(Press-News.org) Over the last decade, research at Michigan Medicine has shown how exposure to toxins in the environment, such as pesticides and carcinogenic PCBs, affect the risk of developing and dying from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Now, investigators have developed an environmental risk score that assesses a person’s risk for developing ALS, as well as for survival after diagnosis, using a blood sample.
The results are published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry.
“For the first time, we have a means collecting a tube of blood and looking at a person’s risk for ALS based on being exposed to scores of toxins in the environment,” said first author Stephen Goutman, M.D., M.S., director of the Pranger ALS Clinic and associate director of the ALS Center of Excellence at University of Michigan.
Researchers obtained over 250 blood samples from participants in Michigan both with and without ALS. They calculated individual risk and survival models using 36 persistent organic pollutants.
Several individual pollutants were significantly associated with ALS risk. However, the risk for developing the disease was most strongly represented by a mixture of pesticides in the blood.
When considering the mixture of these pollutants, a person who was in the highest group of exposure had twice the risk of developing ALS compared to someone in the lowest group of exposure.
“Our results emphasize the importance of understanding the breadth of environmental pollution and its effects on ALS and other diseases,” said senior author Eva Feldman, M.D., Ph.D., James W. Albers Distinguished Professor at U-M, the Russell N. DeJong Professor of Neurology at U-M Medical School and director of the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies at Michigan Medicine.
The research team’s first understanding of the environment’s impact on ALS came in 2016 when investigators found elevated levels of pesticides in the blood of patients with the disease.
They later uncovered that exposure to organic pollutants advances ALS progression and contributes to worse outcomes.
“When we can assess environmental pollutants using available blood samples, that moves us toward a future where we can assess disease risk and shape prevention strategies,” Feldman said.
“Environmental risk scores have been robustly associated with other diseases, including cancers, especially when coupled with genetic risk. This is a burgeoning application that should be further studied as we deal with the consequences of pollutants being detected throughout the globe.”
Additional authors include Jonathan Boss, Dae-Gyu Jang, Ph.D., Bhramar Mukherjee, Ph.D., Rudy J. Richardson, Ph.D., and Stuart Batterman, Ph.D., all of University of Michigan.
This research was supported by the National ALS Registry/Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry at the CDC (grants 1R01TS000289, CDC/ATSDR 200-2013-56856).
This research was also supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes (grants K23ES027221, R01ES030049, R01NS127188, UL1TR002240). Additional support from the NeuroNetwork for Emerging Therapies, the NeuroNetwork Therapeutic Discovery Fund, the Peter R. Clark Fund for ALS Research, the Sinai Medical Staff Foundation, and Scott L. Pranger, University of Michigan.
Paper cited: “Environmental risk scores of persistent organic pollutants associate with higher ALS risk and shorter survival in a new Michigan case/control cohort,” Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2023-332121
END
Drawing a tube of blood could assess ALS risk from environmental toxin exposure
The risk score included 36 pollutants persistently found in the environment
2023-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research grants available: $50,000 to evaluate race in risk calculators
2023-10-30
DALLAS, October 30, 2023 — Multiple 1-year grants of up to $50,000 each are available from the American Heart Association to fund research that evaluates the use of race in heart disease and stroke risk calculators.
The American Heart Association, the single largest non-government supporter of heart and brain health research in the U.S., is offering the funding as part of the De-Biasing Clinical Care Algorithms project. The project is a two-year scientific research strategy, supported in part by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation, to study the complex issue of how race and ethnicity factor into clinical care ...
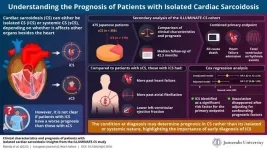
Shedding light on the paradoxical prognosis for patients with cardiac sarcoidosis, a rare and difficult-to-diagnose inflammatory heart condition
2023-10-30
Sarcoidosis is a complex inflammatory disease that causes the harmful accumulation of tiny clumps of cells called granulomas in the body. In most cases, sarcoidosis manifests in the lungs and lymph nodes. However, in approximately 10% of patients, the heart is affected; this condition is known as ‘cardiac sarcoidosis (CS).’ Although relatively rare, CS can cause life-threatening complications, including arrhythmia, heart failure, or sudden cardiac death.
One puzzling aspect of CS is that the condition sometimes involves the heart alone, without manifesting clinically apparent symptoms in other organs. This is referred to as isolated ...
