(Press-News.org) Issues of identity, male-dominated branding and apprehension that their needs will go unmet are among the reasons women are not accessing veterans’ mental health support, according to new research being discussed today (Wednesday, 13 December) at a conference in Cambridge.
The report, I don’t feel like that’s for me: Overcoming barriers to mental healthcare for women veterans, was carried out by the Centre for Military Women’s Research (CMWR) at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), to investigate the low numbers of ex-servicewomen engaging with veteran-specific mental health services.
The report was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) and will be presented today at the CMWR’s inaugural conference in Cambridge, which features international perspectives on sexual violence in the military. This conference is the first in the UK to focus on this topic.
There are approximately a quarter of a million female veterans in England and Wales, making up 13.6% of the veteran community of 1.85million, but the report found many “fall through the gaps” between civilian and military mental health provision.
The researchers interviewed 48 women veterans in England who had experienced a mental health challenge within the past five years, along with 12 mental health professionals. Guidance for working with women veterans in mental health services was co-created with women veterans.
The report found mental health challenges were often not solely related to combat or deployment experiences, and identified several reasons why women veterans may not engage with veteran-specific mental health support, including:
Not identifying with the term ‘veteran’
A lack of awareness of available support for veterans
A perception that veteran services did not understand the needs of women
Male-dominated service branding
Practical barriers associated with care responsibilities
One Royal Air Force veteran, who served between 1989 and 1996, said: “It was only recently that I viewed myself as a veteran, so I kind of dismissed anything to do with the military in terms of accessing any support”
An Army veteran, who served from 1999-2002, added she felt military support organisations were “not going to be able to understand me talking about my sexual assault, sexual harassment, or discrimination. And it would almost feel like that organisation as a whole would be rolling their eyes on the end of the phone.”
Principal investigator Dr Lauren Godier-McBard, Associate Professor and co-director of the Centre for Military Women’s Research at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), said: “Our report found that women veterans experienced mental health challenges for many reasons related to both their military service and transition into civilian life, from facing discrimination or sexual violence in their service role, to struggling with identity or caring responsibilities.
“It appears from the interviews we carried out that many ex-servicewomen feel they fall through the gaps between mental health services for civilians and military veterans. Many did not identify with the word ‘veteran’, considering it to be a male label or preferring to identify with the various other roles in their life, such as being a parent.”
Lead author of the report, Abigail Wood, Research Fellow at the Centre for Military Women’s Research at ARU, added: “To encourage women to approach services in the first place, improving the visibility of women in service branding and materials was seen as critical. Clinician understanding of both the military lifestyle and women’s unique military experiences was considered important, as was giving women veterans the choice of clinicians based on their military background and gender, and the option of women-only treatment groups.
“There are plenty of services that offer support to women veterans, and hopefully this report will assist those services and veterans themselves to ensure that more people reach out for mental health help.”
Patricia Price, peer researcher at ARU and Army veteran, said: "What all women veterans want is to be seen and heard, without pre-judgement, without a tick box and without being seen as the cause of the issue they need support to resolve. We are equally as deserving of support, recognition and respect as each and every other professional member of the Armed Forces and each and every other Armed Forces Veteran is.
“Women in the Armed Forces are entitled to a successful and fulfilling veteran life. We simply must do better for them.”
END
Mental health care gaps for women veterans - report
New research finds ex-servicewomen feel excluded from civilian and military support
2023-12-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
National policy aimed at reducing U.S. greenhouse gases also would improve water quality
2023-12-13
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — A climate policy that raises the price of carbon-intensive products across the entire U.S. economy would yield a side benefit of reducing nitrate groundwater contamination throughout the Mississippi River Basin.
The Gulf of Mexico, an important U.S. fishery, also would see modest benefits from the nitrate reductions. These were among the conclusions of a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The study, led by four early career researchers, three of them from ...
Twenty-year study confirms California forests are healthier when burned — or thinned
2023-12-13
Berkeley — A 20-year experiment in the Sierra Nevada confirms that different forest management techniques — prescribed burning, restoration thinning or a combination of both — are effective at reducing the risk of catastrophic wildfire in California.
