(Press-News.org) As the planet gets hotter, the need for cool living environments is becoming more urgent. But air conditioning is a major contributor to global warming since units use potent greenhouse gases and lots of energy.
Now, researchers from McGill University, UCLA and Princeton have found in a new study an inexpensive, sustainable alternative to mechanical cooling with refrigerants in hot and arid climates, and a way to mitigate dangerous heat waves during electricity blackouts.
The researchers set out to answer how to achieve a new benchmark in passive cooling inside naturally conditioned buildings in hot climates such as Southern California. They examined the use of roof materials that radiate heat into the cold universe, even under direct sunlight, and how to combine them with temperature-driven ventilation. These cool radiator materials and coatings are often used to stop roofs overheating. Researchers have also used them to improve heat rejection from chillers. But there is untapped potential for integrating them into architectural design more fully, so they can not only reject indoor heat to outer space in a passive way, but also drive regular and healthy air changes.
“We found we could maintain air temperatures several degrees below the prevailing ambient temperature, and several degrees more below a reference 'gold standard' for passive cooling,” said Remy Fortin, lead author and PhD candidate at the Peter Guo-hua Fu School of Architecture "We did this without sacrificing healthy ventilation air changes.” This was a considerable challenge, considering air exchanges are a source of heating when the aim is to keep a room cooler than the exterior.
The researchers hope the findings will be used to positively impact communities suffering from dangerous climate heating and heat waves. “We hope that materials scientists, architects, and engineers will be interested in these results, and that our work will inspire more holistic thinking for how to integrate breakthroughs in radiative cooling materials with simple but effective architectural solutions,” said Salmaan Craig, Principal Investigator for the project and Assistant Professor at the Peter Guo-hua Fu School of Architecture.
END
A sustainable alternative to air conditioning
Researchers set out to achieve passive cooling inside naturally conditioned buildings in hot, arid climates
2023-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Microdroplets, macro results: Beckman researchers pursue Energy Earthshots
2023-10-30
Good things come in microscopic packages, according to the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology’s new DROPLETS project.
By packaging electrochemical reactions in smaller-than-standard serving sizes, interdisciplinary researchers aim to produce clean hydrogen, sequester carbon dioxide, and store renewable energies like wind and solar inexpensively and sustainably. Their project, called DROPLETS, received $4.5 million from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science through its Energy Earthshots Initiative.
“If we do this right, we will ...
Landmark menopause toolkit updated to improve assessment and treatment
2023-10-30
Care for women with menopausal health issues should improve globally following the release of an updated Monash University-led toolkit that guides health professionals around the world in assessing and treating them.
Endorsed by the International, Australasian and British Menopause Societies, the Endocrine Society of Australia and Jean Hailes for Women’s Health, the 2023 Practitioner’s Toolkit for Managing the Menopause is designed to be used anywhere in the world.
Published in Climacteric, the Toolkit has been updated and enhanced from the original 2014 Toolkit for practitioners with new advice and therapies based on a systematic review of the latest menopause ...
New antibody could target breast cancers
2023-10-30
An enzyme that may help some breast cancers spread can be stopped with an antibody created in the lab of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Nicholas Tonks. With further development, the antibody might offer an effective drug treatment for those same breast cancers.
The new antibody targets an enzyme called PTPRD that is overabundant in some breast cancers. PTPRD belongs to a family of molecules known as protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), which help regulate many cellular processes. They do this by working in concert with enzymes called kinases to control how other proteins ...
Drawing a tube of blood could assess ALS risk from environmental toxin exposure
2023-10-30
Over the last decade, research at Michigan Medicine has shown how exposure to toxins in the environment, such as pesticides and carcinogenic PCBs, affect the risk of developing and dying from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Now, investigators have developed an environmental risk score that assesses a person’s risk for developing ALS, as well as for survival after diagnosis, using a blood sample.
The results are published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry.
