(Press-News.org) PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [December 20, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading academic cancer centers in the United States—is celebrating six years of working alongside the African Cancer Coalition (ACC), the American Cancer Society (ACS), and the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI), as part of Allied Against Cancer. The collaboration was formed to support and empower the Sub-Saharan African oncology community to advance health system capacity, deliver high-quality cancer care, and improve access for all patients.
Allied Against Cancer’s work involves several initiatives, including the development of NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa. These evidence-based recommendations are based on in-region expert consensus on context-appropriate approaches for treating nearly all adult cancers across more than a dozen countries throughout the region.
NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa are available free-of-charge at NCCN.org/harmonized or via the Virtual Library of NCCN Guidelines® App.
“The oncology community in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) is working with NCCN to enhance the capacity of our professionals to meet the challenge of cancer care in SSA and cases that are increasing at a significant rate,” said Professor Isaac Adewole, Former Nigerian Minister of Health, Co-Chair of ACC. “Allied Against Cancer activities and tools like the NCCN Harmonized Guidelines help us to ensure cancer care can be provided according to the latest research, based on all available resources. Standardizing care according to established best practices allows us to better anticipate what our needs will be, including medication, making it easier to negotiate prices and increase necessary infrastructure as well as participate in clinical trials and international conferences or meetings.”
The first NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa debuted in November of 2017, during the biennial African Organisation for Research and Training in Cancer (AORTIC) International Conference on Cancer in Africa in Kigali, Rwanda.
Since then, the library has grown to 54 NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa, providing best practice cancer treatment recommendations for more than 92% of all adult cancer incidence in the region, including breast, prostate, and cervical cancers, as well as supportive care resources and screening recommendations. Recently, the groups have focused on the development of pediatric guidelines.
“We are honored to be able to work alongside these dedicated local experts across the African oncology community and our Allied Against Cancer collaborators,” said Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, CEO, NCCN. “We hope efforts such as this will continue to promote improvements in care that are both pragmatic and aspirational around the world while supporting our oncology colleagues in their provision of optimal cancer care.”
In 2023 alone, the group published 35 updated guidelines. During the 14th AORTIC International Conference on Cancer in Africa held in Dakar, Senegal in late 2023, oncologists from the region presented on implementation of the harmonized guidelines within their countries, with support from ACS.
“We were fortunate to be able to expand and update the harmonized guidelines this year during meetings in Rwanda, Zimbabwe, and Senegal, in order to continue making progress against the accelerating burden of cancer in Sub-Saharan Africa,” said Shanthi Sivendran, MD, MSCR, MBA, Senior Vice President, Cancer Care Support, ACS. “Our aim is to make sure oncologists and patients across the Sub-Saharan region have access to the tools they need to provide the best care possible while often facing staffing and equipment shortages.”
The library of NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa are endorsed by the Federal Ministries of Health and leading cancer centers in Ethiopia, Liberia, Malawi, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia, representing 44% of the population of Sub-Saharan Africa. To date, the NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa have been downloaded over 56,000 times.
Learn more about Allied Against Cancer’s collaborative work to improve cancer care in Sub-Saharan Africa at alliedagainstcancer.org.
# # #
About the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) is a not-for-profit alliance of leading cancer centers devoted to patient care, research, and education. NCCN is dedicated to improving and facilitating quality, effective, equitable, and accessible cancer care so all patients can live better lives. The NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) provide transparent, evidence-based, expert consensus recommendations for cancer treatment, prevention, and supportive services; they are the recognized standard for clinical direction and policy in cancer management and the most thorough and frequently-updated clinical practice guidelines available in any area of medicine. The NCCN Guidelines for Patients® provide expert cancer treatment information to inform and empower patients and caregivers, through support from the NCCN Foundation®. NCCN also advances continuing education, global initiatives, policy, and research collaboration and publication in oncology. Visit NCCN.org for more information.
END
A new study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University published in the journal Microbiome has found changes in the microbiome in multiple locations in the body are linked to the formation of kidney stones.
The human microbiome comprises trillions of microorganisms, including healthy bacteria. In recent years, research has begun to uncover its role in health and numerous diseases.
The research team examined the gut, urinary and salivary microbiomes in 83 patients who had kidney stones ...
