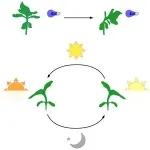
For the sunflower, turning toward the sun requires multiple complex systems
The behavior differs from the well-known light-seeking response of seedlings
2023-10-31
(Press-News.org) A sunflower’s ability to track the sun east to west during the day, and to face east again before the next sunrise, relies on multiple types of photoresponses, according to a new study publishing October 31st in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Stacey Harmer and colleagues at the University of California Davis, US. The results deepen the understanding of this well-known plant behavior, and upend previous assumptions about its dependence on a canonical light-dependent response pathway.
Because plants are rooted in place, they can’t get up and move when a neighbor blocks their light or they find themselves sprouting in a shady spot. Instead, they rely on growth or elongation to maneuver toward the light. There are several molecular systems to facilitate such responses, the best-known of which is called the phototropic response. In this system, blue light falling unevenly on a seedling is sensed by proteins called phototropins, which cause redistribution of a plant hormone, ultimately causing the growing tip to bend toward the light.
Whether the sun-tracking ability of the sunflower, called heliotropism, is a form of phototropic response, involving the same receptors and hormone, has not been clear. To explore this question, the authors compared gene activity patterns of sunflowers bending toward blue light in the lab to sunflowers tracking the sun in the field.
Surprisingly, only a few of the genes whose rapid upregulation is responsible for the phototropic bending in the lab showed significant differences in activity in response to the movement of the sun. Along with these few, they found changes in other light-response systems, including a shade avoidance system that senses far-red light (enriched in shade), which was triggered on the west side of the sunflower stem early in the day, when the sun is in the east. But, complicating the picture further, they showed that depletion of either red and far-red or blue light had little effect on the sunflower’s ability to track the sun, suggesting that multiple systems may coordinate to produce the heliotropic response, allowing it to operate even in the absence of one or more light triggers.
Harmer adds, “We’ve been continually surprised by what we’ve found as we study how sunflowers follow the sun each day. In this paper, we report that they use different molecular pathways to initiate and maintain tracking movements, and that the photoreceptors best known for causing plant bending seem to play a minor role in this remarkable process.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002344
Citation: Brooks CJ, Atamian HS, Harmer SL (2023) Multiple light signaling pathways control solar tracking in sunflowers. PLoS Biol 21(10): e3002344. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002344
Author Countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation (1238040 and 1759942) and the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (CA-D-PLB-2259-H) to SLH. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-31
Order wine at a fancy restaurant, and the sommelier might describe its aroma as having notes of citrus, tropical fruit, or flowers. Yet, when you take a whiff, it might just smell like … wine. How can wine connoisseurs pick out such similar scents?
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Associate Professor Saket Navlakha and Salk Institute researcher Shyam Srinivasan may have the answer. They have found that certain neurons allow fruit flies and mice to tell apart distinct smells. The team ...
2023-10-31
Sunflowers famously turn their faces to follow the sun as it crosses the sky. But how do sunflowers “see” the sun to follow it? New work from plant biologists at the University of California, Davis, published Oct. 31 in PLOS Biology, shows that they use a different, novel mechanism from that previously thought.
“This was a total surprise for us,” said Stacey Harmer, professor of plant biology at UC Davis and senior author on the paper.
Most plants show phototropism – the ability to grow toward a ...
2023-10-31
URBANA, Ill. — A team of animal scientists from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is set to deliver a potential game changer for subsistence farmers in Tanzania: cows that produce up to 20 times the milk of indigenous breeds.
The effort, published in Animal Frontiers, marries the milk-producing prowess of Holsteins and Jerseys with the heat, drought, and disease-resistance of Gyrs, an indigenous cattle breed common in tropical countries. Five generations of crosses result in cattle capable of ...
2023-10-31
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The lungs were once at the forefront of SARS-Cov-2 research, but as reports of organ failure and other serious complications poured in, scientists set out to discover how and why the respiratory virus was causing serious damage to the body's major organs, including the lungs.
An interdisciplinary COVID-19 International Research Team (COV-IRT), which includes UNC School of Medicine’s Jonathan C. Schisler, PhD, found that SARS-CoV-2 alters mitochondria on a genetic ...
2023-10-31
A groundbreaking study published in the journal Research in Aging sheds light on the financial challenges of housing-with-health-services models for low-income older adults. The report explores strategies for ensuring the sustainability of these beneficial efforts.
The study was conducted in partnership with Hebrew SeniorLife, a Harvard Medical School-affiliated nonprofit organization serving older adults in the Greater Boston area. It drew on insights from 31 key informational interviews and three focus groups ...
2023-10-31
The next generation of cardiometabolic biomarkers should pave the way for earlier detection of risk factors for conditions such as obesity, diabetes and heart disease in children, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association published in the journal Circulation.
“The rising number of children with major risk factors for cardiometabolic conditions represents a potential tsunami of preventable disease for our healthcare system,” says the statement’s lead author Michele Mietus-Snyder, M.D., ...
2023-10-31
A new compact, lightweight, gel-free and waterproof electrocardiogram (ECG) sensor offers more comfort and less skin irritation, compared to similar heart monitoring devices on the market.
ECGs help manage cardiovascular disease – which affects around 4 million Australians and kills more than 100 people every day – by alerting users to seek medical care.
The team led by RMIT University in Australia has made the wearable ECG device that could be used to prevent heart attacks for people with cardiovascular disease, including in remote healthcare and ...
2023-10-31
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- A new drug developed by professors from the School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Binghamton University has received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the treatment of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a common genetic disease that mostly affects young boys.
DMD is the most common genetic disease. It leads to the loss of the dystrophin protein in muscle tissues, with progressive weakness and challenges with day-to-day activities. The DMD gene is the largest gene in the human genome, ...
2023-10-31
The antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab deruxtecan is approved for various therapeutic indications. Since March 2023, it can also be used as monotherapy for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic HER2-low breast cancer who have received prior chemotherapy at this disease stage or developed disease recurrence early after adjuvant chemotherapy. Treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan is the first approved therapy for patients with HER2-low breast cancer. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in an early benefit assessment whether the antibody-drug ...
2023-10-31
Children and young people with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) use healthcare services twice as often in the two years before their diagnosis, a study by researchers at the University of Nottingham and King’s College London has found.
The research, published today in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood shows that children with the neurodevelopmental disorder are twice as likely to see their GP, go to hospital for an admission, and even have operations, compared to children without ADHD.
The researchers say the results support the need for healthcare professionals to consider a potential diagnosis of ADHD in children who ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] For the sunflower, turning toward the sun requires multiple complex systems
The behavior differs from the well-known light-seeking response of seedlings