Melatonin and carcinogenesis in mice: The 50th anniversary of relationships
2023-12-18
(Press-News.org)
“[...] murine models proved to be valuable and, in some cases, indispensable for advancing melatonin applications in oncology [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- December 18, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on December 12, 2023, entitled, “Melatonin and carcinogenesis in mice: the 50th anniversary of relationships.”
Fifty years ago, in 1973, Vladimir N. Anisimov and coauthors demonstrated for the first time an inhibitory effect of the pineal gland hormone melatonin on cancer in vivo, namely on transplantable mammary tumors in mice. Subsequently, it was shown in a number of studies that melatonin administration with drinking water at night inhibits chemically induced mammary carcinogenesis in mice and rats.
On the contrary, maintaining female mice and rats under round-the-clock lighting conditions, which suppresses the nighttime production of melatonin, stimulates spontaneous and chemical carcinogen-induced mammary tumor development.
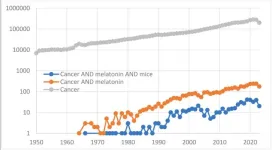
As of today, the query “cancer AND melatonin AND mice” in Pubmed returns about 550 entries. In this new research perspective, researchers Vladimir N. Anisimov and Alexey G. Golubev from N.N. Petrov National Medical Research Center of Oncology outline the history of studies of melatonin effects on cancer in mice, with the main lesson being that the systemic in vivo effects of melatonin on animals may overwhelm the in vitro effects found using tissue explants or cell cultures.
“In particular, the timing of melatonin administration is of crucial importance for using the drug, which is freely available over [the] counter and thus needs no licensing for its applications in oncology.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28537
Correspondence to: Vladimir N. Anisimov
Email: aging@mail.ru
Keywords: cancer, melatonin, mice
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly known as Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28537
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-18
New Haven, Conn. — In a new study by researchers at the Yale School of Public Health, two “forever chemicals” spurred cancer cells in the lab to migrate to new positions, an indication that the chemicals could contribute to cancer metastasis in living organisms.
The study addressed the group of industrial chemicals called per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). The substances are known as “forever chemicals” because they don’t break down in the environment and can build up in the human body. They have the ability to shed water and resist penetration by oils. They are ...
2023-12-18
Survey Highlights:
A majority of Americans (51%) say it takes them weeks to feel less stressed after the holidays, with more than a quarter of moms reporting it takes them a month or more to recover.
71% of respondents say that their biggest regret after the holidays is that they did not take the time to relax and enjoy the season.
Overall, respondents (63%) claimed that the holiday season is more stressful than tax season.
Eating healthy (69%), exercising regularly (64%), and getting enough sleep (56%) are the top three things that respondents have trouble prioritizing during the holiday season.
79% of people surveyed agree that, during the holidays, they are so focused on creating special ...
2023-12-18
Public opinion polls are often considered "the will of the people" but a new study on the role of polls in South Korea shows that they may not always be that transparent.
"Using polls to gauge what people think about politics is not as simple as it sounds, as there are multiple mediating factors between what people think and how their views may be represented in the media," says co-author Sunmin Kim, an assistant professor of sociology at Dartmouth. "Our research shows more broadly, how in a democracy, measuring what people think or want can be a highly haphazard and unpredictable process based on the ways public opinion poll ...
2023-12-18
A team of Brigham researchers analyzed GPT-4’s performance in four clinical decision support scenarios: generating clinical vignettes, diagnostic reasoning, clinical plan generation and subjective patient assessments.
When prompted to generate clinical vignettes for medical education, GPT-4 failed to model the demographic diversity of medical conditions, exaggerating known demographic prevalence differences in 89% of diseases.
When evaluating patient perception, GPT-4 produced significantly different responses by gender or race/ethnicity for 23% of cases.
Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and GPT-4 have the potential to assist in ...
2023-12-18
Apes recognize photos of groupmates they haven’t seen for more than 25 years and respond even more enthusiastically to pictures of their friends, a new study finds.
The work, which demonstrates the longest-lasting social memory ever documented outside of humans, and underscores how human culture evolved from the common ancestors we share with apes, our closest relatives, was published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Chimpanzees and bonobos recognize individuals even though they haven’t seen them for ...
2023-12-18
EMBARGO LIFTS DEC. 18, 2023, AT 3:00 PM U.S. EASTERN TIME
As the world heats up, and the climate shifts, life will migrate, adapt or go extinct. For decades, scientists have deployed a specific method to predict how a species will fare during this time of great change. But according to new research, that method might be producing results that are misleading or wrong.
University of Arizona researchers and their team members at the U.S. Forest Service and Brown University found that the method – commonly referred to as space-for-time substitution – failed to accurately predict how a widespread tree of the Western U.S. called the ...
2023-12-18
Ancient bricks inscribed with the names of Mesopotamian kings have yielded important insights into a mysterious anomaly in Earth’s magnetic field 3,000 years ago, according to a new study involving UCL researchers.
The research, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), describes how changes in the Earth’s magnetic field imprinted on iron oxide grains within ancient clay bricks, and how scientists were able to reconstruct these changes from the names of the kings inscribed on the bricks.
The team hopes that using this “archaeomagnetism,” which looks for signatures ...
2023-12-18
Researchers led by a University of California, Berkeley, comparative psychologist have found that great apes and chimpanzees, our closest living relatives, can recognize groupmates they haven't seen in over two decades — evidence of what’s believed to be the longest-lasting nonhuman memory ever recorded.
The findings also bolster the theory that long-term memory in humans, chimpanzees and bonobos likely comes from our shared common ancestor that lived between 6 million and 9 million years ago.
The team used infrared eye-tracking cameras to record where bonobos and chimps gazed when they were shown side-by-side images of other bonobos ...
2023-12-18
A collaborative team of experimental and computational physical chemists from South Korea and the United States have made an important discovery in the field of electrochemistry, shedding light on the movement of water molecules near metal electrodes. This research holds profound implications for the advancement of next-generation batteries utilizing aqueous electrolytes.
In the nanoscale realm, chemists typically utilize laser light to illuminate molecules and measure spectroscopic properties to visualize molecules. However, studying the behavior of ...
2023-12-18
A study conducted by pre-PhD researcher Pablo S. Valera and recently published in PNAS demonstrates the potential of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to explore metabolites secreted by cancer cells in cancer research. The study, which has been led by Ikerbasque Research Professors Luis Liz-Marzán (from CIC biomaGUNE) and Arkaitz Carracedo (of CIC bioGUNE) and in which other researchers from both centers, also members of the Networking Biomedical Research Centre (CIBER), have participated as well, provides valuable information to guide more specific experiments to reveal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Melatonin and carcinogenesis in mice: The 50th anniversary of relationships