(Press-News.org) Irvine, Calif., Nov. 6, 2023 — Agriculture is one of the hardest human activities to decarbonize; people must eat, but the land-use practices associated with growing crops account for roughly a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine and other institutions evaluate a new solution to this problem, one that eliminates farms altogether.
In a study published today in Nature Sustainability, the UCI-led team of scientists assess the potential for widescale synthetic production of dietary fats through chemical and biological processes. The raw materials for this method are the same as those used by plants: hydrogen in water and carbon dioxide in the air.
“Large-scale synthesis of edible molecules through chemical and biological means without agricultural feedstocks is a very real possibility,” said lead author Steven Davis, UCI professor of Earth system science. “Such ‘food without the farm’ could avoid enormous quantities of climate-warming emissions while also safeguarding biodiverse lands that might otherwise be cleared for farms.”
Davis and his co-authors highlight other environmental and societal benefits of farm-free food in the paper, including a reduction in water use and watershed pollution, local control over food production, diminished risk of weather-related food shortages, and less need for low-paying and physically demanding agricultural labor. Another plus, according to Davis, would be the possibility of returning existing farmlands to a natural state, which could enhance biodiversity and build up natural carbon sinks.
“I like the idea of not depending on photosynthesis for everything we eat,” Davis said. “At whatever scale, synthesizing food will alleviate competition between natural ecosystems and agriculture, thereby avoiding the many environmental costs of farming.”
Davis highlighted the practice of razing tropical rainforests to create space for palm oil plantations. Cookies, crackers, snack chips and a lot of other middle-of-the-store products are made with dietary fats coming from this source. He asked if anybody would notice if the oil used to bake their cookies came from a food refinery up the road instead of a plantation in Indonesia.
The authors of the paper said they focused much of their attention on fats because they are the “simplest nutrients to synthesize thermochemically,” pointing to established large-scale soap-making and polymer chemistry techniques.
The researchers estimated that agriculturally derived fats correspond to roughly 1 to 3 grams of emitted carbon dioxide per thousand calories, whereas molecularly identical fats synthesized from natural gas feedstock using available electricity would produce less than a gram of CO2 equivalent emissions, and nearly zero emissions if using carbon capture from the air and non-emitting sources of electricity.
“The beauty of the fats is that you can synthesize them with processes that don’t involve biology. It’s all chemistry, and because of that, you can operate at higher pressures and temperatures that allow excellent efficiency,” Davis said. “You could therefore build big reactors to do this at large scales.”
A big remaining question is, will people accept food created in this manner?
“Food is a tougher problem than electricity; few people care where the electrons in our wall socket originate, but many people care a lot about where their food comes from,” Davis said. “Processed foods are thus a likely use for synthetic fats. Folks may be less concerned about what kind of fat is in a store-bought cookie or pie crust because they don’t know what’s in there right now.”
Davis’ collaborators on this research project, which received financial support from the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Agriculture, included Ken Caldeira, Carnegie Institution for Science, Stanford, Calif., and Breakthrough Energy, Kirkland Wash.; Kathleen Alexander, Ian McKay and Matthew Shaner, Orca Sciences, Kirkland, Wash.; Juan Moreno-Cruz, University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada; Chaopeng Hong, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen, China.
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UCI is a member of the prestigious Association of American Universities and is ranked among the nation’s top 10 public universities by U.S. News & World Report. The campus has produced five Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UCI has more than 36,000 students and offers 224 degree programs. It’s located in one of the world’s safest and most economically vibrant communities and is Orange County’s second-largest employer, contributing $7 billion annually to the local economy and $8 billion statewide. For more on UCI, visit www.uci.edu.
Media access: Radio programs/stations may, for a fee, use an on-campus ISDN line to interview UCI faculty and experts, subject to availability and university approval. For more UCI news, visit news.uci.edu. Additional resources for journalists may be found at https://news.uci.edu/media-resources/.
END
UC Irvine-led science team shows how to eat our way out of the climate crisis
Researchers explore the benefits of producing farm-free food
2023-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Keeping an eye on the regions when it comes to climate change
2023-11-06
Keeping an eye on the regions when it comes to climate change
Up to now, the results of climate simulations have sometimes contradicted the analysis of climate traces from the past. A team led by the physicist Thomas Laepple from the Alfred Wegener Institute in Potsdam and the climatologist Kira Rehfeld from the University of Tübingen has therefore brought together experts in climate models and climate tracks to clarify how the discrepancies come about. The surprising result has now been published in the journal Nature Geoscience: in a way, both sides ...
