(Press-News.org) The U.S. must reduce racial residential segregation if it is to reduce racial disparities in health outcomes, according to a recently published study by researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine. The research on 220 metropolitan areas nationwide between 1980 and 2020 found strong links between trends in racial residential segregation and racial disparities in early death rates from a variety of causes.
The study is the first known to examine the association between changes in racial segregation over time and long-term trends in mortality among non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic white people ages 65 or younger.
“This work shows that if we’re able to reduce segregation in communities, we can also expect to reduce health disparities, which is a powerful insight for public health policy,” said Michael Siegel, professor of public health and community medicine at the School of Medicine and lead author on the study published in the Journal of Racial and Ethnic Disparities. “It’s not enough to simply identify disparities; we need to find evidence-based ways to reduce them.”
Drawing on federal data on mortality and demographics in metropolitan statistical areas (MSAs), the study looked at changes in residential segregation between 1980 and 2000 and changes in health outcomes between 2001 and 2018, by which time the researchers hypothesized that measurable differences in mortality would be evident.
The researchers found that both baseline levels of racial residential segregation and ongoing changes in segregation accurately predicted trajectories in the racial disparity in death rates among people younger than age 65 from 12 common causes: breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, genitourinary disease, HIV, hypertension, respiratory disease, pregnancy, and firearm homicide.
Striking was the fact that, regardless of baseline levels in 1980, increases in levels of segregation between 1980 and 2000 boosted the likelihood that an MSA would be characterized by greater racial health disparities between 2001 and 2018, almost tripling that likelihood in some cases.
Data analysis characterized three groups of MSAs, two of which had lower levels of baseline segregation and showed slight declines over time in Black-to-white mortality disparities. These groups were projected to see the end of disparities by 2034 and 2075, respectively. The third group had the highest levels of baseline segregation and disparities in death rates and their trajectories rose over time, indicating that racial disparities will continue to worsen.
“These data do not support the notion that racism is a thing of the past or that we’re in a post-racial society. In fact, for some people in some communities, things are getting worse,” Siegel said. “Systemic racism, such as restrictive housing covenants and discriminatory ‘redline’ lending policies, created residential segregation, and equally purposeful change will be needed to eliminate segregation and associated health inequities.”
The authors say that the study opens the door for further investigation to identify the best ways to reduce health disparities by combating residential segregation, and they suggest expansion of such research to include other races and ethnicities.
“I’m very excited about the additional research that our study will inspire,” said Leighla Dergham, MG26, one of the paper’s four graduate student authors, who is enrolled in the School of Medicine’s physician assistant and master of public health dual-degree program. “By identifying an important entry point for meaningful interventions, our research will potentially have great impact on future public health initiatives and policies to reduce racial health disparities associated with segregation.”
END
Reducing inequitable health outcomes requires reducing residential segregation
Study by Tufts University researchers of U.S. metropolitan areas over 40 years shows strong links between residential segregation and disparities in early death rates from common causes
2023-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Manard named recipient of 2023 JAAS Emerging Investigator Lectureship
2023-11-28
Manard named recipient of 2023 JAAS Emerging Investigator Lectureship
Benjamin Manard, an analytical chemist in the Chemical Sciences Division of the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been selected for the 2023 Emerging Investigator Lectureship from the Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry. JAAS is a publication of the Royal Society of Chemistry that shares innovative research on the fundamental theory and application of spectrometric techniques. Manard is the first winner of this award from a Department of Energy ...
Alcohol consumption may have positive and negative effects on cardiovascular disease risk
2023-11-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
November 28, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
Lisa LaPoint, lisa.lapoint@tufts.edu
##
While past research has indicated that moderate alcohol consumption can lower one’s risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), more recent studies suggest that moderate levels of drinking may be hazardous to heart health. ...
Anti-aging effects of 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose on brain diseases via AMPK activation
2023-11-28
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “1,5-anhydro-D-fructose induces anti-aging effects on aging-associated brain diseases by increasing 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α/brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway.”
5’-Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a metabolic sensor that serves as a cellular housekeeper; it also controls energy homeostasis and stress resistance. Thus, correct regulation ...
