(Press-News.org) The gene-editing technology known as CRISPR has led to revolutionary changes in agriculture, health research and more.
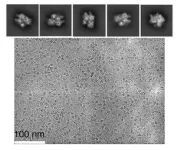
In research published in Nature Catalysis, scientists at Florida State University produced the first high-resolution, time-lapsed images showing magnesium ions interacting with the CRISPR-Cas9 enzyme while it cut strands of DNA, providing clear evidence that magnesium plays a role in both chemical bond breakage and near-simultaneous DNA cutting.
“If you are cutting genes, you don’t want to have only one strand of DNA broken, because the cell can repair it easily without editing. You want both strands to be broken,” said Hong Li, professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and director of the Institute of Molecular Biophysics. “You need two cuts firing close together. Magnesium plays a role in that, and we saw exactly how that works.”
CRISPR-Cas9 is the most widely used tool for genetic manipulation. The technology uses a repurposed enzyme to bind to DNA, allowing alterations at specified locations in a genome.
Scientists have known that magnesium plays a role in this process, but it was unclear exactly how, and no one had been able to capture time-lapsed images of the process up close. By leveraging a slower version of CRISPR-Cas9, this research showed that magnesium ions in the center of the catalysis reaction hold a key to the near-simultaneous cutting.
“I think a lot of times in science, even though you can infer something, you would like the proof,” Li said. “For instance, with magnesium everybody knows you need it, but not seeing it in action, that’s not complete science, right? You don’t have the same level of understanding of how it functions.”
The researchers used the cryo-electron microscope at FSU’s Biological Science Imaging Resource, which can produce images with near-atomic resolution, to observe metal ions and other atoms at work within the CRISPR-Cas9 enzyme. That allowed them to collect data that not only confirmed their earlier hypotheses but also led to the surprising discovery about how magnesium coordinates double-stranded breaks.
CRISPR made its debut in gene editing in 2013, and since then, scientists have worked to increase its dependability and expand its applicability to a variety of diverse organisms and cell types.
“By altering the active sites — the sets of ‘scissors’ that cut target and non-target DNA strands — we can sway the ability of Cas9 to use alternative metals for cutting,” said doctoral candidate and paper co-author Mitchell Roth. “There’s still a lot to explore with CRISPR.”
Understanding how each element affects the enzyme’s functioning gives scientists insight into what avenues for research might yield new knowledge and uses. Li and her team are planning further research to investigate how CRISPR-Cas9 can be retooled for other purposes.
Co-authors on this paper were former postdoctoral researchers Anuska Das and Jay Rai, doctoral candidate Yuerong Shu, undergraduate student Megan L. Medina and former undergraduate student Mackenzie R. Barakat, all of FSU.
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
END
FSU researchers capture high-resolution images of magnesium ions interacting with CRISPR gene-editing enzyme
2023-11-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Online grocery shopping promotes less variety, fewer impulse buys
2023-11-02
ITHACA, N.Y. – Online grocery carts tend to include less variety and fewer fruits and vegetables than those in a trip to a brick-and-mortar supermarket – but online shoppers are less susceptible to unhealthy impulse buys, according to a new Cornell University study.
In an analysis of nearly 2 million shopping trips, the researchers found that within a given household, Instacart baskets are more similar to each other from week to week than in-store carts, with more than twice as many overlapping items between successive trips to the same retailer.
Nutritionally, however, ...
Can AI help boost accessibility? These researchers tested it for themselves
2023-11-02
Generative artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT, an AI-powered language tool, and Midjourney, an AI-powered image generator, can potentially assist people with various disabilities. These tools could summarize content, compose messages or describe images. Yet the degree of this potential is an open question, since, in addition to regularly spouting inaccuracies and failing at basic reasoning, these tools can perpetuate ableist biases.
This year, seven researchers at the University of Washington conducted a three-month autoethnographic study — drawing on their own experiences as people with and without disabilities — to test AI tools’ utility for accessibility. Though ...
