(Press-News.org) Kyoto, Japan – A non-prescription drug abuse crisis in Japan seems only one overdose away. The demand for a particular anti-cough drug has been rising, along with the social impact of its abuse due to its psychosomatic effects.
The ease of obtaining information online about how to acquire over-the-counter medications or OTCs for achieving overdose, however, does not appear to be the real problem.
Now, a study by a team of researchers at Kyoto University suggests that reliable information about OTC abuse needs to be readily available and effectively disseminated.
"We focused on potential OTC abusers at risk of addiction though they did not show sufficient symptoms to justify or necessitate visits to medical institutions or support facilities," says corresponding author Azusa Kariya of KyotoU's Graduate School of Medicine and School of Public Health.
Users of Japan's largest consumer-generated media -- or CGM -- service, Yahoo! Chiebukuro, post their questions and responses about OTCs primarily to learn more about overdosing, such as access to the drugs, their efficacy and effects, and health risks.
Abuse results from two causes: one is from seeking symptomatic relief from some physical pain and overdosing to the point of addiction. The other occurs when people intentionally overdose to cause either self-harm or psychosomatic changes.
Kariya's team also found that OTC abusers and potential abusers sought advice on quitting their drug addiction on the Yahoo! community website. Most poignantly, the team discovered that OTC overdosers resist consulting others in person, making the CGM a convenient source of anonymously obtained information.
"Our study aims to make sense of our CGM data to identify possible overdosers. We could then be better positioned to cooperate with health professionals and seek support from pharmacies to reduce OTC abuse," adds Kariya.
Kariya's team searched the names of commonly abused OTCs, tracked the keywords overdose and OD, and tallied the number of relevant questions posted on the Yahoo! site.
The number of OD-related queries containing the keyword BRON -- an antitussive and expectorant -- has increased sharply, pointing to the significant impact of community-based websites.
Furthermore, the team extracted 467 items of question data that met the eligibility criteria from 528 items of BRON-tagged text data, generating 26 codes and six categories. Three main themes resulted: expectations for overdose, anxieties about overdose, and troubles in quitting overdose.
"The current crisis that mental health professionals are confronting is just the tip of the iceberg. We must dive below to see the scale of abuse hidden from view," reflects Kariya.
###
The paper "Internet-Based Inquiries From Users With the Intention to Overdose With Over-the-Counter" appeared on 23 November 2023 in JMIR Formative Research, with doi: 10.2196/45021
About Kyoto University
Kyoto University is one of Japan and Asia's premier research institutions, founded in 1897 and responsible for producing numerous Nobel laureates and winners of other prestigious international prizes. A broad curriculum across the arts and sciences at undergraduate and graduate levels complements several research centers, facilities, and offices around Japan and the world. For more information, please see: http://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en
END
Like kids in a candy store
Analysis of queries about over-the-counter overdosing reveals pervasive abuse
2023-12-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robots versus humans: Which would children trust more when learning new information?
2023-12-22
In this digital age, children are exposed to overwhelming amounts of information online, some of it unverified and increasingly generated by non-human sources, such as AI-driven language models. As children grow older, the ability to assess a source’s reliability is an important skill in cultivating critical thinking.
Children aged three to five years display selective trust based on the informant’s past accuracy when faced with both humans and robots, according to a study published in the journal Child Development titled, ‘Younger, not older, ...
AI tool aids in screening for nerve disorder
2023-12-22
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), in collaboration with Aster-CMI Hospital, have developed an AI tool that can identify the median nerve in ultrasound videos and detect carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). The study was published in IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control.
CTS arises when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, is compressed at the carpal tunnel part of the wrist, resulting in numbness, tingling or pain. It ...
Big impacts from small changes in cell
2023-12-22
Tiny things matter – for instance, one amino acid can completely alter the architecture of the cell. Researchers at the Universities of Göttingen and Warwick investigated the structure and mechanics of the main component of the cytoskeleton of the cell: a protein known as actin. Actin is found in all living cells where it has a range of important functions – from muscle contraction to cell signalling and cell shape. This protein comes in two different varieties termed “isoforms”, which are known as gamma actin and beta actin. The difference between the two proteins is ...
Jupiter was targeted by exoplanet hunter
2023-12-22
For the first time, an instrument to find planets light years away was used on an object in the Solar System, in a study on Jupiter's winds.
