in the journal Communications Biology, researchers compared the DNA of 30 different kingfisher species to zero in on the genes that might help explain the birds’ diet and ability to dive without sustaining brain damage.
The type of diving that kingfishers do-- what researchers call “plunge-diving”-- is an aeronautic feat. “It’s a high-speed dive from air to water, and it’s done by very few bird species,” says ...
Two regions of the brain critical to integrating semantic information while reading, UTHealth Houston research finds
2023-10-24
Two different regions of the brain are critical to integrating semantic information while reading, which could shed more light on why people with aphasia have difficulty with semantics, according to new research from UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by first author Elliot Murphy, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, and senior author Nitin Tandon, MD, professor and chair ad interim of the department in the medical school, was published today in Nature Communications.
Language depends largely on the integration of vocabulary across multiple words ...
Solar farms in space are possible, say Surrey and Swansea
2023-10-24
It's viable to produce low-cost, lightweight solar panels that can generate energy in space, according to new research from the Universities of Surrey and Swansea.
The first study of its kind followed a satellite over six years, observing how the panels generated power and weathered solar radiation over 30,000 orbits.
The findings could pave the way for commercially viable solar farms in space.
Professor Craig Underwood, Emeritus Professor of Spacecraft Engineering at the Surrey Space Centre at the University of Surrey, said:
“We are very pleased that a mission designed to last one year is still working after six. These detailed data ...
Proven for the first time: The microbiome of fruit and vegetables positively influences diversity in the gut
2023-10-24
Bacterial diversity in the gut plays an important role in human health. The crucial question, however, is where are the sources of this diversity? It is known that an important part of the maternal microbiome is transferred to the baby at birth, and the same happens during the breastfeeding period via breast milk. Further sources were yet to be discovered. However, a team led by Wisnu Adi Wicaksono and Gabriele Berg from the Institute of Environmental Biotechnology at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) has now succeeded in proving that plant microorganisms from fruit and vegetables contribute to the human microbiome. They report this in a study published in ...
NEJM: study supports minimally invasive procedure as aortic stenosis treatment
2023-10-24
Patients with a dysfunctional aortic heart valve who received a new, prosthetic valve through a minimally invasive procedure had similar outcomes at five years as those who underwent open-heart surgery, a new study shows.
The international multicenter study, with key contributions by the Cedars-Sinai heart team and published in The New England Journal of Medicine, offers a more complete picture to the ongoing dialogue comparing the minimally invasive heart procedure—called transcatheter aortic valve replacement, or TAVR—to open-heart surgery.
“Our data at five years validate that TAVR is a good alternative to open-heart surgery in younger patients with aortic ...
New study shows which neighborhoods police spend most time patrolling
2023-10-24
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. – Using anonymized smartphone data from nearly 10,000 police officers in 21 large U.S. cities, research from Indiana University finds officers on patrol spend more time in predominantly Black and Hispanic neighborhoods.
“Research on policing has focused on documented actions such as stops and arrests – less is known about patrols and presence,” said Kate Christensen, assistant professor of marketing at the IU Kelley School of Business.
“Police have discretion in deciding where law enforcement is provided within America’s cities,” she said. “Where police officers are located matters, because it affects ...
Preventing airborne infection without impeding communication with ions and electric field
2023-10-24
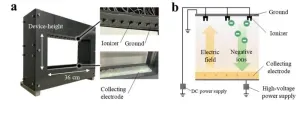
A novel device developed by researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, and Chiba University in a new study utilizes ions and an electric field to effectively capture infectious droplets and aerosols, while letting light and sound pass through to allow communication. The innovation is significant in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, since it shows promise in preventing airborne infection while facilitating communication.
Airborne infections, such as H1N1 influenza, SARS, and COVID-19, are spread by aerosols ...
Small but mighty: the hidden power of broccoli sprouts
2023-10-24
Remember when your parents used to say, “Eat your greens, they are good for you”? Well, they were really onto something. Several studies have shown that higher intakes of cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, one of the most widely consumed vegetables in the United States, are associated with reduced risks of diseases such as diabetes and cancer, thanks to their organosulfur compounds, such as glucosinolates and isothiocyanates that exhibit a broad spectrum of bioactivities including antioxidant activity. However, few studies have focused on ...
Are retrospective adjustments to sustainability reports helping CEOs score a bonus?
2023-10-24
A lack of clarity around sustainability reporting is allowing ASX-listed companies to retrospectively alter figures, ensuring CEO bonus pay tied to these metrics is realised, new research suggests.
Sustainability reports serve as critical tools for investors, regulators and other stakeholders to gauge a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. They highlight issues such as environmental pollution and worker safety that might otherwise be overlooked.
Close to 90% of ASX top 200 companies provide detailed ESG information. Many of these ...
Cathode active materials for lithium-ion batteries could be produced at low temperatures
2023-10-24
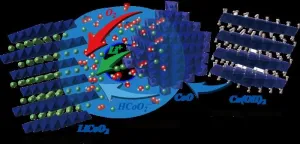
Layered lithium cobalt oxide, a key component of lithium-ion batteries, has been synthesized at temperatures as low as 300°C and durations as short as 30 minutes.
Lithium ion batteries (LIB) are the most commonly used type of battery in consumer electronics and electric vehicles. Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) is the compound used for the cathode in LIB for handheld electronics. Traditionally, the synthesis of this compound requires temperatures over 800°C and takes 10 to 20 hours to complete.
A team of researchers at Hokkaido University and Kobe University, led by Professor Masaki Matsui at Hokkaido University’s Faculty of Science, have developed a new method to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
Ancient mind-body practice proven to lower blood pressure in clinical trial
SwRI to create advanced Product Lifecycle Management system for the Air Force
Natural selection operates on multiple levels, comprehensive review of scientific studies shows
Developing a national research program on liquid metals for fusion
AI-powered ECG could help guide lifelong heart monitoring for patients with repaired tetralogy of fallot
Global shark bites return to average in 2025, with a smaller proportion in the United States
Millions are unaware of heart risks that don’t start in the heart
What freezing plants in blocks of ice can tell us about the future of Svalbard’s plant communities
A new vascularized tissueoid-on-a-chip model for liver regeneration and transplant rejection
Augmented reality menus may help restaurants attract more customers, improve brand perceptions
Power grids to epidemics: study shows small patterns trigger systemic failures
[Press-News.org] Older adults from distressed communities attend less cardiac rehab after heart proceduresResearchers say reducing barriers must be prioritized