(Press-News.org) African honeyguide birds understand and respond to the culturally distinct signals made by local human honey hunters, suggesting cultural coevolution between species, according to a new study. Although the animal kingdom is full of interspecific mutualism, systems in which humans successfully cooperate with wild animals are rare. One such relationship involves the greater honeyguide (Indicator indicator), a small African bird known to lead humans to wild bees’ nests. Humans open the nests to collect honey, and the honeyguides eat the exposed beeswax. Human honey hunters in different parts of Africa often use specialized and culturally distinct calls to signal they are looking for a honeyguide partner and to maintain cooperation while following a guiding bird. For example, honey hunters from the Yao cultural group in northern Mozambique use a loud trill followed by a grunt (“brrr-hm”). In contrast, honey hunters from the Hadza cultural group of northern Tanzania use a melodic whistle. These successful calls have been maintained in these groups for generations. In a series of field experiments across these areas, Claire Spottiswoode and Brian Wood investigated whether honeyguides are more likely to respond to signals of their local human culture than to those of another culture or to arbitrary human sounds. Spottiswoode and Wood discovered that honeyguides in the Yao area were more than three times more likely to initiate a guiding response to the Yao’s distinct call than the Hadza’s whistle. Conversely, honeyguides in the Hadza area were more than three times as likely to respond to the Hadza’s whistle than the Yao’s brrr-hm. According to the authors, the geographic variation and coordination between signal and response observed in this behavioral system suggests cultural coevolution between honeyguides and humans has occurred. In a related Perspective, William Searcy and Stephen Nowicki discuss the study and its findings in greater detail.
For reporters interested in trends, this study builds on previous work published in a July 2016 Report in Science, which demonstrated the reciprocal signaling in honeyguides and honey hunters in Mozambique.
END
Honeyguide birds learn distinct signals made by honey hunters from different cultures
2023-12-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Two studies demonstrate on-demand quantum entanglement in ultracold molecules
2023-12-07
The controlled creation of quantum entanglement with molecules has been a long-standing challenge in quantum science. Now, in two new studies, researchers report a method for tailoring the quantum states of individual molecules to achieve quantum entanglement on demand. Their strategy presents a promising new platform for the advancement of quantum technologies such as computation and sensing. Quantum entanglement is one of the key defining features of quantum mechanics. It is central to many quantum applications. Because of their rich internal structure ...
Trees in wetter forests more sensitive to drought than trees in drier regions – a finding with policy implications
2023-12-07
Annual tree-ring growth records from more than 122 species of trees show that trees growing in wetter forests are more sensitive to increasing drought. The findings – which tackle a research question that has yielded contradictory results in the past – suggest that land management and policy focused solely on drought effects in drier regions overestimates the resilience of forests in wetter regions. Forests cover roughly 30% of Earth’s surface and, in addition to providing a host of valuable ecosystem services and harboring huge biodiversity, they play a crucial role in the planet’s carbon cycle, absorbing more atmospheric carbon than all other terrestrial ...
A new 66 million-year history of carbon dioxide offers little comfort for today
2023-12-07
A massive new review of ancient atmospheric carbon-dioxide levels and corresponding temperatures lays out a daunting picture of where the Earth’s climate may be headed. The study covers geologic records spanning the past 66 million years, putting present-day concentrations into context with deep time. Among other things, it indicates that the last time atmospheric carbon dioxide consistently reached today’s human-driven levels was 14 million years ago—much longer ago than some existing assessments indicate. It asserts that long-term climate is highly sensitive to greenhouse gas, with cascading effects that may evolve over many millennia.
The ...
Grunt or whistle: successful honey-hunters know how to communicate with wild honey-seeking birds
2023-12-07
In many parts of Africa, humans cooperate with a species of wax-eating bird called the greater honeyguide, Indicator indicator, which leads them to wild bees’ nests with a chattering call. By using specialised sounds to communicate with each other, both species can significantly increase their chances of accessing calorie-dense honey and beeswax.
Human honey-hunters in different parts of Africa use different calls to communicate with honeyguides. In a new study, researchers have discovered that honeyguide birds in Tanzania and Mozambique discriminate among honey-hunters’ calls, responding much more readily to ...
Geoscientists map changes in atmospheric CO2 over past 66 million years
2023-12-07
Embargoed: Not for Release Until 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Thursday, Dec. 7 2023.
Today atmospheric carbon dioxide is at its highest level in at least several million years thanks to widespread combustion of fossil fuels by humans over the past couple centuries.
But where does 419 parts per million (ppm)—the current concentration of the greenhouse gas in the atmosphere—fit in Earth’s history?
That’s a question an international community of scientists, featuring key contributions by University of Utah geologists, is sorting out by examining a plethora of markers in the geologic record that offer ...
Ancient stars made extraordinarily heavy elements
2023-12-07
How heavy can an element be? An international team of researchers has found that ancient stars were capable of producing elements with atomic masses greater than 260, heavier than any element on the periodic table found naturally on Earth. The finding deepens our understanding of element formation in stars.
We are, literally, made of star stuff. Stars are element factories, where elements constantly fuse or break apart to create other lighter or heavier elements. When we refer to light or heavy elements, we’re talking about their atomic mass. Broadly speaking, atomic ...
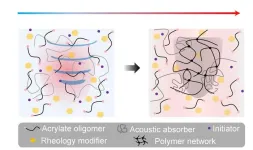
Soundwaves harden 3D-printed treatments in deep tissues
2023-12-07
DURHAM, N.C. -- Engineers at Duke University and Harvard Medical School have developed a bio-compatible ink that solidifies into different 3D shapes and structures by absorbing ultrasound waves. Because it responds to sound waves rather than light, the ink can be used in deep tissues for biomedical purposes ranging from bone healing to heart valve repair.
This work appears on December 7 in the journal Science.
The uses for 3D-printing tools are ever increasing. Printers create prototypes of medical devices, design flexible, ...
Physicists ‘entangle’ individual molecules for the first time, hastening possibilities for quantum information processing
2023-12-07
For the first time, a team of Princeton physicists have been able to link together individual molecules into special states that are quantum mechanically “entangled.” In these bizarre states, the molecules remain correlated with each other—and can interact simultaneously—even if they are miles apart, or indeed, even if they occupy opposite ends of the universe. This research was recently published in the journal Science.
“This is a breakthrough in the world of molecules because of the fundamental importance of quantum entanglement,” said Lawrence Cheuk, assistant professor of physics at Princeton ...
Wild birds lead people to honey — and learn from them
2023-12-07
Key takeaways
People in parts of Africa communicate with a wild bird, the greater honeyguide, to locate bee colonies and harvest their honey and beeswax.
A study by UCLA anthropologist Brian Wood and other authors show how this partnership is maintained and varies across cultures.
They demonstrate the bird’s ability to learn distinct vocal signals traditionally used by different honey-hunting communities.
In parts of Africa, people communicate with a wild bird — the greater honeyguide — in order to locate bee colonies and harvest their stores of honey and beeswax.
It’s a rare example of ...
Evolving trends in cosmetic breast augmentation: New data
2023-12-07
November 30, 2023 – Ongoing quality improvement data submitted by Board-certified plastic surgeons highlight current trends in surgical technique in cosmetic breast augmentation using implants, reports a study in the December issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"The findings illustrate evolving trends in breast enhancement over the past 16 years, including factors like the location of the incision and the type and positioning of implants," comments lead author Michael J. Stein, ...