These treatments also improve forest health, making trees more resilient to stressors like drought and bark beetles, and they do not negatively impact plant or wildlife biodiversity within individual tree stands, the research found. The findings of the experiment, called the Fire Surrogate Study, were published today in the journal Ecological Applications.
“The research ...
Caregiving can be stressful, but it could also lower risk of depression
2023-12-12
Becoming a caregiver to an aging parent or spouse can be stressful, but a new study from a researcher at The University of Texas at Austin is questioning the idea that family caregiving is also a risk factor for depression.
The study, published in the journal Advances in Life Course Research, found that depression in adult caregivers is mostly driven by having a loved one experiencing serious health problems, while becoming a caregiver is associated with fewer symptoms of depression.
“Decades of research on this topic indicate that there are positive and negative aspects to being a caregiver,” said Sae Hwang Han, ...
UCF researcher discovers new technique for photon detection
2023-12-12
University of Central Florida researcher Debashis Chanda, a professor at the NanoScience Technology Center, has developed a new technique to detect photons — elementary particles that span from visible light to radio frequencies and are instrumental in carrying cellular communication.
The advancement could lead to more precise and efficient technologies in various fields, from improving medical imaging and communication systems to enhancing scientific research and even potentially bolstering security measures.
Photon detection has typically relied on change/modulation of voltage or ...
Fat flies live longer on a diet at any age
2023-12-12
Old, obese flies get healthier and live longer if put on a diet, University of Connecticut researchers report on Dec. 8 in PNAS. If the effect holds true for humans, it would mean it’s never too late for obese people to improve their health with diet.
For way too many of us, eating too much goes along with getting old and a tendency to be obese. Different health organizations define obesity differently, but all agree it means having too much body fat, and is associated with a host of diseases related to metabolism including heart disease and diabetes. Many animal studies have shown that eating less—meaning sharply ...
European Policy Lab gathers stakeholders to map forest policy opportunities and barriers
2023-12-12
ForestPaths’ first Policy Lab convened stakeholders in Helsinki, Finland, on 27-29 September 2023. Nineteen carefully selected participants with diverse expertise – including research, policy, governance, civil society, value chain professionals, and forestry practitioners – engaged in discussions on forest-based policymaking and modelling related to climate change and biodiversity.
Tasked with considering policy actions given different timescales, governance paradigms, enablers, and barriers, participants contributed ...
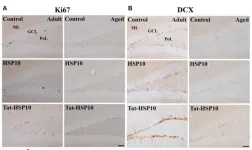
Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes in the hippocampus
2023-12-12
“Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major cellular change observed in the hippocampus during aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes by facilitating neuronal plasticity and reducing age-related genes in the hippocampus.”
In this new study, researchers Hyo Young Jung, Hyun Jung Kwon, Kyu ...
MIT researchers observe a hallmark quantum behavior in bouncing droplets
2023-12-12
In our everyday classical world, what you see is what you get. A ball is just a ball, and when lobbed through the air, its trajectory is straightforward and clear. But if that ball were shrunk to the size of an atom or smaller, its behavior would shift into a quantum, fuzzy reality. The ball would exist as not just a physical particle but also a wave of possible particle states. And this wave-particle duality can give rise to some weird and sneaky phenomena.
One of the stranger prospects comes from a thought experiment known as the “quantum bomb tester.” The experiment proposes that a quantum particle, such ...
Smoking causes brain shrinkage
2023-12-12
Smoking shrinks the brain, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The good news is that quitting smoking prevents further loss of brain tissue — but still, stopping smoking doesn’t restore the brain to its original size. Since people’s brains naturally lose volume with age, smoking effectively causes the brain to age prematurely, the researchers said.
The findings, published in Biological Psychiatry: Global Open Science, help explain why smokers are at high risk of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
“Up until recently, scientists have overlooked ...
Mammogram rates increase when patients schedule themselves
2023-12-12
PHILADELPHIA— Having the ability to self-schedule mammograms was associated with a 15 percentage point increase following through with getting the screening, according to research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The paper was published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
“Self-scheduling helps make the path to mammogram completion a little smoother, where you don’t have to find the time to call a scheduling line, wait on hold, or go back and forth trying to find an appointment that works for your schedule,” said the study’s lead author, Kimberly Waddell, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Mental health care gaps for women veterans - reportNew research finds ex-servicewomen feel excluded from civilian and military support