GFH009: A potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies
2023-12-28
(Press-News.org)
“[...] the results of this preclinical investigation program suggest that induction of apoptosis is a key component of GFH009’s anti-tumor mechanism of action [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- December 28, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on December 20, 2023, entitled, “The pharmacodynamic and mechanistic foundation for the antineoplastic effects of GFH009, a potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.”
To evade cell cycle controls, malignant cells rely upon rapid expression of select proteins to mitigate pro-apoptotic signals resulting from damage caused by both cancer treatments and unchecked over-proliferation. Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9)-dependent signaling induces transcription of downstream oncogenes promoting tumor growth, especially in hyperproliferative ‘oncogene-addicted’ cancers, such as human hematological malignancies (HHMs). In this new study, researchers Fusheng Zhou, Lili Tang, Siyuan Le, Mei Ge, Dragan Cicic, Fubo Xie, Jinmin Ren, Jiong Lan, and Qiang Lu from GenFleet Therapeutics Inc. and Sellas Life Sciences Group aimed to summarize current knowledge underlying the mechanism of action (MOA) of GFH009 and explain its robust anti-cancer activity.
“Understanding GFH009’s MOA allows for a more optimal clinical development path, given the potential for meaningful benefits in patients with hematological malignancies.”
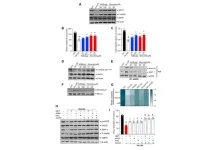
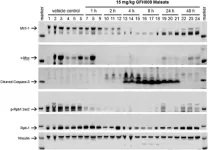
GFH009, a potent, highly selective CDK9 small molecule inhibitor, demonstrated antiproliferative activity in assorted HHM-derived cell lines, inducing apoptosis at IC50 values below 0.2 μM in 7/10 lines tested. GFH009 inhibited tumor growth at all doses compared to controls and induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner.
Twice-weekly injections of GFH009 maleate at 10 mg/kg significantly prolonged the survival of MV-4-11 xenograft-bearing rodents, while their body weight remained stable. There was marked reduction of MCL-1 and c-MYC protein expression post-drug exposure both in vitro and in vivo. Through rapid ‘on-off’ CDK9 inhibition, GFH009 exerts a proapoptotic effect on HHM preclinical models triggered by dynamic deprivation of crucial cell survival signals.
“Our results mechanistically establish CDK9 as a targetable vulnerability in assorted HHMs and, along with the previously shown superior class kinome selectivity of GFH009 vs other CDK9 inhibitors, strongly support the rationale for currently ongoing clinical studies with this agent in acute myeloid leukemia and other HHMs.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28543
Correspondence to: Jiong Lan
Email: jlan@genfleet.com
Keywords: GFH009, CDK9, cancer, leukemia, cell cycle
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly known as Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28543
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-28
“Angelica gigas Nakai (AG), a traditional medicinal herb, is garnering scientific attention for its potential in addressing a variety of health conditions.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 27, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Angelica gigas extract inhibits acetylation of eNOS via IRE1α sulfonation/RIDD-SIRT1-mediated posttranslational modification ...
2023-12-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a Viewpoint article published Dec. 27, 2023, in JAMA Surgery, three Johns Hopkins researchers urge the medical community to dismiss a widely held, but scientifically unsupported belief that many people who are transgender and gender diverse (TGD), and undergo gender affirming surgery (GAS), later regret their decision to undergo such procedures.
The researchers are:
Harry Barbee, Ph.D., assistant professor and interdisciplinary social scientist at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
Bashar ...
2023-12-28
Climate change is the biggest global health threat in the 21st century, and the rising temperatures have undermined the health and safety of the working population, as well as caused labor losses, which are closely tied to social-economic development. Although the future temperatures increase in China has been forecasted by state-of-the-art climate change projections, to what extent the influence on labor has not been well studied. In a paper published in Science Bulletin, a Chinese research team presents evidence of future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios. This study was led by Cunrui Huang, a professor at the Vanke School of Public ...
2023-12-28
Supraglacial environments mainly consist of four main types of habitats for microbes and viruses, including snow, ice, meltwater, and cryoconites (the granular sediment on glacier surfaces). The paper revealed that there were more than 10,000 viral species in global supraglacial environments. This is a 15-fold expansion of DNA viral genomic inventory ever known. These viruses mainly belong to bacteriophages, viruses infecting bacteria. Liu et al., also found the viral communities showed a clear regional and habitat distribution pattern, with polar glacier samples separated from mountain ...
2023-12-28
Scientists at MIT, the University of Birmingham, and elsewhere say that astronomers’ best chance of finding liquid water, and even life on other planets, is to look for the absence, rather than the presence, of a chemical feature in their atmospheres.
The researchers propose that if a terrestrial planet has substantially less carbon dioxide in its atmosphere compared to other planets in the same system, it could be a sign of liquid water — and possibly life — on that planet’s surface.
What’s more, this new signature is within the sights of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). While scientists have proposed ...
2023-12-28
- The nomination of the new generation of FGFR2/3 inhibitor for the treatment of tissue-agnostic solid tumors, bringing the total number of PCCs nominated by Insilico in 2023 to six.
- ISM8001 is an oral, highly selective, covalent inhibitor that demonstrated superior potency in multiple FGFR2/3-driven efficacy models, and also in gatekeeper and molecular brake mutant resistant models.
- The program once again demonstrates Insilico's ability to efficiently generate novel molecules with high quality that are currently available for partnering.
Insilico Medicine ("Insilico"), a generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven clinical-stage drug discovery ...
2023-12-28
(WASHINGTON, Dec. 28, 2023) – Lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a CAR T-cell therapy, is a cost effective second line treatment for relapsed and refractory (hard to treat) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (r/r DLBCL), according to a study published today in Blood Advances. The study is the first of its kind to incorporate healthcare expenses, societal productivity losses, and patient quality of life in assessing the drug’s cost-effectiveness.
"In our study, we incorporated the often-overlooked societal costs associated with cancer treatment, which are typically neglected in ...
2023-12-28
This new method is based on the exsolution process activated by microwave radiation. Exsolution is a method of generating metallic nanoparticles on the surface of ceramic materials. "At elevated temperatures and in a reducing atmosphere (usually hydrogen), metal atoms migrate from the structure of the material to its surface, forming metal nanoparticles anchored to the surface. This anchoring significantly increases the strength and stability of these nanoparticles, which positively impacts the efficiency of these catalysts," explains Beatriz García Baños, a researcher in the Microwave Area of the ITACA Institute at the UPV.
In the work now ...
2023-12-28
Brigham researchers’ findings from next-generation sequencing suggest that revising current cancer care guidelines could allow approximately 6,000 more patients in the U.S. to benefit from immunotherapy treatment each year
Immunotherapy is a highly effective treatment for patients whose cancers harbor mismatch repair deficiency, and a new study identifies more cancer patients who could benefit from this form of therapy. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, found that nearly six percent of endometrial cancer patients and one percent of colorectal cancer patients with mismatch repair deficiency were ...
2023-12-28
Health care systems in the United States have gradually embraced the concept that mental health should be treated on par with physical health, especially in light of increased rates of anxiety and depression during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
To improve access to mental health treatment, many Medicaid programs have required their managed care organizations to pay for behavioral health and physical health together. That’s in contrast to the traditional approach in which behavioral health, including treatment for substance use disorders, was “carved out” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] GFH009: A potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies