Study unveils a role of mitochondria in dietary fat processing
2023-12-20
(Press-News.org)
The maintenance of a balanced lipid homeostasis is critical for our health. While consumption of excessive amounts of fatty foods contributes to metabolic diseases such as obesity and atherosclerosis, fat is an indispensable component of our diet. Digested lipids supply the body with essential building blocks and facilitate the absorption of important vitamins. In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers led by Professor Manolis Pasparakis and their collaborators Professor Aleksandra Trifunovic and Professor Christian Frezza at the Excellence Cluster CECAD of the University of Cologne, and Professor Jörg Heeren at the University of Hamburg, report on a new mechanism that regulates the processing and transport of dietary lipids by the intestine.
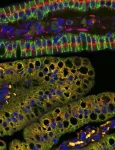
The researchers studied the function of mitochondria – organelles acting as powerhouses of the cell – in enterocytes, cells that line the intestine and specialize in the absorption and transport of nutrients from digested food. They found that disruption of mitochondrial function in the intestines of mice caused abnormal accumulation of dietary fat in enterocytes and impaired delivery of lipids to the peripheral organs.
A key finding of the study was that, when mitochondria did not function properly, enterocytes showed impaired packaging and transport of lipids in the form of chylomicrons. Chylomicrons are crucial carriers of dietary fats, and their proper formation and transport are essential for the absorption of nutrients.
“This discovery marks a significant leap forward in understanding the crucial role of mitochondria in dietary lipid transport and metabolism,” said Dr Chrysanthi Moschandrea, the lead author of the study. The implications of this discovery go beyond the realm of basic research. “These findings provide new perspectives for the better understanding of the gastrointestinal symptoms in patients suffering from mitochondrial disease, and may also lead to new therapeutic approaches,” added Professor Aleksandra Trifunovic.
The maintenance of a balanced lipid homeostasis is critical for our health. While consumption of excessive amounts of fatty foods contributes to metabolic diseases such as obesity and atherosclerosis, fat is an indispensable component of our diet. Digested lipids supply the body with essential building blocks and facilitate the absorption of important vitamins. In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers led by Professor Manolis Pasparakis and their collaborators Professor Aleksandra Trifunovic and Professor Christian Frezza at the Excellence Cluster CECAD of the University of Cologne, and Professor Jörg Heeren at the University of Hamburg, report on a new mechanism that regulates the processing and transport of dietary lipids by the intestine.
The researchers studied the function of mitochondria – organelles acting as powerhouses of the cell – in enterocytes, cells that line the intestine and specialize in the absorption and transport of nutrients from digested food. They found that disruption of mitochondrial function in the intestines of mice caused abnormal accumulation of dietary fat in enterocytes and impaired delivery of lipids to the peripheral organs.
A key finding of the study was that, when mitochondria did not function properly, enterocytes showed impaired packaging and transport of lipids in the form of chylomicrons. Chylomicrons are crucial carriers of dietary fats, and their proper formation and transport are essential for the absorption of nutrients.
“This discovery marks a significant leap forward in understanding the crucial role of mitochondria in dietary lipid transport and metabolism,” said Dr Chrysanthi Moschandrea, the lead author of the study. The implications of this discovery go beyond the realm of basic research. “These findings provide new perspectives for the better understanding of the gastrointestinal symptoms in patients suffering from mitochondrial disease, and may also lead to new therapeutic approaches,” added Professor Aleksandra Trifunovic.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-20
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have developed a new technique allowing the binding interfaces on two interacting proteins to be characterized, and validated it by describing the homophilic interaction between LAMP2A molecules
Tokyo, Japan – Proteins are building blocks of our bodies, but they do not work solo. They form partners to facilitate in different biological processes that keep us going. However, analyzing how proteins interact at a molecular level can be challenging. Now, a research team from Japan reveals the secrets behind these “protein partnerships”.
In a study published recently in Protein Science, researchers ...
2023-12-20
University of Virginia Alzheimer’s researchers have discovered how harmful tau proteins damage the essential operating instructions for our brain cells, a finding which could lead to new treatments.
