(Press-News.org) Care for women with menopausal health issues should improve globally following the release of an updated Monash University-led toolkit that guides health professionals around the world in assessing and treating them.
Endorsed by the International, Australasian and British Menopause Societies, the Endocrine Society of Australia and Jean Hailes for Women’s Health, the 2023 Practitioner’s Toolkit for Managing the Menopause is designed to be used anywhere in the world.
Published in Climacteric, the Toolkit has been updated and enhanced from the original 2014 Toolkit for practitioners with new advice and therapies based on a systematic review of the latest menopause research and best practice.
As well as outlining the latest general treatment guidelines, it offers bone health guidance as part of a menopause health assessment. For example, clear guidelines about when menopause hormone therapies (MHT) might be needed to prevent bone loss and osteoporosis in asymptomatic women were lacking in 2014.
The update also incorporates new medications including fezolinetant (hot flushes), ospemifene (painful sex), and vaginal DHEA (vaginal dryness), with some soon to be available in Australia.
First author and Monash University Women’s Health Research Program head Professor Susan Davis, who also led development of the 2014 Toolkit, said the update included some new therapies but did not support MHT for cognitive symptoms or clinical depression.
“For cognitive symptoms, clinical trials have not shown a benefit of MHT for cognitive function,” Professor Davis said. “The most robust studies have shown it to be no better than placebo.
“Regarding depression, menopause may cause symptoms such as low mood, anxiety, irritability, and mood swings, but clinical depression needs to be assessed and managed in its own right. Menopause might exacerbate underlying depression but should not be assumed to be the cause of clinical depression.”
Professor Davis said the advice was now much clearer around preventing bone loss and fracture.
“To our knowledge this is the only document that provides guidance for using hormone therapy to prevent fracture,” she said. “Other recommendations have been vague such as ‘can be used to prevent bone loss/fracture’ or ‘use to treat osteopenia’.”
Senior author Dr Rakib Islam, from the Monash University School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine Women's Health Research Program, said the updates would make a difference for many.
"The 2023 Practitioner’s Toolkit is the most up-to-date evidence-based practical guidance for health care providers to menopause care globally," he said.
Professor Davis said it was important for women to see their GP if they experienced troubling physical or mental health symptoms, and the update aimed to ensure GPs were well equipped.
“We have updated this as part of an NHMRC Grant to upskill GPs and to embed the care algorithms into GP practice software in the MenoPROMPT study program, which aims to improve care for women who need it,” she said. “This is a very important feature of this update.”
The paper’s authors said the recommendations needed to be applied in the context of local availability and the cost of investigations and drug therapies. “Most importantly, the Toolkit provides the full spectrum of available options and therefore can be used to support shared decision making, and patient-informed care,” they wrote.
END
Landmark menopause toolkit updated to improve assessment and treatment
2023-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New antibody could target breast cancers
2023-10-30
An enzyme that may help some breast cancers spread can be stopped with an antibody created in the lab of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Nicholas Tonks. With further development, the antibody might offer an effective drug treatment for those same breast cancers.
The new antibody targets an enzyme called PTPRD that is overabundant in some breast cancers. PTPRD belongs to a family of molecules known as protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), which help regulate many cellular processes. They do this by working in concert with enzymes called kinases to control how other proteins ...
Drawing a tube of blood could assess ALS risk from environmental toxin exposure
2023-10-30
Over the last decade, research at Michigan Medicine has shown how exposure to toxins in the environment, such as pesticides and carcinogenic PCBs, affect the risk of developing and dying from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Now, investigators have developed an environmental risk score that assesses a person’s risk for developing ALS, as well as for survival after diagnosis, using a blood sample.
The results are published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry.
“For the first time, we have a means collecting ...
Research grants available: $50,000 to evaluate race in risk calculators
2023-10-30
DALLAS, October 30, 2023 — Multiple 1-year grants of up to $50,000 each are available from the American Heart Association to fund research that evaluates the use of race in heart disease and stroke risk calculators.
The American Heart Association, the single largest non-government supporter of heart and brain health research in the U.S., is offering the funding as part of the De-Biasing Clinical Care Algorithms project. The project is a two-year scientific research strategy, supported in part by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation, to study the complex issue of how race and ethnicity factor into clinical care ...
