(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — People with celiac disease, or intolerance to dietary gluten, may soon have more food options, thanks to an unlikely source: sourdough bread. Sourdough contains less gluten than other breads, making it more tolerable for people with gluten sensitivities. Now, Penn State and Colorado State University researchers are studying whether bacteria in the yeast starter needed to make sourdough bread might help reduce gluten in other bread products.
Gluten is a protein naturally found in cereal grains such as wheat, barley and rye that can trigger an immune response in people with gluten intolerance and celiac disease. Gluten intolerances, characterized by adverse gastrointestinal symptoms upon consumption of gluten-containing food products, are estimated to affect approximately 7% of the U.S. population, according to the National Institutes of Health. Of this number, 1% suffer from celiac disease. Incidence of celiac disease has increased 7.5% per year over the last several decades, mirroring a continually increasing prevalence of all autoimmune disorders worldwide.
Funded by a $500,000 grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, co-principle investigators Josephine Wee, Penn State assistant professor of food science, and Charlene Van Buiten, Colorado State University assistant professor of food science and human nutrition, will not only investigate if sourdough starter microbiomes can detoxify gluten in bread products, making them safe for individuals with celiac disease, but also whether they can be selected and manipulated to boost bread quality and safety.
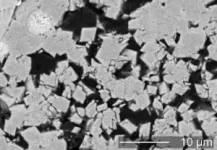
Conventional bread dough uses baker’s yeast in place of naturally present yeast and bacteria — known as sourdough fermentation, Wee explained. Sourdough bread is made by the fermentation of dough with wild Lactobacillaceae and yeast. Sourdough bread is leavened with “starter cultures,” or communities of naturally occurring bacteria and yeast that are portioned and maintained through a series of passages at room temperature. These communities are collectively known as the sourdough microbiome.
“A study of 500 sourdough starters collected from around the world showed that no two starters are exactly alike, and presently, little is known about the ability of sourdough microbiomes,” Wee said. “Outcomes from this work will use whole food microbiomes to develop fermentation technologies that will address the next generation of consumer demands for high-quality ‘clean label’ products with reduced gluten immunogenicity.”
Immunogenicity is the ability of cells or tissues to provoke an undesirable immune response. Clean label means making a product using as few ingredients as possible and making sure those ingredients are items that consumers recognize and think of as wholesome, or less processed — ingredients that consumers might use at home.
Bread production worldwide exceeds 100 million tons annually, valued at $201 billion, according to Custom Markets Insights. However, bread is also a major contributor to food waste due to spoilage or overproduction and changing consumer preferences, Wee pointed out. She added that current bread-manufacturing practices fall short in meeting demands, necessitating innovative approaches to improve quality and reduce waste.
“With combined expertise in food microbiology and nutritional biochemistry, our team is interested in characterizing the relationship between the sourdough microbiome, bread quality and gluten immunogenicity,” Wee said. “We hope the findings of this research will influence functional outcomes of bread quality and safety.”
Van Buiten is a Penn State alumna, graduating with a doctoral degree in food science in 2017.
END
Study of sourdough starter microbiomes to boost bread quality and safety
USDA grant to fund research that may benefit those with celiac disease
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UT receives National Institute of Justice awards for forensics research
2023-12-05
The Forensic Anthropology Center at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, has received two grants totaling over $580,000 from the Office of Justice Program’s National Institute of Justice, the research, development and evaluation agency of the U.S. Department of Justice. A longtime grantee across numerous forensics research topics, the center – which includes the Anthropological Research Facility, also known as the Body Farm – is known worldwide for its research and training.
The first of the two new research projects will help law enforcement locate clandestine graves, and the second will help inform how relic DNA in the soil affects forensic ...
Newly identified biomarkers may detect early cognitive decline via blood test
2023-12-05
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — For some people, extreme stressors like psychiatric disorders or childhood neglect and abuse can lead to a range of health problems later in life, including depression, anxiety and cardiovascular disease. A new study led by researchers in the Penn State Center for Healthy Aging identified genetic indicators that can predict another health problem, the decline of cognitive abilities, among people who have been affected by these extreme stressors.
The team recently published their findings ...
Researchers predict climate change-driven reduction in beneficial plant microbes
2023-12-05
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Bacteria that benefit plants are thought to be a critical contributor to crops and other ecosystems, but climate change may reduce their numbers, according to a new study by an international team of researchers. They published their findings in Nature Food.
