(Press-News.org)
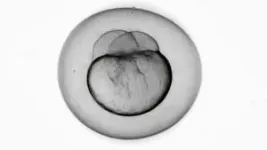
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have published an atlas of zebrafish development, detailing the gene expression programs that are activated within nearly every cell type during the first five days of development, a period in which embryos mature from a single cell into distinct cell types. These diverse cells become tissues and organs that form juvenile fish capable of swimming and looking for food. The findings are published in Developmental Cell.
“Perhaps surprisingly, tiny zebrafish provide us with significant insight into human development and disease. Many of the gene expression programs that direct embryonic growth are similar across fish, people, and other animals,” said Christopher McBain, Ph.D., scientific director of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), which conducted the work. “Since zebrafish are visibly transparent, fertilize eggs externally, and are easy to study genetically, they represent a unique and effective way to model human disease.”
The process of embryonic development is orchestrated by instructions in DNA that direct different programs of gene expression within individual cells, which give different cell types their unique functional characteristics. To create the atlas, the study team used a method called single-cell RNA sequencing to identify gene expression programs over the course of five days, with samples taken every two to 12 hours. The resulting atlas follows nearly 490,000 cells continuously over 120 hours after fertilization, with an average of 8,621 transcripts and 1,745 genes detected per cell. The study team then sorted these data among known cell types and cell states during development.
To highlight the atlas’ utility, the team focused on the development of understudied cells, including intestinal cells called BEST4+ cells, which are linked to gastrointestinal diseases and cancer in people. Little is known about how these cells develop because they are absent in other common model organisms, such as mice. By using the atlas, the team computationally predicted the full developmental program of BEST4+ cells, including signals that initiate the cells’ development and transcription factors that carry out the process. These findings can be evaluated in model organisms or clinical samples to better understand the role of BEST4+ cells in human disease.
“Our atlas on early zebrafish development is an extremely thorough resource that describes the expression program of hundreds of cell types across 62 developmental stages,” said senior author Jeffrey A. Farrell, Ph.D., an Earl Stadtman Investigator and head of NICHD’s Unit on Cell Specification and Differentiation. “From this atlas, we made discoveries about understudied cells, including intestinal cells involved in human diseases, smooth muscle that surrounds the intestine, and cells that surround blood vessels. There are many more advances waiting to be uncovered, and we look forward to seeing what the research community can do with our open-source atlas.”
The atlas is publicly accessible to the broader research community at https://daniocell.nichd.nih.gov. In addition to browsing the data online through the website, data may also be downloaded in additional formats for reanalysis. A timelapse of early zebrafish development is available for viewing, as well as microscopy images related to the study. To learn more about the NIH Zebrafish Facility, visit the NIH Virtual Tour.
REFERENCE:
Sur A., et. al. Single-cell analysis of shared signatures and transcriptional diversity during zebrafish development.Developmental Cell DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.11.001 (2023)
###
About the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD): NICHD leads research and training to understand human development, improve reproductive health, enhance the lives of children and adolescents, and optimize abilities for all. For more information, visit www.nichd.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
END
Estimated to be worth USD 50.1 billion by 2030, a Surrey team of researchers has uncovered the potential of the growing dog-friendly travel market. The Covid-19 pandemic drove an increase in UK household dog ownership, creating a need for tourism providers to adapt to accommodate these four-legged family members.
The Surrey team set out to understand why people travel with their dogs, how they feel about it, and what challenges they face doing so.
Lori Hoy, PhD Researcher and lead author of the study at the University of Surrey, said:
"Some reports suggest that the UK dog population stands at 11 million, with 29% of UK adults having a dog in their ...
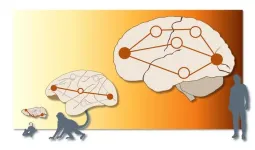
In a study comparing human brain communication networks with those of macaques and mice, EPFL researchers found that only the human brains transmitted information via multiple parallel pathways, yielding new insights into mammalian evolution.
