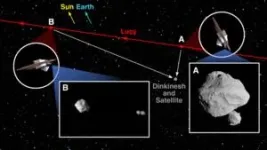
(Press-News.org) After the Southwest Research Institute-led Lucy mission flew past the asteroid Dinkinesh, the team discovered that it is even more “marvelous” as its newly discovered satellite is now shown to be a double-lobed moonlet. As NASA’s Lucy spacecraft continued to return data acquired during its first asteroid encounter on Nov. 1, 2023, the team discovered that Dinkinesh’s surprise satellite is itself a contact binary, made of two smaller objects touching each other.
In the first image of Dinkinesh and its satellite taken at closest approach, the two lobes of the contact binary lined up, one behind the other, appearing to be one body from Lucy’s point of view. When the team downlinked additional images captured after the closest encounter, the data revealed that Dinkenesh has a double moonlet.
“Contact binaries seem to be fairly common in the solar system,” said John Spencer, Lucy deputy project scientist, of the Boulder, Colorado, branch of the San Antonio-based SwRI. “We haven’t seen many up close, and we’ve never seen one orbiting another asteroid. We’d been puzzling over odd variations in Dinkinesh’s brightness that we saw on approach, which gave us a hint that Dinkinesh might have a moon of some sort, but we never suspected anything so bizarre!”
Lucy’s primary goal is to survey the never-before-visited Jupiter Trojan asteroids. The mission team added the first encounter with this small, main-belt asteroid in January 2023. The Dinkinesh encounter would serve as an inflight test of the spacecraft’s novel terminal tracking system, which keeps tabs on the target as the spacecraft buzzes past. The excellent performance of that system at Dinkinesh allowed the team to capture multiple perspectives on the system, characterizing the asteroids’ shapes and making this unexpected discovery.
“It is puzzling, to say the least,” said SwRI’s Hal Levison, the Lucy principal investigator. “I would have never expected a system that looks like this. In particular, I don’t understand why the two components of the satellite have similar sizes. This is going to be fun for the scientific community to figure out.”
Lucy took the second image about six minutes after closest approach from approximately 1,010 miles (1,630 km) away. The spacecraft traveled around 960 miles (1,500 km) between the two released images.
“It’s truly marvelous when nature surprises us with a new puzzle,” said Tom Statler, Lucy program scientist from NASA headquarters in Washington. “Great science pushes us to ask questions that we never knew we needed to ask.”
The team is continuing to downlink and process the remainder of the encounter data. Dinkinesh and its satellite pair are the first asteroids Lucy has explored. Over Lucy’s 12-year journey, that tally will include eight target asteroids with three known satellites among them, including the newly discovered contact binary. After skimming the inner edge of the main asteroid belt, Lucy is now heading back toward Earth for a gravity assist in December 2024. That close flyby will propel the spacecraft back through the main asteroid belt, where it will observe the asteroid Donaldjohanson in 2025 and continue its journey to reach the Trojan asteroids in 2027.
Lucy’s principal investigator is based out of the Boulder, Colorado, branch of Southwest Research Institute, headquartered in San Antonio. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provides overall mission management, systems engineering, and safety and mission assurance. Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, built the spacecraft. Lucy is the 13th mission in NASA’s Discovery Program. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Discovery Program for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
END
SwRI-led Lucy observes first-ever contact binary orbiting an asteroid
NASA spacecraft discovers Dinkinesh moonlet is two smaller objects in contact
2023-11-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New dates for landslides reveal past Seattle fault earthquakes
2023-11-07
New maps of more than 1,000 deep-seated landslides in the Puget Lowlands of Washington State provide evidence of the last major earthquake along the Seattle Fault about 1,100 years ago—and may also hold traces of older earthquakes along the fault.
Clusters of landslides offer a potential record of earthquakes, if researchers can determine when the landslides occurred. The new study published in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America combines information about the location of these Puget Lowlands landslides along with new dates obtained from measuring the surface roughness of the landslides.
The ...
Obesity linked to neurodegeneration through insulin resistance
2023-11-07
Researchers led by Mroj Alassaf at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in the United States have discovered a link between obesity and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. Using the common fruit fly, the research shows that a high-sugar diet — a hallmark of obesity — causes insulin resistance in the brain, which in turn reduces the ability to remove neuronal debris, thus increasing the risk of neurodegeneration. Publishing November 7th in the open access journal PLOS Biology, the research will impact therapies designed to reduce the risk of developing ...