Brine shrimp of the genus Artemia are small crustaceans that can thrive in environments where sodium concentrations are as high as 25% (more than eight times typical ocean sea water). Also known by the household pet trademark ‘sea monkeys,’ these animals are abundant in inland salt lakes where brine-fly larvae are the only other animals known to exist.
The mechanisms which permit brine shrimp to tolerate some of the harshest environments are only partially understood. Previously known adaptive features include a tight protective layer (integument) to avoid water loss and the increased extrusion of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions ...
Quality of life for people with dementia living in residential and nursing home care substantially improved after staff took part in a digital training programme that was specially adapted to Covid-19 restrictions. The training also led to a significant drop in the prescription of potentially harmful sedative medications to residents.
The iWHELD programme supported care home staff in delivering personalised care and encouraging meaningful social interactions. Through a digital platform featuring live coaching sessions led by trained coaches, the programme supported ...
UC Riverside scientists have discovered a stealth molecular weapon that plants use to attack the cells of invading gray mold.
If you’ve ever seen a fuzzy piece of fruit in your fridge, you’ve seen gray mold. It is an aggressive fungus that infects more than 1,400 different plant species: almost all fruits, vegetables, and many flowers. It is the second most damaging fungus for food crops in the world, causing billions in annual crop losses.
A new paper in the journal Cell Host & Microbe describes how plants send tiny, innocuous-seeming lipid “bubbles” filled with RNA across enemy lines, into the cells of the aggressive mold. Once ...
People who received gentle electric currents on the back of their heads learned to maneuver a robotic surgery tool in virtual reality and then in a real setting much more easily than people who didn’t receive those nudges, a new study shows.
The findings offer the first glimpse of how stimulating a specific part of the brain called the cerebellum could help health care professionals take what they learn in virtual reality to real operating rooms, a much-needed transition in a field that increasingly relies on digital simulation training, said author and Johns Hopkins University roboticist Jeremy ...
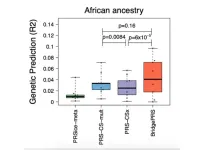
A team of scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has developed a groundbreaking statistical technique, “BridgePRS,” to enhance disease prediction in people of non-European ancestry, particularly those of African descent. This development represents a substantial step towards reducing health care inequities and a future of more personalized and precise medical interventions based on genetic information. Details of their work were published in Nature Genetics on Wednesday, December 20.
Current polygenic risk scores (PRS), essential tools for predicting disease risk encoded in our ...
A groundbreaking new technique invented by researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Science may revolutionize the field of synthetic biology. Known as CReATiNG (Cloning Reprogramming and Assembling Tiled Natural Genomic DNA), the method offers a simpler and more cost-effective approach to constructing synthetic chromosomes. It could significantly advance genetic engineering and enable a wide range of advances in medicine, biotechnology, biofuel production and even space exploration.
CReATiNG works by cloning and reassembling natural DNA segments from yeast, allowing scientists to create synthetic chromosomes that can replace their native counterparts in cells. ...
IOP Publishing (IOPP) has secured its first ‘Read and Publish’ transformative agreement in Taiwan, demonstrating its dedication to expanding open access (OA) to research in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region and at scale globally.
The three-year transformative agreement with the Physics Research Promotion Centre, which is part of the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC), will enable 20 Taiwanese universities to offer their researchers unlimited OA publishing at no cost to them. The agreement will also allow authors to retain copyright ...
Adjuvant therapies to help infertile women conceive by IVF - especially those whose treatments have been unsuccessful in the past - are now a common feature both before and during the treatment cycle. Now, a new analysis of the evidence for many nutritional supplements and diets thought to improve outcome in IVF has concluded that adopting a Mediterranean diet during treatment would offer a single ‘straightforward approach’ with good evidence of benefit in contrast to that of a Western diet.
Evidence from studies of nine commonly used nutritional supplements was found to be inconsistent and not always of good quality. The analysis, by Professor Roger ...
A review in the Journal of Internal Medicine explores the potential of non-invasive interventions such as light, sound, and magnets to stimulate gamma brain waves for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Such strategies may be beneficial because Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by reduced fast brain oscillations in the gamma range (30–100 Hz).
The authors note that recent studies reveal that it is feasible and safe to induce 40 Hz brain activity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease through a range of methods. Also, preliminary evidence suggests that such treatment can yield beneficial ...