We find ourselves at a time when it has become almost commonplace to discover planets orbiting another star, with more than 5,000 already registered. The first distant worlds to incorporate this list were mainly giant planets, similar to but also very different in many ways from Jupiter and Saturn.
Astrophysicists have already begun to obtain data on the atmospheres of exoplanets, but fundamental ...
Pandemic lessons: Insights into how mobility restrictions affect healthcare costs
2023-12-22
Osaka, Japan - As the world grappled with lockdowns and restrictions brought by the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University conducted an extensive study to elucidate the link between changes in human mobility and the impact on medical costs associated with lifestyle-related diseases.
Dr. Haruka Kato and Professor Atsushi Takizawa of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology at Osaka Metropolitan University were concerned by the negative health effects resulting from the restriction of ...
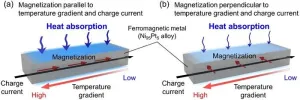
Controlling thermoelectric conversion in magnetic materials by magnetization direction
2023-12-22
1. NIMS has succeeded in directly observing the "anisotropic magneto-Thomson effect," a phenomenon in which the heat absorption/release proportional to an applied temperature difference and charge current (i.e., Thomson effect) changes anisotropically depending on the magnetization direction in magnetic materials. This research is expected to lead to further development of basic physics and materials science related to the fusion area of thermoelectrics and spintronics, as well as to development of new functionalities to control thermal energy with magnetism.
2. The Thomson effect has long been known as one of the fundamental ...
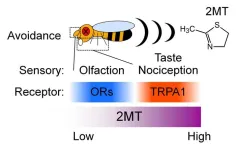
Stinky, bitter, and painful: A novel insect repellent attacks multiple sensory pathways
2023-12-22
Okazaki, Japan – crop damage in agriculture and the transmission of vector-borne diseases by insect pests have become worldwide threat nowadays. Chemical treatments such as insecticides and repellents have been a major strategy against insect pests for centuries. Due to limited understanding of mechanisms of insect avoidance behavior, however, development of insect repellents has been delayed. To discover compounds that effectively repel insect pests, it is important to focus on key molecules associated with sensory, particularly aversive, responses. In this study, researchers ...
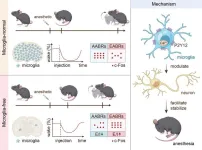
Microglia act as a “facilitator and stabilizer” for anesthesia
2023-12-22
Though it may be a surprise to the millions of people who undergo general anesthesia every year for medical procedures, the biological mechanism for how different anesthetics block consciousness is still not fully understood. However, researchers may be one step closer after uncovering the way small immune cells in the brain called microglia are impacted by general anesthesia.
The research was presented in a paper published in eLife on 22/Dec/2023.
“We found that microglia play an important role in regulating the body’s response to general anesthesia. ...
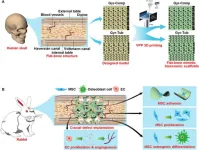
3D-printed flat-bone-mimetic bioceramic scaffolds for cranial restoration
2023-12-22
The cranial bone in the human body performs very important functions, such as protecting the brain and enabling the passage of the cranial nerves that are essential to physiological functioning. Critical-sized cranial defects can disrupt both the physical and psychological well-being of patients. Restoration of critical-sized cranial defects by cranioplasty is challenging for reconstructive surgeons, who prefer to use autologous bone grafts. The acquisition of autologous bone requires additional surgeries concomitant with risks such as free flap loss, infection, deep venous thrombosis, and nerve injury. These limitations necessitate the development ...
TTUHSC's Reddy elected fellow by the National Academy of Inventors
2023-12-22
P. Hemachandra Reddy, Ph.D., a professor in the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Medicine’s Department of Internal Medicine who has researched healthy aging, dementia and other neurodegenerative diseases for more than 20 years, recently was named to the 2023 class of Fellows for the National Academy of Inventors (NAI).
The NAI is a member organization comprised of U.S. and international universities and governmental and nonprofit research institutes with more than 4,600 individual inventor members and fellows spanning more than 300 institutions worldwide. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
Share of migratory wild animal species with declining populations despite UN treaty protections worsens from 44% to 49% in two years; 24% face extinction, up 2%
One in 20 babies experiences physical abuse, global review finds
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
[Press-News.org] Like kids in a candy storeAnalysis of queries about over-the-counter overdosing reveals pervasive abuse