(Press-News.org) Monitoring glucose levels is one of the key elements in health monitoring. A research team has now developed a battery-independent fluorescent nanosensor based on single-wall carbon nanotubes and an inactive form of the enzyme glucose oxidase (GOx). Because the enzyme is not in its active form, the analyte is not consumed during the measurement, and continuous, reversible, and non-invasive bioimaging of glucose levels in body fluids and tissues is possible, the team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Blood glucose levels are typically measured using GOx-based electrochemical sensors. However, these sensors produce toxic hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct and, furthermore, require bulky electrical circuits and batteries, making it difficult to prepare implantable devices for continuous measurement. Tiny SWCNTs, on the other hand, can be integrated into tissues and provide bioimaging information: when excited by light, SWCNTs produce a near-infrared fluorescence signal that travels through tissue and can be easily recorded using non-invasive bioimaging techniques.
Unfortunately, making GOx-based SWCNT nanosensors is difficult because the most effective technology for loading molecules onto SWCNTs—sonication—essentially inactivates the GOx molecules. Now, Markita P. Landry and her research team at the University of California in Berkeley, USA, have disproved the assumption that GOx-based sensors require active GOx for successful glucose sensing. Using sonication, they prepared GOx-loaded SWCNT sensors that reliably, selectively, and sensitively detected glucose, as demonstrated for glucose measurements in serum, plasma, and mouse brain slices.
The researchers explained this surprising finding by the ability of the inactive GOx enzyme to bind glucose without converting it. Binding alone was sufficient to modulate the fluorescence signal. To be completely independent of GOx activity, the researchers also constructed a GOx enzyme that even lacked the reactive group for glucose conversion. The resulting apo-GOx-SWCNT sensor detected glucose in body fluids and mouse brain slices as reliably as the original conjugate of SWCNT and natural GOx.
The researchers point out that the use of inactive GOx molecules has major advantages. For example, the manufacturing process of the GOx-SWCNT nanosensors can be simplified by using sonication as an effective preparation step. In addition, as the analyte is not consumed by the enzyme reaction, no toxic byproducts are produced, and the measurements are intrinsically reversible, allowing for non-invasive continuous glucose monitoring in tissue fluids.
(2738 characters)
About the Author
Dr. Markita P. Landry is an Associate Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Berkeley College of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, USA. The Landry Lab's work develops synthetic biomimetic nanocomposites to impart control over nanomaterial interactions with biological systems for applications in molecular imaging and targeted biodelivery.
END
Continuous glucose monitoring
Tissue-integrated sensitive glucose nanosenor using inactive glucose oxidase enzyme
2024-01-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers receive USDA grant to study changing food spending patterns
2024-01-02
After a long day, there’s the age-old question of do we eat out or stay in?
Over the last decade, that answer has increasingly shifted to eating out.
In that timeframe, households have increasingly spent more money on food outside of the home than what's spent on eating at home. In that same time, the farmer’s share of the food dollar eaten outside of the home has declined while the share of food eaten at home has increased.
With a more than $550,000 grant from the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, researchers George Davis and Anubhab Gupta, in the Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics in Virginia Tech's College ...
High adolescent BMI increases risk of early chronic kidney disease, according to JAMA study by Hebrew University researchers
2024-01-02
New study finds that adolescent obesity significantly heightens the risk of developing early chronic kidney disease in young adulthood. Even those with high-normal BMI are at risk. Severe obesity poses the highest risk, but even mild obesity and being overweight contribute significantly to this increased risk for both males and females. Lowering obesity rates in adolescents is crucial to better managing the risk of kidney disease and subsequent cardiovascular issues. This study emphasizes the need for preventive measures and management of risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease ...
Healthy omega-3 fats may slow deadly pulmonary fibrosis, research suggests
2024-01-02
Could healthy fats found in nuts and fish slow the progression of potentially deadly lung scarring known as pulmonary fibrosis and delay the need for lung transplants?
