Brain health after COVID-19, pneumonia, heart attack, or critical illness
JAMA Network Open
2023-12-28
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: The findings of this study including 345 participants suggest that post–COVID-19 brain health was impaired but, overall, no more than the brain health of patients from 3 non–COVID-19 cohorts of comparable disease severity. Long-term associations with brain health might not be specific to COVID-19 but associated with overall illness severity and hospitalization. This information is important for putting understandable concerns about brain health after COVID-19 into perspective.
Authors: Daniel Kondziella, M.D., M.Sc., Dr.Philos., and Michael Eriksen Benros, M.D., Ph.D., of Copenhagen University Hospital in Copenhagen, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.49659?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=122823
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.49659)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-28
About The Study: In this study of children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection in Canadian pediatric emergency departments, although children infected with SARS-CoV-2 reported increased chronic symptoms, few of these children developed post–COVID-19 condition, and overall quality of life did not differ from children with negative SARS-CoV-2 tests.
Authors: Stephen Freedman, M.D.C.M., M.Sc., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2023-12-28
About The Study: In this study of 465,000 individuals, a higher self-reported frequency of adding salt to foods was associated with a higher risk of chronic kidney disease in the general population. These findings suggest that reducing the frequency of adding salt to foods at the table might be a valuable strategy to lower chronic kidney disease risk in the general population.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of Tulane University in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
2023-12-28
A research team, led by Professor Yongwon Seo in the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST has unveiled a highly efficient method for desalinating seawater using hydrate-based desalination (HBD) technology. The breakthrough is expected to have far-reaching implications for the application of hydrate-based desalination techniques, with the ability to calculate optimal temperatures for enhanced efficiency.
Hydrate desalination technology, known for its eco-friendly freshwater production capabilities, offers a low-energy solution that can be effectively used in treating high concentrations of brine or contaminated water. By ...
2023-12-28
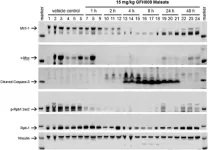
“[...] the results of this preclinical investigation program suggest that induction of apoptosis is a key component of GFH009’s anti-tumor mechanism of action [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- December 28, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on December 20, 2023, entitled, “The pharmacodynamic and mechanistic foundation for the antineoplastic effects of GFH009, a potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.”
To evade cell cycle controls, malignant cells rely upon rapid expression of select proteins to mitigate pro-apoptotic signals ...
2023-12-28
“Angelica gigas Nakai (AG), a traditional medicinal herb, is garnering scientific attention for its potential in addressing a variety of health conditions.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 27, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Angelica gigas extract inhibits acetylation of eNOS via IRE1α sulfonation/RIDD-SIRT1-mediated posttranslational modification ...
2023-12-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a Viewpoint article published Dec. 27, 2023, in JAMA Surgery, three Johns Hopkins researchers urge the medical community to dismiss a widely held, but scientifically unsupported belief that many people who are transgender and gender diverse (TGD), and undergo gender affirming surgery (GAS), later regret their decision to undergo such procedures.
The researchers are:
Harry Barbee, Ph.D., assistant professor and interdisciplinary social scientist at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
Bashar ...
2023-12-28
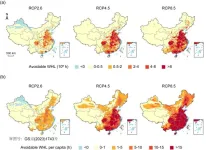
Climate change is the biggest global health threat in the 21st century, and the rising temperatures have undermined the health and safety of the working population, as well as caused labor losses, which are closely tied to social-economic development. Although the future temperatures increase in China has been forecasted by state-of-the-art climate change projections, to what extent the influence on labor has not been well studied. In a paper published in Science Bulletin, a Chinese research team presents evidence of future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios. This study was led by Cunrui Huang, a professor at the Vanke School of Public ...
2023-12-28
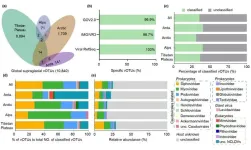
Supraglacial environments mainly consist of four main types of habitats for microbes and viruses, including snow, ice, meltwater, and cryoconites (the granular sediment on glacier surfaces). The paper revealed that there were more than 10,000 viral species in global supraglacial environments. This is a 15-fold expansion of DNA viral genomic inventory ever known. These viruses mainly belong to bacteriophages, viruses infecting bacteria. Liu et al., also found the viral communities showed a clear regional and habitat distribution pattern, with polar glacier samples separated from mountain ...
2023-12-28
Scientists at MIT, the University of Birmingham, and elsewhere say that astronomers’ best chance of finding liquid water, and even life on other planets, is to look for the absence, rather than the presence, of a chemical feature in their atmospheres.
The researchers propose that if a terrestrial planet has substantially less carbon dioxide in its atmosphere compared to other planets in the same system, it could be a sign of liquid water — and possibly life — on that planet’s surface.
What’s more, this new signature is within the sights of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). While scientists have proposed ...
2023-12-28
- The nomination of the new generation of FGFR2/3 inhibitor for the treatment of tissue-agnostic solid tumors, bringing the total number of PCCs nominated by Insilico in 2023 to six.
- ISM8001 is an oral, highly selective, covalent inhibitor that demonstrated superior potency in multiple FGFR2/3-driven efficacy models, and also in gatekeeper and molecular brake mutant resistant models.
- The program once again demonstrates Insilico's ability to efficiently generate novel molecules with high quality that are currently available for partnering.
Insilico Medicine ("Insilico"), a generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven clinical-stage drug discovery ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Brain health after COVID-19, pneumonia, heart attack, or critical illness
JAMA Network Open