(Press-News.org) Like several immunosuppressive biologics, the JAK inhibitor upadacitinib is also approved for the treatment of Crohn's disease. Commissioned by the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA), the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has now investigated in an early benefit assessment whether the drug offers an added benefit versus the appropriate comparator therapy to patients with moderate to severe active Crohn's disease who have had an inadequate response, lost response or are intolerant to conventional therapy or a biologic agent.
Therefore, an added benefit is not proven due to a lack of suitable study data. The studies presented by the company in its dossier only compared different concentrations of upadacitinib and placebo.
Selection of biologics as appropriate comparator therapy
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease in which inflammation can occur throughout the digestive tract. Among others, immunosuppressive biologics such as the TNF-α antagonists adalimumab or infliximab, the integrin inhibitor vedolizumab or the interleukin inhibitor ustekinumab are used to suppress disease flares. The first biologic approved for the treatment of Crohn's disease was infliximab in 1999.
In its commission for assessment to IQWiG, the G-BA distinguished between two situations: inadequate or absent response or intolerance to a conventional therapy on the one hand and to a biologic on the other. In both research questions, upadacitinib was to be compared with a TNF-α antagonist (adalimumab or infliximab) or an integrin inhibitor (vedolizumab) or an interleukin inhibitor (ustekinumab). Affected patients who had already received a biologic without success were to be treated with another biologic from this spectrum. Pure dosage changes were not an option; the G-BA assumed that this option had already been exhausted for those affected.
Although the manufacturer confirms the usefulness of these comparator therapies, it does not present any randomized controlled trials suitable for deriving an added benefit. In all three approval studies mentioned by it, the drug was only compared with placebo and with other doses of upadacitinib. The biologics that the G-BA cited as appropriate comparator therapies were also not allowed to be used as concomitant treatments.
This leads to the following conclusion: An added benefit of upadacitinib in comparison with the appropriate comparator therapy is not proven for patients with moderate to severe active Crohn's disease who have had an inadequate response, lost response or are intolerant to conventional therapy or a biologic agent.
Where are the direct comparisons?
"Biologics have been approved and used in the therapeutic indication of Crohn's disease for over twenty years - and yet we are still presented with studies in which new immunosuppressive substances are only compared with placebo or with themselves in different doses," says Daniela Preukschat from IQWiG's Drug Assessment Department, wondering. The situation is similar for other therapeutic indications, for example ulcerative colitis, also a chronic inflammatory bowel disease. A study on Crohn's disease, which was used in the benefit assessment procedure for risankizumab, shows that there is another way: the benefit assessment compared risakizumab with ustekinumab. "Manufacturers can certainly start studies early before market entry to provide meaningful evidence for care," says Preukschat. This shows: You just have to want it."
G‑BA decides on the extent of added benefit
The dossier assessment is part of the early benefit assessment according to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG) supervised by the G-BA. After publication of the dossier assessment, the G-BA conducts a commenting procedure and makes a final decision on the extent of the added benefit.
You can find an overview of the results of IQWiG’s benefit assessment in an English extract. In addition, the website informedhealth.org published by IQWiG provides easily understandable information on this benefit assessment.
END
Upadacitinib in active Crohn’s disease: no added benefit proven due to lack of comparative studies
Although biologics have been used in Crohn's disease for over 20 years, there are hardly any comparative studies versus established drugs. Placebo comparisons are unsuitable for assessing the added benefit
2023-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adapting to climate change: Individuals take action while governments plan
2023-10-24
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — While governments may take the lead in planning and financing climate change adaptation measures, such as incentivizing green infrastructure, individuals currently are most often the ones implementing actions to adapt to climate change, according to new research. The analysis, conducted by an international consortium of researchers from 20 institutions, including Penn State, in 12 countries, published in Nature Climate Change.
“The evidence suggests that individuals and households are the primary adaptation actors — the ones actually implementing ways to ...
New clues to early development of schizophrenia
2023-10-24
Philadelphia, October 24, 2023 – Schizophrenia is a severe neuropsychiatric disease that remains poorly understood and treated. Schizophrenia onset is typically in adolescence or early adulthood, but its underlying causes are thought to involve neurodevelopmental abnormalities. Because human prenatal and postnatal brain tissue is exceedingly difficult to procure and therefore study, researchers have had limited opportunities to identify early disease mechanisms, especially during the critical prenatal period. Now, a pair of studies that appear in Biological Psychiatry, ...
What an animated taco reveals about curiosity and patience
2023-10-24
DURHAM, N.C. -- Curiosity paradoxically increases people’s patience for an answer, while simultaneously making them more eager to hear it, finds a new study by Duke neuroscientists.
