Unearthing how a carnivorous fungus traps and digests worms
New study examines molecular process at play through each stage of predation
2023-11-21
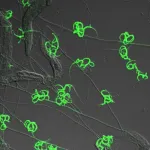
(Press-News.org) A new analysis sheds light on the molecular processes involved when a carnivorous species of fungus known as Arthrobotrys oligospora senses, traps and consumes a worm. Hung-Che Lin of Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan, and colleagues present these findings November 21st in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
A. oligospora usually derives its nutrients from decaying organic matter, but starvation and the presence of nearby worms can prompt it to form traps to capture and consume worms. A. oligospora is just one of many species of fungi that can trap and eat very small animals. Prior research has illuminated some of the biology behind this predator-prey relationship (such as certain genes involved in A. oligospora trap formation) but for the most part, the molecular details of the process have remained unclear.
To boost understanding, Lin and colleagues performed a series of lab experiments investigating the genes and processes involved at various stages of A. oligospora predation on a nematode worm species called Caenorhabditis elegans. Much of this analysis relied on a technique known as RNAseq, which provided information on the level of activity of different A. oligospora genes at different points in time. This research surfaced several biological processes that appear to play key roles in A. oligospora predation.
When A. oligospora first senses a worm, the findings suggest, DNA replication and the production of ribosomes (structures that build proteins in a cell) both increase. Next, the activity increases of many genes that encode proteins that appear to assist in the formation and function of traps, such as secreted worm-adhesive proteins and a newly identified family of proteins dubbed “trap enriched proteins” (TEP).
Finally, after A. oligospora has extended filamentous structures known as hyphae into a worm to digest it, the activity is boosted of genes coding for a variety of enzymes known as proteases—in particular, a group known as metalloproteases. Proteases break down other proteins, so these findings suggest that A. oligospora uses proteases to aid in worm digestion.
These findings could serve as a foundation for future research into the molecular mechanisms involved in A. oligospora predation and other fungal predator-prey interactions.
The authors add, “Our comprehensive transcriptomics and functional analyses highlight the role of increased DNA replication, translation, and secretion in trap development and efficacy. Furthermore, a gene family that is largely expanded in the genomes of nematode-trapping fungi were found to be enriched in traps and critical for trap adhesion to nematodes. These results furthered our understanding of the key processes required for fungal carnivory.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002400
Citation: Lin H-C, de Ulzurrun GV-D, Chen S-A, Yang C-T, Tay RJ, Iizuka T, et al. (2023) Key processes required for the different stages of fungal carnivory by a nematode-trapping fungus. PLoS Biol 21(11): e3002400. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002400
Author Countries: Taiwan, United States
Funding: Funding for this work was provided by the Academia Sinica Investigator Award AS-IA-111-L02 and the Ministry of Science and Technology MOST grant 110-2311-B-001-047-MY3 to Y.-P.H. Computing was also supported by a research allocation from NSF XSEDE (TG-MCB190010) to E.M.S. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-21
In Germany, taxing sugar-sweetened beverages could prevent or postpone cases of type 2 diabetes, extend healthy lifespans and save up to €16.0 billion in societal costs over the next 20 years, according to a new study led by Karl Emmert-Fees of the Technical University of Munich, published November 21st in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
The World Health Organization has recommended that governments worldwide lessen the social and economic burden of cardiometabolic disease by taxing sugar-sweetened beverages. These taxes either reduce consumption by increasing the price, such as the one peso per liter ...
2023-11-21
A simulation study conducted by a team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) demonstrates that a soft drink tax in Germany would have significant positive effects. In all of the simulated variants evaluated, less sugar was consumed and the rate of illness dropped. This would be a way to reduce costs to the national economy and alleviate the burden on the health care system. There is, however, a difference between taxes aimed at reducing soft drink consumption and taxes aimed at bringing about changes in product formulation.