Infection with common cat-borne parasite associated with frailty in older adults
2023-11-07
A common, cat-borne parasite already associated with risk-taking behavior and mental illness in humans may also contribute to exhaustion, loss of muscle mass, and other signs of “frailty” in older adults, suggests a study published Nov. 6 in the Journal of Gerontology: Medical Science.
The research, by an international team of scientists including University of Colorado Boulder, University of Maryland School of Medicine and the University of A Coruña in Spain, is the latest to explore how the tiny, single-celled ...
Cracking the code: Genome sequencing reveals why songbirds are larger in colder climates
2023-11-07
Scientists have unlocked the genetic basis underlying the remarkable variation in body size observed in song sparrows, one of North America’s most familiar and beloved songbirds. This discovery also provides insights into this species’ capacity to adapt to the challenges of climate change.
The study, published today in Nature Communications, used genomic sequencing to successfully pinpoint eight genetic variants, or DNA mutations, largely responsible for the nearly threefold difference in body size observed across the song sparrow range from Mexico to Alaska. For instance, song sparrows that live year-round ...
Study supports use of reduced-dose of direct oral anticoagulants for many older adults with two or more chronic medical conditions
2023-11-07
A nationwide study of 21,878 older nursing home residents with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) found a higher rate of bleeding and little difference in the effectiveness of standard versus reduced-dose treatment using direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
“Given the potential harms and unclear benefits of standard DOAC dosing, our results support the use of reduced-dose DOACs for many older adults with multiple chronic medical conditions,” said Dr. Sarah Berry, MD, MPH, of Hebrew SeniorLife’s Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research.
DOACs can prevent serious thrombotic events like stroke in residents with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation ...
Would you buy soap from an AI-powered robot dog?
2023-11-07
It’s not “Take Your Dog to Work Day,” but Associate Professor of Marketing, Entrepreneurship and Innovation Mark Yi-Cheon Yim has an adorable pup on his desk at UMass Lowell’s Pulichino Tong Business Center.
As Yim pats the top of the dog’s head, its ears lift, its tail wags and it yelps in delight. When Yim scratches under its chin, the dog appears to smile as its head sways in appreciation.
For a moment, you almost forget that the dog – a Sony aibo, which has been around for 24 years (168 dog years) and retails for $2,900 – is an artificial ...
Report: Political violence threatens health of US democracy
2023-11-07
Political violence is eroding the overall health of democracy in the United States, according to more than 100 global scholars surveyed for a new report.
The report, released today by Johns Hopkins University’s SNF Agora Institute and Protect Democracy, identifies how and to what extent experts believe violence is interfering with American democracy. Those surveyed were most concerned about elections, with more than half suggesting that U.S. electoral processes have a high potential of breaking down in the future.
“Political violence is occurring, and it comes in waves,” said co-author Lilliana Mason, an associate ...
Measuring skin water loss predicts anaphylaxis during food allergy tests
2023-11-07
Food allergies can quickly turn a casual meal into a life-threatening situation.
Anaphylaxis – a severe allergic reaction that may include a skin rash, nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing, and shock – from a food allergy sends 200,000 people to the emergency room annually in the United States.
Because pinpointing a food allergy could mean life or death, an accurate diagnosis is critical.
Oral food challenges – when a patient ingests increasing doses up to a full serving of the suspected food allergen under ...
Apps for depression: Effective, but with room for improvement
2023-11-07
A study involving the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) has found that the use of applications for depression can have a significant effect on treating the symptoms of this increasingly prevalent mental illness, especially when used in hybrid treatments, i.e. those that combine technology with the involvement of a professional. That is one of the main conclusions from the research done by the team led by Carme Carrion, principal investigator at the eHealth Lab, based on their compilation and analysis of the most painstaking scientific research in this field in recent years.
The members of this research group, which is affiliated ...
Food insecurity associated with liver disease in teens
2023-11-07
Boston (Nov. 7, 2023) — Teens from low-income families experiencing food insecurity are developing the most common form of liver disease twice as often as those who have easier access to food, likely because they rely on low-cost, ultra-processed foods, according to a study scheduled for presentation at The Liver Meeting, held by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Participation in the food assistance program Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, known as SNAP, seems to protect young people against liver disease.
“The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
[Press-News.org] SwRI-led Lucy observes first-ever contact binary orbiting an asteroidNASA spacecraft discovers Dinkinesh moonlet is two smaller objects in contact