(Press-News.org) Neutron stars have fascinated and puzzled scientists since the first detected signature in 1967. Known for their periodic flashes of light and rapid rotation, neutron stars are among the densest objects in the universe, with a mass comparable to that of the Sun but compressed into a sphere only about 20 kilometers in diameter. These stellar objects exhibit a peculiar behavior known as a “glitch”, where the star suddenly speeds up its spin. This phenomenon suggests that neutron stars might be partly superfluid. In a superfluid, rotation is characterized by numerous tiny vortices, each carrying a fraction of angular momentum. A glitch occurs when these vortices escape from the star's inner crust to its solid outer crust, thereby increasing the star's rotational speed.
The key ingredient for this study lies in the concept of a “supersolid” – a state that exhibits both crystalline and superfluid properties – which is predicted to be a necessary ingredient of neutron star glitches. Quantized vortices nest within the supersolid until they collectively escape and are consequently absorbed by the outer crust of the star, accelerating its rotation. Recently, the supersolid phase has been realized in experiments with ultracold dipolar atoms, providing a unique opportunity to simulate the conditions within a neutron star.
The recent study by researchers at the University of Innsbruck and the Austrian Academy of Sciences as well as the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso and the Gran Sasso Science Institute in Italy demonstrates that glitches can occur in ultracold supersolids, serving as versatile analogues for the inside of neutron stars. This groundbreaking approach allows for a detailed exploration of the glitch mechanism, including its dependence on the quality of the supersolid. “Our research establishes a strong link between quantum mechanics and astrophysics and provides a new perspective on the inner nature of neutron stars”, says first author Elena Poli. Glitches provide valuable insights into the internal structure and dynamics of neutron stars. By studying these events, scientists can learn more about the properties of matter under extreme conditions.
“This research shows a new approach to gain insights into the behavior of neutron stars and opens new avenues for the quantum simulation of stellar objects from low-energy Earth laboratories”, emphasizes Francesca Ferlaino.
The study has been published in Physical Review Letters and was financially supported by the Austrian Science Fund FWF and the European Research Council ERC, among others.
Publication: Glitches in rotating supersolids. Elena Poli, Thomas Bland, Samuel J. M. White, Manfred J. Mark, Francesca Ferlaino, Silvia Trabucco and Massimo Mannarelli. Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 223401 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.223401 [arXiv: 2306.09698]
END
Unlocking neutron star rotation anomalies: Insights from quantum simulation
Combining quantum mechanics and astrophysics sheds light on neutron star glitches
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Z-scheme heterojunction g-C3N5/Bi5O7I high-efficiency mercury removal photocatalyst
2023-12-05
They published their work on October. 23 in Energy Material Advances.
"It is imperative to develop energy-saving, safe and sustainable photocatalytic mercury removal technology," said paper author Wu Jiang, professor with College of Energy and Mechanical Engineering of Shanghai University of Electric Power. "Currently, thermocatalytic technologies account for most of the market, but they are constrained in terms of manufacturing costs and sustainability."
Wu ...
Medicare is overpaying for generic drugs
2023-12-05
Medicare is the single largest provider of health insurance in the United States, serving 63.8 million senior citizens as of 2022. Three-quarters of these recipients are enrolled in optional Medicare Part D plans, which provide outpatient prescription drug coverage to seniors through private insurance companies. In 2022, Medicare paid more than $160 Billion for prescription drugs, making it the single largest payer of pharmaceuticals in the US.
While Medicare is meant to keep healthcare affordable for seniors, millions of Americans still face steep costs ...
Forecasting forest health using models to predict tree canopy height
2023-12-05
Tree height is an important indicator of a forest’s maturity and overall health. Forest restoration projects rely on tree height as a predictor and measurement of success, but forecasting a forest’s future tree height based on observations alone is almost impossible. There are too many factors that contribute to the growth and health of trees.
Because so many factors can impact how a tree develops, researchers enhanced a predictive model called the Allometric Scaling and Resource Limitations (ASRL) model and then deployed it using ...