UMass hydrogeologists develop innovative way to predict saltwater intrusion into groundwater using Plymouth, Mass. as test case
2023-11-02
November 2, 2023
UMass Hydrogeologists Develop Innovative Way to Predict Saltwater Intrusion into Groundwater Using Plymouth, Mass. as Test Case
Working closely with local conservation group, researchers develop new model to predict climate-change driven saltwater intrusion that is transferable to other vulnerable coastal communities
AMHERST, Mass. – As the world warms and ice sheets melt, the ocean continually rises. The greater Boston area can expect to see between one and six feet of sea level rise by 2100, according to recent ...
Looking sharp! Shark skin is unique and may have medical use, too
2023-11-02
By David L. Chandler
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Sharks differ from other fish in many ways, including an apparently remarkable ability to heal from wounds, according to reports of sharks recovering from injuries sustained in the wild. While this healing ability has not yet been documented in controlled laboratory conditions, some of the chemical compounds found in shark skin may have significant biomedical potential.
To investigate this possibility, two dermatology researchers from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden carried out research on a small shark, the spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) and other cartilaginous fish species at the ...
A known environmental hazard can change the epigenetics of cells
2023-11-02
Epigenetics, the chemical mechanisms that controls the activity of genes, allows our cells, tissues and organs to adapt to the changing circumstances of the environment around us. This advantage can become a drawback, though, as this epigenetic regulation can be more easily altered by toxins than the more stable genetic sequence of the DNA.
An article recently published at Science with the collaboration of the groups of Dr. Manel Esteller, Director of the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute ...
Golden Retriever Lifetime Study data uncovers potential connection between sterilization, hemangiosarcoma
2023-11-02
DENVER/Nov. 2 – A scientific analysis published in Veterinary and Comparative Oncology using Golden Retriever Lifetime Study data notes a potential correlation between canine sterilization and hemangiosarcoma development. This startling finding has been previously suggested by experts but still is poorly understood.
The authors note that the likelihood of diagnosing hemangiosarcoma appears consistently low across all sexes and neutering statuses until about eight years of age. Beyond this point, intact and neutered male ...
Herbivory limits vegetation restoration success at sites worldwide, new meta-analysis shows
2023-11-02
Excluding herbivores – or reintroducing their predators – may aid restoration efforts in many locations, suggests a new meta-analysis of more than 600 global studies. According to the analysis, herbivores at restoration sites reduced vegetation abundance by 89%, on average, a larger effect than they had at relatively undisturbed sites. Herbivores also suppressed plant diversity at these locations. Vegetation is a primary foundation of most ecosystems. However, in many, it has been dramatically degraded, contributing to the loss of biodiversity and ...
Southern hemisphere dominates decline in global water availability
2023-11-02
Driven in part by large-scale atmospheric climate modes, the Southern Hemisphere accounts for more than 95% of the recent decline in global water availability, according to a new study. Global land water availability has varied due to climate change and increased human water use. Although this crucial resource underpins livelihoods, socioeconomic development, and ecosystems worldwide, it remains unclear how water availability has changed in recent decades and what is driving these changes at a global scale. Yongqiang Zhang and colleagues combine various data, including streamflow observations of large river basins of ...
Researchers caution that biodiversity benefit-sharing needs a radically new approach
2023-11-02
At the 2022 COP-15 meeting, signatories of the Convention on Biological Diversity reached a new agreement called the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which contained provisions to establish a separate, multilateral benefit-sharing mechanism for the use of “digital sequence information” (DSI), that is, the biological data associated with, or derived from, genetic resources such as nucleotide sequences and epigenetic, protein, and metabolite data.
In a new Policy Forum analysis published ...
Research outlines how sex differences have evolved
2023-11-02
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 18:00hrs GMT Thursday 2 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People and animals
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and Heidelberg University in Germany have shown that sex differences in animals vary dramatically across species, organs and developmental stages, and evolve quickly at the gene level but slowly at the cell type level.
Mammals have different traits depending on sex, like antlers in male deer. These are known as ‘sexually dimorphic’ traits, and include differences which aren’t visible, ...