When describing brain communication networks, EPFL senior postdoctoral researcher Alessandra Griffa likes to use travel metaphors. Brain signals are sent from a source to a target, establishing a polysynaptic pathway that intersects multiple brain regions “like a road with many stops along the way.”
She explains that structural brain ...
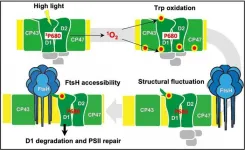
Photosynthesis refers to the fundamental biological process of the conversion of light energy into chemical energy by chlorophyll (a green pigment) containing plants. This seemingly routine process in plants sustains all the biological life and activities on Earth. First reaction of photosynthesis occurs at a site called photosystem II (PSII), present on the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast where light energy is transferred to chlorophyll molecules. PSII is made up of a complex group of proteins, including the D1 and D2 reaction center proteins.
Light ...
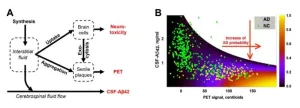
Despite affecting millions worldwide, Alzheimer's disease (AD) has long lacked effective treatments due to a fundamental inadequacy of our understanding of its etiology and pathogenesis. The absence of an integrative theory connecting the molecular origins of AD with disturbances at the organelle and cell levels, changes in relevant biomarkers, and population-level prevalence has hindered progress. Even though most scientists only hope that an integrative theory of AD will emerge soon, scientists from Zarbio and Georgia State University discovered sufficient data to formulate a framework for such a theory.
The molecular and cellular ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – In a first-of-its-kind study of aardvarks, Oregon State University researchers spent months in sub-Saharan Africa collecting poop from the animal and concluded that aridification of the landscape is isolating them, which they say could have implications for their long-term survival.
“Everyone had heard of aardvarks and they are considered very ecologically important but there has been little study of them,” said Clint Epps, a wildlife biologist at Oregon State. “We wanted to see if we could collect enough data to begin to understand them.”
In ...
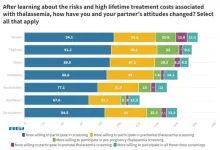
- Insights from Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences at Chiang Mai University, on raising thalassemia awareness in Thailand.
Thalassemia, a genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin production, poses a significant public health challenge in Thailand, with a high prevalence and substantial healthcare costs. According to Thailand's Ministry of Public Health, approximately 18-24 million or 30-40 percent of the Thai population carries the thalassemia gene.
Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, shared his views on BGI Genomics Global 2023 State of Thalassemia Awareness ...
(Denver—December 18, 2023) – Adopting a lung nodule program (LNP) may increase the detection of early lung cancer for patients who are not eligible for lung cancer screening under existing age eligibility criteria, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
LNPs are established to follow up on lung nodules that are frequently identified during routine imaging for reasons other than suspected lung cancer or lung cancer screening.
The research was conducted by a team led by Dr. Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist ...
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart defects – the most common birth defects in the United States – is associated with improved outcomes. Despite its importance, however, overall prevalence of prenatal diagnosis is low (12-50 percent). A recent multi-center study surveyed caretakers of infants who received congenital heart surgery in the Chicago area and found that social determinants or influencers of health constitute significant barriers to prenatal diagnosis from the patients’ perspective.
In ...
In a new analysis of data spanning more than three decades in the eastern United States, a team of scientists found a concerning trend – an increasing number of wildfires across a large swath of America.
“It’s a serious issue that people aren’t paying enough attention to: We have a rising incidence of wildfires across several regions of the U.S., not only in the West,” said Victoria Donovan, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of forest management at the UF/IFAS ...
Long-term care facilities that scheduled part-time Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) with more hours and more consistently with the same co-workers had reduced turnover, according to research led by Washington State University. The findings could help address staffing challenges that affect millions of patients at long-term care facilities nationwide.
Using a model based on real scheduling data of thousands of nurse aides, the researchers estimated that a one-hour increase in CNAs’ weekly hours worked could reduce turnover by 1.9%. Also, the analysis found that by scheduling ...