The toxic protein, the researchers found, warps the shape of the nuclei of nerve cells, or neurons. This alters the function of genes contained inside and reprograms the cells to make more tau.
While the protein has long been a prime suspect in Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative “tauopathies,” the new research from UVA’s ...
2023-12-20
Fraunhofer USA, a leading nonprofit research organization dedicated to applied research and development services, is proud to announce the release of its Annual Report, Focus 2023. The report underscores Fraunhofer USA's commitment to fostering transatlantic collaboration, strengthening university-government partnerships, and driving impactful technology transfer.
Transatlantic Collaboration: A Pillar of Innovation
In the pursuit of global innovation, Fraunhofer USA continues to play a pivotal role in fostering transatlantic collaboration. The annual report highlights the organization's successful partnerships with Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft research institutes, resulting in groundbreaking ...
2023-12-20
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [December 20, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading academic cancer centers in the United States—is celebrating six years of working alongside the African Cancer Coalition (ACC), the American Cancer Society (ACS), and the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI), as part of Allied Against Cancer. The collaboration was formed to support and empower the Sub-Saharan African oncology community to advance health system capacity, ...
2023-12-20
A new study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University published in the journal Microbiome has found changes in the microbiome in multiple locations in the body are linked to the formation of kidney stones.
The human microbiome comprises trillions of microorganisms, including healthy bacteria. In recent years, research has begun to uncover its role in health and numerous diseases.
The research team examined the gut, urinary and salivary microbiomes in 83 patients who had kidney stones ...
2023-12-20
Brine shrimp of the genus Artemia are small crustaceans that can thrive in environments where sodium concentrations are as high as 25% (more than eight times typical ocean sea water). Also known by the household pet trademark ‘sea monkeys,’ these animals are abundant in inland salt lakes where brine-fly larvae are the only other animals known to exist.
The mechanisms which permit brine shrimp to tolerate some of the harshest environments are only partially understood. Previously known adaptive features include a tight protective layer (integument) to avoid water loss and the increased extrusion of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions ...
2023-12-20
Quality of life for people with dementia living in residential and nursing home care substantially improved after staff took part in a digital training programme that was specially adapted to Covid-19 restrictions. The training also led to a significant drop in the prescription of potentially harmful sedative medications to residents.
The iWHELD programme supported care home staff in delivering personalised care and encouraging meaningful social interactions. Through a digital platform featuring live coaching sessions led by trained coaches, the programme supported ...
2023-12-20
UC Riverside scientists have discovered a stealth molecular weapon that plants use to attack the cells of invading gray mold.
If you’ve ever seen a fuzzy piece of fruit in your fridge, you’ve seen gray mold. It is an aggressive fungus that infects more than 1,400 different plant species: almost all fruits, vegetables, and many flowers. It is the second most damaging fungus for food crops in the world, causing billions in annual crop losses.
A new paper in the journal Cell Host & Microbe describes how plants send tiny, innocuous-seeming lipid “bubbles” filled with RNA across enemy lines, into the cells of the aggressive mold. Once ...
2023-12-20
People who received gentle electric currents on the back of their heads learned to maneuver a robotic surgery tool in virtual reality and then in a real setting much more easily than people who didn’t receive those nudges, a new study shows.
The findings offer the first glimpse of how stimulating a specific part of the brain called the cerebellum could help health care professionals take what they learn in virtual reality to real operating rooms, a much-needed transition in a field that increasingly relies on digital simulation training, said author and Johns Hopkins University roboticist Jeremy ...
2023-12-20
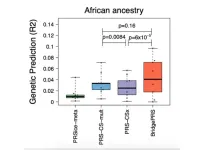
A team of scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has developed a groundbreaking statistical technique, “BridgePRS,” to enhance disease prediction in people of non-European ancestry, particularly those of African descent. This development represents a substantial step towards reducing health care inequities and a future of more personalized and precise medical interventions based on genetic information. Details of their work were published in Nature Genetics on Wednesday, December 20.
Current polygenic risk scores (PRS), essential tools for predicting disease risk encoded in our ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study unveils a role of mitochondria in dietary fat processing