(Press-News.org) Receiving at least one dose of a covid-19 vaccine before the first infection is strongly associated with a reduced risk of developing post-covid-19 condition, commonly known as long covid, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The findings, based on data for more than half a million Swedish adults, show that unvaccinated individuals were almost four times as likely to be diagnosed with long covid than those who were vaccinated before first infection.
The researchers stress that causality cannot be directly inferred from this observational evidence, but say their results “highlight the importance of primary vaccination against covid-19 to reduce the burden of post-covid-19 condition in the population.”
The effectiveness of covid-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe complications of acute covid-19 are already known, but their effectiveness against long covid is less clear because most previous studies have relied on self-reported symptoms.
To address this, researchers investigated the effectiveness of primary covid-19 vaccination (the first two doses and the first booster dose within the recommended schedule) against post-covid-19 condition using data from the SCIFI-PEARL project, a register based study of the covid-19 pandemic in Sweden.
Their findings are based on 589,722 adults (aged 18 and over) from the two largest regions of Sweden with a first covid-19 infection registered between 27 December 2020 and 9 February 2022.
Individuals were followed from a first covid-19 infection until a diagnosis of post-covid-19 condition, vaccination, reinfection, death, emigration or end of follow-up (30 November 2022), whichever came first. Average follow-up was 129 days in the total study population (vaccinated: 197 days, not vaccinated: 112 days).
Individuals who had received at least one covid-19 vaccine dose before infection were considered vaccinated.
A range of factors including age, sex, existing conditions, number of healthcare contacts during 2019, education level, employment status, and dominant virus variant at time of infection were also accounted for in the analysis.
Of 299,692 vaccinated individuals with covid-19, 1,201 (0.4%) were diagnosed with post-covid-19 condition during follow-up, compared with 4,118 (1.4%) of 290,030 unvaccinated individuals.
Those who received one or more covid-19 vaccines before the first infection were 58% less likely to receive a diagnosis of post-covid-19 condition than unvaccinated individuals.
And vaccine effectiveness increased with each successive dose before infection (a dose-response effect). For example, the first dose reduced the risk of post-covid-19 condition by 21%, two doses by 59%, and three or more doses by 73%.
This is an observational study, which provides less conclusive evidence of causality, and the researchers point to several limitations such as limited data on post-covid-19 condition symptoms and that the diagnosis code is not yet validated, the potential impact of reinfections on vaccine effectiveness, and expectations about the protective effect of vaccination.
However, this was a large, well designed study based on high quality, individual level registry data with a low risk of self-reporting bias, suggesting that the results are robust.
As such, the authors conclude: “The results from this study highlight the importance of complete primary vaccination coverage against covid-19, not only to reduce the risk of severe acute covid-19 infection but also the burden of post-covid-19 condition in the population.”
These findings, combined with evidence from other studies, highlight the association between the immune system and the development of post-viral conditions, and underline the importance of timely vaccination during pandemics, say researchers in a linked editorial.
They call for continued investigation into the evolution of long term residual symptoms of covid-19 and other viral illnesses as well as steps to “improve the accuracy of recording both recovery and continued illness after infection, and in quantifying key family, social, financial, and economic outcomes.”
“Such estimates are fundamental to unlocking the funding required for future research and increased investment in specialist clinical services offering treatment and rehabilitation to support patients with post-viral conditions,” they conclude.
END
COVID vaccination before infection strongly linked to reduced risk of developing long covid
Unvaccinated individuals almost four times as likely to be diagnosed than those vaccinated before first infection
2023-11-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Iron infusion before bowel surgery reduces need for blood transfusion
2023-11-23
Change in clinical practice would have clear benefits for patients undergoing major bowel surgery, according to analysis conducted by researchers from UCL and the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital.
The study, published in The British Journal of Surgery, provides evidence that giving iron intravenously before colorectal surgery improves outcomes for patients, reducing the need for blood transfusion by 33%.
Anaemia is a common problem in patients undergoing bowel surgery due to bleeding from the gut and blood loss during the operation. Anaemia is also associated ...