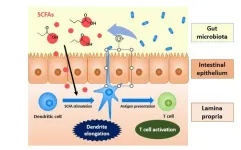
Intestinal bacteria metabolite promotes capture of antigens by dendritic cells
2023-10-30
Dendritic cells play a key role in the mammalian immune system. These cells are present throughout the human body and are known to capture foreign bodies, i.e., antigens, using extendable “arms” called dendrites. Once captured, dendritic cells present these substances to immune T cells, thereby initiating an immune response. Dendritic cells are responsive to their environment and capable of changing their morphology and other attributes dynamically. For instance, dendritic cells in the intestine’s mucosa (inner layer) capture harmful bacteria by extending their dendrites through the epithelium (outermost layer) ...
Virtual meetings tire people because we're doing them wrong
2023-10-30
New research suggests sleepiness during virtual meetings is caused by mental underload and boredom. Earlier studies suggested that fatigue from virtual meetings stems from mental overload, but new research from Aalto University shows that sleepiness during virtual meetings might actually be a result of mental underload and boredom.
‘I expected to find that people get stressed in remote meetings. But the result was the opposite – especially those who were not engaged in their work quickly became ...
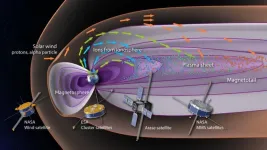
The importance of the Earth’s atmosphere in creating the large storms that affect satellite communications
2023-10-30
A study from an international team led by researchers from Nagoya University in Japan and the University of New Hampshire in the United States has revealed the importance of the Earth’s upper atmosphere in determining how large geomagnetic storms develop. Their findings reveal the previously underestimated importance of the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding the factors that cause geomagnetic storms is important because they can have a direct impact on the Earth’s magnetic field such ...
Using lasers to ‘heat and beat’ 3D-printed steel could help reduce costs
2023-10-30
Researchers have developed a new method for 3D printing metal that could help reduce costs and make more efficient use of resources.
The method, developed by a research team led by the University of Cambridge, allows structural modifications to be ‘programmed’ into metal alloys during 3D printing, fine-tuning their properties without the ‘heating and beating’ process that’s been in use for thousands of years.
The new 3D printing method combines the best qualities of both worlds: the complex shapes that 3D printing makes possible, and the ability to engineer ...
Positive messages can mitigate harm from objectified fitness posts
2023-10-30
PULLMAN, Wash. – A few words of body appreciation can help counter the negative impact of viewing objectified images of female fitness influencers, according to a Washington State University study.
While fitness influencers say they want to inspire good physical health, research has found that their social media posts often inspire negative mental health, especially among younger women. The WSU experimental study, published in the journal Health Communication, revealed that the negative impact ...
Extreme heat projected to increase cardiovascular deaths
2023-10-30
For immediate release on Oct. 30, 2023 at 5 a.m. ET
Cardiovascular-related deaths due to extreme heat are expected to increase between 2036 and 2065 in the United States, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health. The researchers, whose work is published in Circulation, predict that adults ages 65 and older and Black adults will likely be disproportionately affected.
While extreme heat currently accounts for less than 1% of cardiovascular-related deaths, the modeling analysis predicted this will change because of a projected rise in summer ...
Heat-related cardiovascular deaths in the U.S. may more than double within decades
2023-10-30
Research Highlights:
Cardiovascular deaths from extreme heat in the United States are projected to increase by 162% by the middle of the century, based on a hypothetical scenario where currently proposed U.S. policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have been successfully implemented.
A more dire scenario forecasts cardiovascular deaths from extreme heat could increase by 233% in the next 13-47 years if there are only minimal efforts to reduce emissions.
The percentage increase in deaths ...
Penn research projects increase in US cardiovascular deaths due to extreme heat
2023-10-30
PHILADELPHIA— The number of heat related cardiovascular deaths in the United States will increase over the next four decades, according to a new analysis from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Extreme heat can impact heart health in many ways, including increased heart rate, changes in blood pressure, and increased inflammation. Left untreated, these issues can be deadly. The findings, published today in Circulation, also indicate that older adults and Black adults will experience greater increases in excess cardiovascular deaths due to extreme heat.
“As global temperatures rise, analyzing how demographic and environmental trends ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
[Press-News.org] Drawing a tube of blood could assess ALS risk from environmental toxin exposureThe risk score included 36 pollutants persistently found in the environment