The collaboration, including Francisco Dini-Andreote, professor of plant science at Penn State, characterized the abundances and distributions of plant beneficial bacteria (PBB) from soils collected across the globe. The researchers ...
Addicted to your phone? New tool identifies overuse of digital media
2023-12-05
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- The rapidly evolving nature of digital media presents a challenge for those who study digital addiction – social networks like TikTok and video games like Fortnite might be popular now, but they could be irrelevant in a matter of years. A new tool developed by researchers from Binghamton University, State University of New York will make it easier for clinicians and researchers to measure digital media addiction as new technologies emerge.
“We wanted to create a tool that was immediately useful in the clinic and lab, that reflects current understandings about how digital addiction works, that wouldn't go obsolete once the next big tech ...
International consensus report on gaps and opportunities for the clinical translation of precision diabetes medicine
2023-12-05
Boston, MA - A new international consensus report on precision medicine in diabetes prevention and care highlights the significant advancements in precision medicine in diabetes prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis while also shedding light on numerous knowledge gaps.
The report, Second international consensus report on gaps and opportunities for the clinical translation of precision diabetes medicine, was published in Nature Medicine on October 5, 2023.
Supported by the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), and the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the consensus report was made possible through a huge collaborative ...
Depression, constipation, and urinary tract infections may precede MS diagnosis
2023-12-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, TUESDAY, DECEMBER 5, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – In some diseases, the underlying processes can start years before a diagnosis is made. A new study finds that people who later develop multiple sclerosis (MS) are more likely to have conditions like depression, constipation and urinary tract infections five years before their MS diagnosis than people who do not develop MS. The study, which is published in the December 5, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, also found that sexual problems and bladder infections, or cystitis, ...
Chemists create organic molecules in a rainbow of colors
2023-12-05
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Chains of fused carbon-containing rings have unique optoelectronic properties that make them useful as semiconductors. These chains, known as acenes, can also be tuned to emit different colors of light, which makes them good candidates for use in organic light-emitting diodes.
The color of light emitted by an acene is determined by its length, but as the molecules become longer, they also become less stable, which has hindered their widespread use in light-emitting applications.
MIT chemists have now come up with a way to make these molecules more stable, allowing them to synthesize acenes of varying lengths. Using their new approach, ...
NCCN summit navigates solutions for financial and other cancer-related hardships
2023-12-05
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [December 5, 2023] — Today, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—hosted a Patient Advocacy Summit to explore the role of navigation throughout the cancer process. A diverse group of subject matter experts addressed the impact patient navigation has on care and how to utilize navigators to reduce economic burdens and disparities in care. The speakers included patients and advocates, policymakers, health care providers, and health data analysts.
The summit featured a series of best practice presentations highlighting some of the tools available to assist in various ...
Incarcerated women punished at higher rates for minor infractions than men, UTEP study shows
2023-12-05
EL PASO, Texas (Dec. 5, 2023) – A new study from The University of Texas at El Paso reveals a gender disparity in prison infractions that disproportionately affects women.
The study, led by Melinda Tasca, Ph.D., an associate professor in the Department of Criminal Justice and Security Studies at UTEP, and published in Justice Quarterly, analyzed the disciplinary infraction records of more than 20,000 males and females in a large western state prison, who were released between 2010 and 2013.
The researchers set out to answer three questions: ...
Conference on microplastics in water: characterization, cure and prevention
2023-12-05
Plastics are ubiquitous in all aspects of modern life, including food packaging, health care and household products. There has been a massive increase in plastics production over the past several decades and there has been serious attention paid to managing plastic wastes, particularly focused on recycling/reuse. However, as of the present time it has not been feasible, either technically or economically, to achieve a fully circular system. Those plastic materials that are not processed for reuse, known as end-of-life pastics, end up in landfillsor in other waste processing systems (e.g., incineration) or advanced recycling (eg., pyrolysis) or directly disposed in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Next-generation CAR-T designs that could transform cancer treatment
As health care goes digital, patients are being left behind
A clinicopathologic analysis of 740 endometrial polyps: risk of premalignant changes and malignancy
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
Women more likely to choose wine from female winemakers
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
Largest image of its kind shows hidden chemistry at the heart of the Milky Way
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
[Press-News.org] Study of sourdough starter microbiomes to boost bread quality and safetyUSDA grant to fund research that may benefit those with celiac disease