Sugary beverages increase the risk of obesity and illnesses such as diabetes. Several countries have therefore introduced taxes on soft drinks. In Germany ...
2023-11-21
An analysis of 5.8 million authors across all scientific disciplines shows that the gender gap is closing, but there is still a long distance to go. The new research by John Ioannidis of the Meta-Research Innovation Center at Stanford (METRICs) at Stanford University, US, and colleagues, publishes November 21st in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
There is a strong gender gap in science which manifests itself in many ways. One of the most prominent ones is the relative representation of men and women among the scientists whose work receive the most attention in the ...
2023-11-21
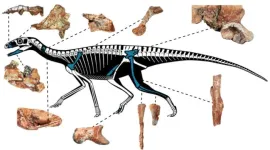
A set of fossils recovered in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil’s southernmost state, has brought an extra layer of complexity to the study of the evolutionary history of silesaurids, a family of dinosauriforms (dinosaurs and their close relatives) that lived in the Triassic period between 247 million and 208 million years ago.
In an article published in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, researchers affiliated with institutions in Brazil and the United States show that even with the new fossil assemblage ...
2023-11-21
NEW YORK – November 20, 2023 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation (CRF), in conjunction with the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2023 conference, CRF's annual scientific symposium, announced today the launch of the CRF Scientific Excellence Top 10 (SET-10), a new global annual ranking recognizing academic contributions to interventional cardiovascular medicine.
The SET-10 initiative, aligning with CRF's commitment to advancing the field, aims to recognize and celebrate the extraordinary contributions made by medical and academic ...
2023-11-21
Tuesday, Nov. 21, 2023, CLEVELAND: Cleveland Clinic researchers analyzed genes and brain tissue of patients with Alzheimer’s and found that differences in brain immunometabolism – the interactions between the immune system and the ways cells create energy – may contribute to women’s increased risk for the disease and its severity.
The findings, published in Alzheimer’s and Dementia, offer important insight into developing sex-specific treatment and prevention options for Alzheimer’s disease, the sixth-leading ...
2023-11-21
Hearing loss affects more than 60 percent of adults aged 70 and older in the United States and is known to be related to an increased risk of dementia. The reason for this association is not fully understood.
To better understand the connection, a team of University of California San Diego and Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute researchers employed hearing tests and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine whether hearing impairment is associated with differences in specific brain regions.
In the November 21, 2023 issue of the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, researchers reported that individuals enrolled in this observational ...
2023-11-21
University of Sussex researchers have developed a more energy-efficient alternative to transmit data that could potentially replace Bluetooth in mobile phones and other tech devices. With more and more of us owning smart phones and wearable tech, researchers at the University of Sussex have found a more efficient way of connecting our devices and improving battery life. Applied to wearable devices, it could even see us unlocking doors by touch or exchanging phone numbers by shaking hands.
Professor Robert Prance and Professor Daniel ...
2023-11-21
Day by day, we communicate with our office colleagues to accomplish tasks that are necessary to function. The more than 200 different types of cells in our bodies do the same thing, but the way they communicate with each other isn't as simple as sending an email.
Researchers like Ioannis Zervantonakis are still trying to understand how these cells actually communicate with each other. The assistant professor of bioengineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering recently received a National Institute of General Medical Sciences Maximizing Investigators' Research Award, and his project ...
2023-11-21
Digital payment platforms such as Venmo work great for sharing a dinner bill with friends, buying gifts at a pop-up shop or making payments without cash or credit cards.
But these digital payment platforms have a dark side: They can be misused for drug dealing and other illicit activity, suggest researchers from the University of California, Davis. And social media apps such as TikTok and Instagram can act as marketing tools for digital drug dealing.
“While platforms like Venmo revolutionize financial interactions, they also highlight the need for ongoing vigilance and adaptive regulatory measures,” said Pantelis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Unearthing how a carnivorous fungus traps and digests worms
New study examines molecular process at play through each stage of predation