“For the first time, we have a means collecting ...
Research grants available: $50,000 to evaluate race in risk calculators
2023-10-30
DALLAS, October 30, 2023 — Multiple 1-year grants of up to $50,000 each are available from the American Heart Association to fund research that evaluates the use of race in heart disease and stroke risk calculators.
The American Heart Association, the single largest non-government supporter of heart and brain health research in the U.S., is offering the funding as part of the De-Biasing Clinical Care Algorithms project. The project is a two-year scientific research strategy, supported in part by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation, to study the complex issue of how race and ethnicity factor into clinical care ...
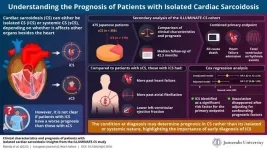
Shedding light on the paradoxical prognosis for patients with cardiac sarcoidosis, a rare and difficult-to-diagnose inflammatory heart condition
2023-10-30
Sarcoidosis is a complex inflammatory disease that causes the harmful accumulation of tiny clumps of cells called granulomas in the body. In most cases, sarcoidosis manifests in the lungs and lymph nodes. However, in approximately 10% of patients, the heart is affected; this condition is known as ‘cardiac sarcoidosis (CS).’ Although relatively rare, CS can cause life-threatening complications, including arrhythmia, heart failure, or sudden cardiac death.
One puzzling aspect of CS is that the condition sometimes involves the heart alone, without manifesting clinically apparent symptoms in other organs. This is referred to as isolated ...
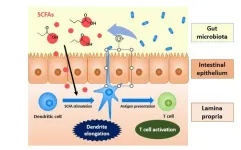
Intestinal bacteria metabolite promotes capture of antigens by dendritic cells
2023-10-30
Dendritic cells play a key role in the mammalian immune system. These cells are present throughout the human body and are known to capture foreign bodies, i.e., antigens, using extendable “arms” called dendrites. Once captured, dendritic cells present these substances to immune T cells, thereby initiating an immune response. Dendritic cells are responsive to their environment and capable of changing their morphology and other attributes dynamically. For instance, dendritic cells in the intestine’s mucosa (inner layer) capture harmful bacteria by extending their dendrites through the epithelium (outermost layer) ...
Virtual meetings tire people because we're doing them wrong
2023-10-30
New research suggests sleepiness during virtual meetings is caused by mental underload and boredom. Earlier studies suggested that fatigue from virtual meetings stems from mental overload, but new research from Aalto University shows that sleepiness during virtual meetings might actually be a result of mental underload and boredom.
‘I expected to find that people get stressed in remote meetings. But the result was the opposite – especially those who were not engaged in their work quickly became ...
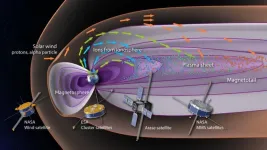
The importance of the Earth’s atmosphere in creating the large storms that affect satellite communications
2023-10-30
A study from an international team led by researchers from Nagoya University in Japan and the University of New Hampshire in the United States has revealed the importance of the Earth’s upper atmosphere in determining how large geomagnetic storms develop. Their findings reveal the previously underestimated importance of the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding the factors that cause geomagnetic storms is important because they can have a direct impact on the Earth’s magnetic field such ...
Using lasers to ‘heat and beat’ 3D-printed steel could help reduce costs
2023-10-30
Researchers have developed a new method for 3D printing metal that could help reduce costs and make more efficient use of resources.
The method, developed by a research team led by the University of Cambridge, allows structural modifications to be ‘programmed’ into metal alloys during 3D printing, fine-tuning their properties without the ‘heating and beating’ process that’s been in use for thousands of years.
The new 3D printing method combines the best qualities of both worlds: the complex shapes that 3D printing makes possible, and the ability to engineer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] A sustainable alternative to air conditioningResearchers set out to achieve passive cooling inside naturally conditioned buildings in hot, arid climates