(Press-News.org) After conducting the first scoping review of its kind, researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have developed an evidence based interactive mapping tool to assist policymakers as they consider regulating the concentration of THC in cannabis products and as more potent products move into the marketplace.
Their review, funded by the State of Colorado, was released today in the American Journal of Public Health (AJPH).
“We looked at studies that measured adverse or beneficial effects of high concentration cannabis products. From that, we were able to produce an open access, interactive map of the evidence so that anyone looking for research on it can find what is available,” said Lisa Bero, PhD, chief scientist for the Center for Bioethics and Humanities and research professor for the Colorado School of Public Health. “During the review we also discovered that research on cannabis is out of sync with the higher concentrations found in today’s products.”
The review notes that while smoking cannabis has been declining, routes of administration that use higher-concentration THC, such as vaping and dabbing, have been increasing, as well as the THC concentration of smoked products.
As of February 2023, 37 states allowed medical cannabis, and 19 states had legalized recreational cannabis, providing access to these more potent products. Several states have begun to regulate the amount of THC in them due to the risk of harmful effects, but lawmakers have been eager for more accurate and easily accessible data to write appropriate legislation.
“Our map is a public health good that can be used to find the studies that have been done on high concentration cannabis products. For example, they could look for all studies that have been conducted on mental health outcomes,” Bero said.
The map includes 452 studies that meets three criteria: studies involving humans; highly concentrated cannabis exposure; and any health outcomes regardless of whether they were classified as beneficial or adverse.
“While many of these studies need to be expanded to keep up with current trends, it opens up a conversation that could lead to broader research and collaboration between medical experts and state governments as well as close the knowledge gaps about these products,” Bero said.
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes, and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado - that treat more than two million adult and pediatric patients each year. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by over $690 million in research grants. For more information, visit www.cuanschutz.edu.
END
New interactive evidence-based mapping tool gives policymakers more insight into highly concentrated cannabis products
The tool aims to assist state governments looking to regulate more potent products and could lead to expanded research
2023-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Independent monitoring of the WHO pandemic agreement is non-negotiable, experts say
2023-11-08
An accountability framework, including independent monitoring of state compliance, is critical for the pandemic agreement's success, according to researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and affiliates at Spark Street Advisors. The paper and findings are published in BMJ Global Health.
“Countries signing up to a pandemic agreement is no guarantee of its effective implementation,” said Nina Schwalbe, adjunct assistant professor in the Department of Population and Family Health and principal visiting fellow at Columbia Mailman School. “Countries' lack of compliance with ...
NASA’s Webb findings support long-proposed process of planet formation
2023-11-08
Scientists using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope just made a breakthrough discovery in revealing how planets are made. By observing water vapor in protoplanetary disks, Webb confirmed a physical process involving the drifting of ice-coated solids from the outer regions of the disk into the rocky-planet zone.
Theories have long proposed that icy pebbles forming in the cold, outer regions of protoplanetary disks — the same area where comets originate in our solar system — should be the fundamental seeds of planet formation. The main requirement of these theories is that pebbles should drift inward toward the star due to friction in the gaseous disk, ...
UTIA faculty member serves as editor of the Journal of Food Distribution Research
2023-11-08
Carlos Trejo-Pech, an associate professor in the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, is a newly appointed editor of the Journal of Food Distribution Research.
“It is a great honor and big responsibility to serve as a journal editor of a publication outlet in the agricultural economics and agribusiness discipline,” said Trejo-Pech. “We, the editors, are committed to disseminating the results of high-quality research.”
The journal was established in 1969 under the auspices of the Food Distribution Research Society, the only body of scholars and practitioners in the United States dedicated ...
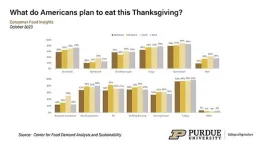
October Consumer Food Insights Report highlights thanksgiving meal plans
2023-11-08
October Consumer Food Insights Report highlights Thanksgiving meal plans
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Nearly eight in 10 Americans will celebrate the upcoming Thanksgiving holiday with a special meal, according to the October 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainabilityassesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue ...