Abortion bans linked to increase in children entering foster system, researchers find
2023-11-06
BOSTON – In June 2022, the U.S. Supreme Court overruled Roe v. Wade, effectively ending 50 years of federal protections to abortion care. As of October 2023, twenty-six states have since enacted laws to ban or restrict abortion access, with 14 states completely banning the procedure. Today, an estimated 25 million American women of childbearing age, or about one third of women ages 15 to 45, live in areas where abortion care is severely restricted. Historically, many states were able to restrict access to abortion even before 2022 through Targeted Regulation of Abortion Providers (TRAP) laws; these laws decrease ...
A blood test shows MS worsening 1 to 2 years before it happens
2023-11-06
Multiple sclerosis patients whose blood tests reveal elevated NfL, a biomarker of nerve damage, could see worsening disability one to two years later, according to a new study spearheaded by researchers at UC San Francisco.
The study is the first to quantify the timeframe preceding disability worsening in which injury to the central nervous system takes place, said co-first author Ahmed Abdelhak, MD, of the UCSF Department of Neurology and the Weill Institute for Neurosciences.
Almost 1 million Americans ...
Major study validates Owkin’s best in class AI diagnostic for colorectal cancer biomarker aimed at optimizing patient access to immunotherapy
2023-11-06
Article in Nature Communications demonstrates that with 96% sensitivity, AI diagnostic MSIntuit™ CRC can rule out almost half of the MSS population of colorectal cancer patients unlikely to respond to checkpoint inhibitor therapy from additional screening.
Such AI-enabled solutions have the potential to improve lab efficiency, addressing global pathology shortages and reducing testing burden to match the right patients to the right therapies.
Paris and New York., 6 Nov 2023 – In a peer-reviewed study published today in Nature Communications, a team of scientists ...
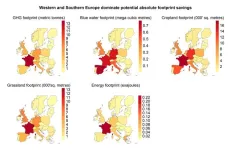
Food waste prevention in Europe can generate major footprint savings
2023-11-06
New research shows that European food consumption draws unnecessarily excessively on global resources, which is why researchers are calling for political action. Many of the foods that are consumed in Europe are produced in countries outside Europe. Food loss – and waste later in the chain, (read more on waste terms below) – occurs along the food supply chain, from the primary agricultural sector in Europe or rest of the world, until it feeds mouths in Europe.
“Halving Europe’s food loss and waste, together with a redistribution of global food resources, could solve the challenges of food shortages in the ...
NIH grant expands UIC brain bank into citywide effort to study epilepsy, brain cancer
2023-11-06
A new virtual brain bank spanning five Chicago academic medical centers and led by University of Illinois Chicago will create a powerful new resource for clinical care and research on epilepsy, brain tumors and neurological disorders.
A $5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health will create a network of brain tissue research at UIC, Northwestern University, Lurie Children’s Hospital, Rush University and University of Chicago. The institutions will utilize a data platform developed at UIC called INTUITION that combines tissue data with clinical, functional, genetic and 3D imaging information to assist clinicians treating patients and help researchers better understand ...
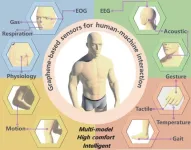
Carbon-based sensors are poised to facilitate a seamless human-machine interface
2023-11-06
Interaction between machines and humans is paramount to the development of the new technologies of the metaverse, which are designed to augment the human experience through cloud computing and extended reality (XR). Graphene, a two-dimensional carbon material, has emerged as an ideal candidate for wearable sensor technology, paving the way for a new era of seamless human-machine interaction (HMI).
A team of material scientists led by Tian-Ling Ren from Tsinghua University in Beijing, China recently outlined the state of graphene-based HMI sensor technology ...
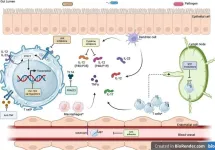
Chronic liver diseases: What new insights are there?
2023-11-06
Fatty liver diseases (FLD) have become a significant health concern worldwide, affecting millions. The two most common types of FLD are non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic-associated liver disease (ALD). NAFLD is associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, while ALD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. Both NAFLD and ALD can progress to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and, ultimately, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a primary liver cancer with a poor prognosis.
Significant ...
Future therapies for managing inflammatory bowel disease
2023-11-06
Ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that affect the gastrointestinal tract. In recent decades, there have been significant advances in the understanding of IBD pathophysiology and the development of new treatments.
The International Organisation for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IOIBD) developed the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) programs, which recommend specific treatment goals for UC and CD in children ...
A joint research team from South Korea and the United States has identified a new gene classification system for gastric cancer
2023-11-06
- A multicenter study of the MD Anderson, Korea University, Yonsei University, and other institutions
- Establishing subtypes of gastric cancer classification to lay the foundation of personalized treatment
Professor Sang Cheul Oh of the Division of Oncology/Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Professor Sang‑Hee Kang of the Department of Surgery, Korea University’s Guro Hospital, and Professor Sun Young Yim of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine announced a new genetic classification system ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] UC Irvine-led science team shows how to eat our way out of the climate crisisResearchers explore the benefits of producing farm-free food