The first report on telomere-to-telomere gap-free reference genome of wild blueberry (Vaccinium duclouxii)
2023-11-23
Blueberry, a common Vaccinium species with small-sized berries, is known for its delicious taste, balanced sweetness and acidity, and rich nutritional content. It is abundant in various vitamins and antioxidants. However, the limited genetic resources for cultivated blueberries have significantly hindered their development and utilization. Therefore, utilizing wild blueberries' genetic resources for breeding is paramount to enhancing the resilience and quality of cultivated varieties.
Vaccinium duclouxii, native to the southwestern region of China, is an endemic wild blueberry ...
Chinese-Russian cooperation has strengthened significantly in the past 30 years, analysis shows
2023-11-22
Chinese and Russian cooperation has grown significantly in the past three decades thanks to joint work on energy trade, politics and official visits, analysis shows.
There was a ‘limited’ Sino–Russian cooperation intensity in 1992–1995, which grew from then until 2007 and then rose. The bilateral relationship grew progressively, with no exponential growth or peaks, according to the study.
There were no or dramatic changes following Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea.
The ...
Researchers develop new method for prenatal genetic testing
2023-11-22
A team of investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed a non-invasive genetic test that can screen the blood of pregnant individuals to survey all genes for fetal DNA sequence variants. The team evaluated the test by examining blood samples from 51 pregnant persons, finding that the test was able to capture variants that were inherited from the mother as well as new variants that were not present in the mother and associated with prenatal diagnoses. ...
Genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in Kazakh women
2023-11-22
“Our study may reveal previously uncharacterized population-specific variants that may increase the risk of BC in the Kazakh population.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on October 4, 2023, entitled, “Determination of genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in women of Kazakh ethnicity.”
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common type of cancer among women in Kazakhstan. To date, little data are available on the spectrum of genetic variation in Kazakh women with BC.
In this new study, researchers Gulnur Zhunussova, Nazgul Omarbayeva, ...
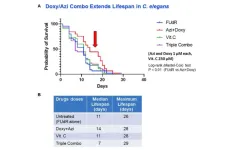
Mitochondria-targeting antibiotics extend lifespan in C. elegans
2023-11-22
“Our ultimate goal is to find existing FDA-approved drugs and dietary supplements that can not only increase lifespan but also improve healthspan.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Antibiotics that target mitochondria extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
Aging is a continuous degenerative process caused by a progressive decline of cell and tissue functions in an organism. It is induced by the accumulation of damage that affects normal cellular processes, ...
Adding a few servings of whole grains linked to slower memory decline in Black people
2023-11-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 22, 2022
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people who eat more foods with whole grains, including some breads and cereals, quinoa, and popcorn, may have a slower rate of memory decline compared to Black people who eat fewer whole grain foods, according to a study published in the November 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The researchers did not see a similar trend in white participants.
The study does not prove that eating more whole grains slows memory decline; it only shows an association.
The study found that among Black ...
Researchers obtain promising results against capacity loss in vanadium batteries
2023-11-22
An article by researchers at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF) in Brazil describes a successful strategy to mitigate charge capacity loss in vanadium redox flow batteries, which are used by electric power utilities among other industries and can accumulate large amounts of energy. The article is published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
CDMF is a Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) funded by FAPESP and hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in São Paulo state.
The study involved computer ...
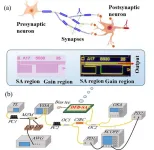
Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230140 discusses photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network.
Brain science and brain-like intelligence are the cutting-edge science and technology that countries all over the world compete to seize. The rapid rise and vigorous development of emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, 5G/6G, big data, autonomous driving, and the Internet of Things has led to the explosive growth of global data. Due to the memory wall effect, the conventional von Neumann architecture performs low energy efficiency. Electronic ...
Multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230021 overviews multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip.
Compared with traditional artificial neural networks, spiking neural networks (SNN) are more biologically authentic, more powerful, and less power-consuming due to their spatiotemporal coding and event-driven characteristics. In recent years, optical computing has been widely considered as a hardware acceleration platform, where nonlinear computing poses a challenge. Photonic SNN provides an ultra-fast and energy-efficient platform for high-performance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] COVID vaccination before infection strongly linked to reduced risk of developing long covidUnvaccinated individuals almost four times as likely to be diagnosed than those vaccinated before first infection