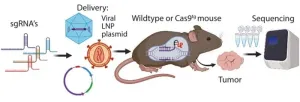
The double-edge sword of CRISPR application for in vivo studies
2023-11-28
“The Achilles’ heel of CRISPR application is the delivery of sgRNA/Cas9 to the desired tissues.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 28, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on November 27, 2023, entitled, “The double-edge sword of CRISPR application for in vivo studies.”
In this new paper, researcher Martin K. Thomsen from Aarhus University begins his editorial by discussing a hallmark paper that was published a decade ago by Platt et al. on the in vivo ...
UTA research examines how to stay on task
2023-11-28
Our ability to pay attention to tasks—a key component of our everyday lives—is heavily influenced by factors like motivation, arousal and alertness. Maintaining focus can be especially challenging when the task is boring or repetitive.
“In many activities, it is difficult to maintain a high level of focus over time. Our research asks why this is the case,” said Matthew K. Robison, assistant professor of psychology at The University of Texas at Arlington.
He and colleagues at the University ...
Research spotlight: Improvements in HIV care in Black and White men who have sex with men
2023-11-28
Katherine Rich, MD MPH, resident in the MGH Department of Medicine, is the first author of a recently published paper in JAMA Network Open, “Projected Life Expectancy Gains from Improvements in HIV Care in Black and White Men Who Have Sex With Men.” Aima Ahonkhai, MD MPH and Emily Hyle, MD MSc, physician investigators in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital, are co-senior authors.
What Question Were You Investigating?
Substantial inequities persist across the HIV care continuum in the US; Black people with HIV bear a disproportionate disease burden due, ...
Sylvester study: Country of birth a key factor in assessing risk for conditions favorable to stomach cancer development
2023-11-28
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Nov. 28, 2023) – Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have found that country of birth – not just geographic region – is a key risk factor for gastric intestinal metaplasia, a precursor lesion of stomach cancer.
Although stomach cancer, often called gastric cancer, is relatively rare in the United States, it is much more common and deadly among Hispanics, non-Hispanic Black people, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders than among the white population.
Sylvester and the University of Miami Health System serve a widely diverse racial and ethnic population, including ...
Carnegie Mellon University's XRTC will drive research into VR, AR innovations
2023-11-28
Virtual, augmented and other extended reality technologies present the possibility to transform health care, education, entertainment, communication and more.
And that transformation is close.
Headsets and haptic gloves could connect doctors and patients thousands of miles apart in a virtual hospital. Sensors could monitor someone's health or help teachers know if their students are paying attention. Scanners could allow objects from a person's home to appear in their favorite video game. Glasses could help people with visual impairments navigate the world around them. Extended ...
UTHealth Houston School of Dentistry researcher awarded $2 million grant by NIH to study pharmacotoxicity of areca nut
2023-11-28
A five-year, $2 million grant to study the pharmacological effects of the areca nut, commonly known as the betel nut, was awarded to a UTHealth Houston researcher by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The study, led by Alan Myers, PharmD, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology with UTHealth Houston School of Dentistry, will investigate how chemicals in the areca nut are metabolized in the body’s organs, particularly in the liver, and how that process is disrupted by alcohol or menthol.
“On the global level, areca nut chewing has been around since antiquity, but still poses a major public health ...
Heart over head? Stages of the heart’s cycle affect neural responses
2023-11-28
Optimal windows exist for action and perception during the 0.8 seconds of a heartbeat, according to research published November 28th in the open access journal PLOS Biology. The sequence of contraction and relaxation is linked to changes in the motor system and its ability to respond to stimulation, and this could have implications for treatments for depression and stroke that excite nerve cells.
The ways in which we perceive and engage with the world are influenced by internal bodily processes such as heartbeats, respiration and digestion. Cardiac activity can influence auditory and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
[Press-News.org] Reducing inequitable health outcomes requires reducing residential segregationStudy by Tufts University researchers of U.S. metropolitan areas over 40 years shows strong links between residential segregation and disparities in early death rates from common causes