Green macroalga caulerpa has replaced seagrass in Florida’s Indian River Lagoon
2023-12-05
The Indian River Lagoon was considered one of the last “unpolluted coastal lagoons” in Florida in the 1970s. Fast forward to today and most of the 156-mile lagoon is now considered impaired because of external sources of nutrients including human waste, fertilizers, stormwater runoff, agriculture, rainfall and sub-marine groundwater discharge.
As a result, the lagoon – especially the Northern Indian River Lagoon and Banana River – has experienced various harmful algal blooms, catastrophic seagrass losses, and is the epicenter of Florida ...
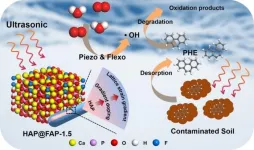
Novel mineral piezocatalysts offer innovative approaches for soil remediation
2023-12-05
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) removal in the soil environment is of great significance for repairing the long-term damaged ecosystem. However, the poor mass transfer process and low catalytic activity in most conventional methods lead to limited removal efficiency. A team of scientists has constructed a gradient F-doping hydroxyapatite core-shell structure (HAP@FAP) with the coupling effect of flexoelectricity and piezoelectricity for degradation of PAHs in soil that provide innovative approaches for soil remediation. Their work was published in the journal Industrial Chemistry & Materials in October 2023.
The poor mass ...
Florida wildflowers and pollinators get a boost with two grants
2023-12-05
The Daniels Lab at the Florida Museum of Natural History was recently awarded two grants to help support pollinators in Florida. The Florida Department of Transportation has set aside $155,002 for the team to plant and monitor thousands of milkweeds along roads in North Florida, and Duke Energy Florida will distribute $144,421 over three years to evaluate the establishment of pollinator habitat at its new solar site Alachua County.
Pollinators are declining on a global scale, the collateral damage of continued habitat destruction and urbanization, among other stressors. ...
Glyphosphate: a silver-bullet weed killer no more
2023-12-05
For decades, corn and soy farmers have heavily relied on one herbicide: glyphosate. Crops bred to resist glyphosate have been extremely successful, with over 90% of corn and soy hectares planted with glyphosate-resistant varieties by 2014. But as Christopher Landau and colleagues document, the chemical was not quite the “silver bullet” it was promised to be. With an entire industry using the same chemical—the US and Canada alone apply more than 130 million kg annually—evolutionary selection pressures on weed plants have been intense. Since 1996, there have been 354 confirmed cases of glyphosate ...
Blue light exposure and aging
2023-12-05
In a study on fruit flies, daily low-intensity blue light exposure (BLE), similar to that experienced daily by billions of humans in the form of LED lighting and device screens, changed flies at the sub-cellular level, affecting processes related to aging and circadian rhythms. Xiaoyun Wang and colleagues exposed fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) to different durations of daily low-intensity BLE and then analysed the consequences to the cellular makeup of the insects, as compared to flies raised in darkness. The authors paid particular attention to ...
Toxicity at Wikipedia
2023-12-05
A study links hostility on Wikipedia to lost productivity on the site. Wikipedia, the largest reference work ever created, is written and edited by tens of thousands of volunteers, known as Wikipedians. Despite the fact that anyone can edit any page, studies show that Wikipedia is generally a reliable source of information. Ivan Smirnov and colleagues studied how the volunteer labor that keeps the site working is affected by hostile comments in the “user talk” pages connected to each editor. Toxic comments were identified by a toxicity detection algorithm devised by the Perspective API ...
Reliable research and evidence-based recommendations scarce for women who exercise according to menstrual cycle
2023-12-05
Hamilton, ON, December 5, 2023 – There is no shortage of advice for women on what to eat, how to train, or what supplements to take during their menstrual cycles, but a new review by an international team of scientists has found little evidence to support such recommendations.
In fact, they found sparse research on women and exercise at all, and even less on the effect of their periods on sports performance, physiology, or physical fitness.
The authors of the paper, from McMaster University, Manchester Metropolitan University and the Australian Catholic University in Melbourne, are calling for much more high quality, standardized research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
[Press-News.org] Unlocking neutron star rotation anomalies: Insights from quantum simulationCombining quantum mechanics and astrophysics sheds light on neutron star glitches