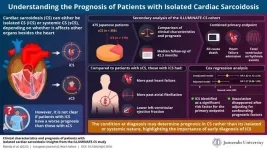
Shedding light on the paradoxical prognosis for patients with cardiac sarcoidosis, a rare and difficult-to-diagnose inflammatory heart condition
2023-10-30
Sarcoidosis is a complex inflammatory disease that causes the harmful accumulation of tiny clumps of cells called granulomas in the body. In most cases, sarcoidosis manifests in the lungs and lymph nodes. However, in approximately 10% of patients, the heart is affected; this condition is known as ‘cardiac sarcoidosis (CS).’ Although relatively rare, CS can cause life-threatening complications, including arrhythmia, heart failure, or sudden cardiac death.
One puzzling aspect of CS is that the condition sometimes involves the heart alone, without manifesting clinically apparent symptoms in other organs. This is referred to as isolated ...
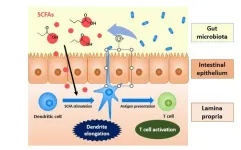
Intestinal bacteria metabolite promotes capture of antigens by dendritic cells
2023-10-30
Dendritic cells play a key role in the mammalian immune system. These cells are present throughout the human body and are known to capture foreign bodies, i.e., antigens, using extendable “arms” called dendrites. Once captured, dendritic cells present these substances to immune T cells, thereby initiating an immune response. Dendritic cells are responsive to their environment and capable of changing their morphology and other attributes dynamically. For instance, dendritic cells in the intestine’s mucosa (inner layer) capture harmful bacteria by extending their dendrites through the epithelium (outermost layer) ...
Virtual meetings tire people because we're doing them wrong
2023-10-30
New research suggests sleepiness during virtual meetings is caused by mental underload and boredom. Earlier studies suggested that fatigue from virtual meetings stems from mental overload, but new research from Aalto University shows that sleepiness during virtual meetings might actually be a result of mental underload and boredom.
‘I expected to find that people get stressed in remote meetings. But the result was the opposite – especially those who were not engaged in their work quickly became ...
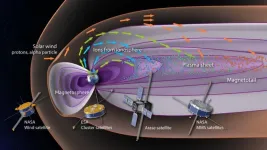
The importance of the Earth’s atmosphere in creating the large storms that affect satellite communications
2023-10-30
A study from an international team led by researchers from Nagoya University in Japan and the University of New Hampshire in the United States has revealed the importance of the Earth’s upper atmosphere in determining how large geomagnetic storms develop. Their findings reveal the previously underestimated importance of the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding the factors that cause geomagnetic storms is important because they can have a direct impact on the Earth’s magnetic field such ...
Using lasers to ‘heat and beat’ 3D-printed steel could help reduce costs
2023-10-30
Researchers have developed a new method for 3D printing metal that could help reduce costs and make more efficient use of resources.
The method, developed by a research team led by the University of Cambridge, allows structural modifications to be ‘programmed’ into metal alloys during 3D printing, fine-tuning their properties without the ‘heating and beating’ process that’s been in use for thousands of years.
The new 3D printing method combines the best qualities of both worlds: the complex shapes that 3D printing makes possible, and the ability to engineer ...
Positive messages can mitigate harm from objectified fitness posts
2023-10-30
PULLMAN, Wash. – A few words of body appreciation can help counter the negative impact of viewing objectified images of female fitness influencers, according to a Washington State University study.
While fitness influencers say they want to inspire good physical health, research has found that their social media posts often inspire negative mental health, especially among younger women. The WSU experimental study, published in the journal Health Communication, revealed that the negative impact ...
Extreme heat projected to increase cardiovascular deaths
2023-10-30
For immediate release on Oct. 30, 2023 at 5 a.m. ET
Cardiovascular-related deaths due to extreme heat are expected to increase between 2036 and 2065 in the United States, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health. The researchers, whose work is published in Circulation, predict that adults ages 65 and older and Black adults will likely be disproportionately affected.
While extreme heat currently accounts for less than 1% of cardiovascular-related deaths, the modeling analysis predicted this will change because of a projected rise in summer ...