The research might help teachers and students alike by describing a side of curiosity that encourages us to stay engaged instead of seeking immediate relief.
Die-hard fans of the Hulu show, "The Bear" are left on the edge of their seats each Sunday, wondering what's going to happen in the scrappy Chicago hotdog shop next week. But the new study from Duke helps explain why viewers may choose to avoid spoilers ...
UC Davis, Mars researchers discover scalable production technique for low-calorie sugar substitute
2023-10-24
Scientists at the University of California, Davis, in partnership with the Mars Advanced Research Institute, have announced a significant breakthrough in the production of low-calorie sugar substitutes, such as allulose. This discovery could help address one of the primary obstacles to the widespread adoption of these alternatives: production costs.
Allulose, also known as D-psicose, is a naturally occurring rare sugar that provides a viable alternative to sucrose (table sugar). It has a similar taste, texture and functionality, making it an attractive option for those seeking to reduce their sugar intake. By activating a natural process in a microorganism, researchers have developed ...
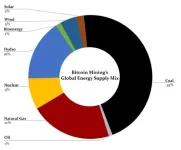
Bitcoin mining has “very worrying” impacts on land and water, not only carbon, UN-led study reveals
2023-10-24
American Geophysical Union
24 October 2023
AGU Release No. 23-39
For Immediate Release
This press release and accompanying multimedia are available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/bitcoin-mining-has-very-worrying-impacts-on-land-and-water-not-only-carbon/
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, news@agu.org (UTC-4 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Kaveh Madani, United Nations University, madani@unu.edu (UTC-4 hours)
By the numbers, global bitcoin mining in 2020-2021:
Used 173 terawatt ...
How eggs of the Zika-carrying mosquito survive desiccation
2023-10-24
Eggs of the mosquito that carries Zika virus can tolerate extended desiccation by altering their metabolism, according to a new study publishing October 24th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Anjana Prasad, Sunil Laxman, and colleagues at the Institute for Stem Cell Science and Regenerative Medicine in Bengaluru, India and the Indian Institute of Technology in Mandi, India. The finding offers potential new ways to control the spread of this mosquito.
Cells are made mostly of water, and desiccation is a potentially fatal event for any organism, since the structures of many proteins and other cellular molecules are dependent ...
How mosquito-controlling bacteria might also enhance insect fertility
2023-10-24
A new study reveals biological mechanisms by which a specific strain of bacteria in the Wolbachia genus might enhance the fertility of the insects it infects—with potentially important implications for mosquito-control strategies. Shelbi Russell of the University of California Santa Cruz, US, and colleagues report these findings in the open access journal PLOS Biology on October 24th.
Different strains of Wolbachia bacteria naturally infect a number of different animals worldwide, such as mosquitos, butterflies, and fruit flies. Wolbachia can manipulate the fertility of their ...
Ancient landscape discovered beneath East Antarctic Ice Sheet
2023-10-24
The research team, led by Durham University, UK, used satellite data and radio-echo sounding techniques to map a 32,000 km2 area of land underneath the vast ice sheet.
They discovered a landscape that appears to have been formed by rivers at least 14 million years ago and possibly even before the initial growth of the East Antarctic ice around 34 million years ago.
This newly discovered landscape consists of ancient valleys and ridges, not dissimilar in size-and-scale to the glacially-modified landscape of North Wales, ...
Cleveland Clinic selected by Wellcome Leap for Two Quantum Computing Research Projects
2023-10-24
Cleveland Clinic has been selected by Wellcome Leap to lead a quantum computing research project, while also playing a significant role in another led by Algorithmiq — both in collaboration with IBM Quantum.
The two contracts were won through Wellcome Leap’s Quantum for Bio Challenge, which will award up to $40 million to 12 researchers globally for research focused on accelerating the development of quantum computing applications for healthcare. Wellcome Leap is a U.S.- based non-profit organization founded by the Wellcome Trust to accelerate and increase ...
SLAC scientists shed light on potential breakthrough biomedical molecule
2023-10-24
Scientists from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have gained valuable insights into producing nitroxide, a molecule with potential applications in the biomedical field. While nitric oxide (NO) has long been on researchers' radar for its significant physiological effects, its lesser-known cousin, nitroxide (HNO), has remained largely unexplored.
The study, published recently in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, was born out of a joint endeavor between teams at SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser and Stanford ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Upadacitinib in active Crohn’s disease: no added benefit proven due to lack of comparative studiesAlthough biologics have been used in Crohn's disease for over 20 years, there are hardly any comparative studies versus established drugs. Placebo comparisons are unsuitable for assessing the added benefit