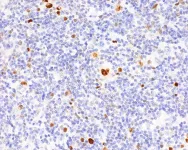
Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Small change, big effect
2023-11-08
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is one of the most common types of lymphoma in young adults. It is characterized by the presence of enlarged B lymphocytes, which are unusual in that they bear on their surface the identifying markers of many other immune cells – such as those found on phagocytes, dendritic cells, or T cells. Now, a team led by Stephan Mathas from the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC) has explained how these changes take place in the cells and what impact they have. The ECRC is a joint institution of the Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“Many different ...
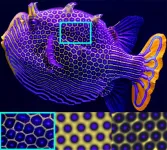
How animals get their stripes and spots
2023-11-08
Nature has no shortage of patterns, from spots on leopards to stripes on zebras and hexagons on boxfish. But a full explanation for how these patterns form has remained elusive.
Now engineers at the University of Colorado Boulder have shown that the same physical process that helps remove dirt from laundry could play a role in how tropical fish get their colorful stripes and spots. Their findings were published Nov. 8 in the journal Science Advances.
“Many biological questions are fundamentally ...
A fifth of European Red List flora and fauna species may be at risk of extinction
2023-11-08
A new analysis of 14,669 threatened species of plants and animals found in Europe reveals that about one fifth face the risk of extinction, and that agricultural land-use change poses a significant threat to these species. Axel Hochkirch of the Musée National d’Histoire Naturelle, Luxembourg, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on November 8, 2023.
The variety of species of living things—biodiversity—is declining around the world, as more and more species face the risk of extinction. Many efforts, including some by governments and nonprofit organizations, aim to reduce the loss ...
Head lice evolution mirrors human migration and colonization in the Americas
2023-11-08
A new analysis of lice genetic diversity suggests that lice came to the Americas twice – once during the first wave of human migration across the Bering Strait, and again during European colonization. Marina Ascunce, currently at the USDA-ARS, and colleagues, report these findings in a new study published November 8 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
The human louse is a wingless, blood-sucking parasite that lives its entire life on its host. It is one of the oldest known parasites to live on humans, and the two species have coevolved ...
A digital detox may not improve wellbeing: social media users who reduced their use for a week saw decreases in positive emotions as well as in negative ones
2023-11-08
A digital detox may not improve wellbeing: social media users who reduced their use for a week saw decreases in positive emotions as well as in negative ones
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293467
Article Title: Restricting social networking site use for one week produces varied effects on mood but does not increase explicit or implicit desires to use SNSs: Findings from an ecological momentary assessment study
Author Countries: UK
Funding: This work was supported by the Economic and Social Research ...
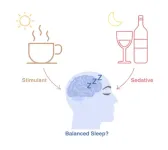
Financial traders may seek better sleep by self-medicating with caffeine and alcohol to balance the effects of the stimulant and the sedative, per micro-longitudinal study
2023-11-08
Financial traders may seek better sleep by self-medicating with caffeine and alcohol to balance the effects of the stimulant and the sedative, per micro-longitudinal study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0291675
Article Title: Sleep, alcohol, and caffeine in financial traders
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Natural selection operates on multiple levels, comprehensive review of scientific studies shows
Developing a national research program on liquid metals for fusion
AI-powered ECG could help guide lifelong heart monitoring for patients with repaired tetralogy of fallot
Global shark bites return to average in 2025, with a smaller proportion in the United States
Millions are unaware of heart risks that don’t start in the heart
What freezing plants in blocks of ice can tell us about the future of Svalbard’s plant communities
A new vascularized tissueoid-on-a-chip model for liver regeneration and transplant rejection
Augmented reality menus may help restaurants attract more customers, improve brand perceptions
Power grids to epidemics: study shows small patterns trigger systemic failures
Computational insights into the interactions of andrographolide derivative SRJ09 with histone deacetylase for the management of beta thalassemia
A genetic brake that forms our muscles
CHEST announces first class of certified critical care advanced practice providers awarded CCAPP Designation
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop an innovative prussian-blue based electrode for effective and efficient cesium removal
Self-organization of cell-sized chiral rotating actin rings driven by a chiral myosin
Report: US history polarizes generations, but has potential to unite
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
How can you rescue a “kidnapped” robot? A new AI system helps the robot regain its sense of location in dynamic, ever-changing environments
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
[Press-News.org] New interactive evidence-based mapping tool gives policymakers more insight into highly concentrated cannabis productsThe tool aims to assist state governments looking to regulate more potent products and could lead to expanded research