UVA pulmonary researchers looked at the association between blood-plasma levels of omega-3 fatty acids – the heart-healthy fats found in foods such as salmon and flaxseeds – and the progression of pulmonary fibrosis, as well as how long patients could go without needing a transplant. The researchers found that higher levels of omega-3 were associated with better lung function and longer transplant-free survival.
While more research ...
Predicting COVID-19 variant waves with AI
2024-01-02
An AI model can predict which SARS-CoV-2 variants are likely to cause new waves of infection. Current models used to predict the dynamics of viral transmission do not predict variant-specific spread. Retsef Levi and colleagues studied what factors could shape the viral spread based on analysis of 9 million SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequences collected by the Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data (GISAID) from 30 countries, along with data on vaccination rates, infection rates, and other factors. The patterns that emerged from this analysis ...
Cultivated kelp can now be as good as wild kelp
2024-01-02
Norway’s exports products derived from from tangle kelp (Laminoria hyperborea) and knotted kelp (Ascophyllum nodosu) to the tune of more than NOK 1 billion a year. The industry mainly extracts alginate from kelp, which is used in over 600 different products as diverse as paint, soft serve ice cream, sauces, bandages, nappies, acid reflux medicine and material for encapsulating cells and medicine. However, the market is far from saturated.
“Alginate is becoming a scarce commodity on the global market. There are great opportunities here if we could cultivate more kelp that yielded alginate of good enough quality,” says Finn Aachmann, a professor at the Norwegian ...
Researchers identify new coding mechanism that transfers information from perception to memory
2024-01-02
Our memories are rich in detail: we can vividly recall the color of our home, the layout of our kitchen, or the front of our favorite café. How the brain encodes this information has long puzzled neuroscientists.
In a new Dartmouth-led study, researchers identified a neural coding mechanism that allows the transfer of information back and forth between perceptual regions to memory areas of the brain. The results are published in Nature Neuroscience.
Prior to this work, the classic understanding of brain organization was that perceptual regions of the brain represent the world "as it is," with the ...
A novel switch to turn genes on/off on cue, a promising step toward safer gene therapy
2024-01-02
Just like a doctor adjusts the dose of a medication to the patient’s needs, the expression of therapeutic genes, those modified in a person to treat or cure a disease via gene therapy, also needs to be maintained within a therapeutic window. Staying within the therapeutic window is important as too much of the protein could be toxic, and too little could result in a small or no therapeutic effect.
Although the principle of therapeutic window has been known for a long time, there has been no strategy to implement it safely, limiting the potential applications of gene therapy in the clinic. ...
Food insecurity among low-income adults dropped nearly 5% during pandemic-era SNAP expansion
2024-01-01
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 1 January 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only ...
A tidy cell seems to keep aging at bay
2024-01-01
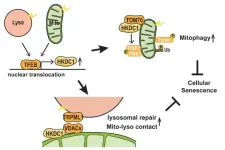
Osaka, Japan – Just as healthy organs are vital to our well-being, healthy organelles are vital to the proper functioning of the cell. These subcellular structures carry out specific jobs within the cell, for example, mitochondria power the cell and lysosomes keep the cell tidy.
Although damage to these two organelles has been linked to aging, cellular senescence, and many diseases, the regulation and maintenance of these organelles has remained poorly understood. Now, researchers at Osaka University have identified a protein, HKDC1, that plays a key role in maintaining these two organelles, thereby acting to prevent ...
Chemical synthesis using titanium dioxide: An eco-friendly and innovative approach
2024-01-01
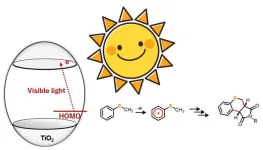
Heterocyclic compounds are organic molecules with a ring structure comprising at least two or more elements. In most cases, these rings are composed of carbon atoms along with one or more other elements such as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. They are highly sought-after as raw materials in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry, owing to their versatility and excellent physiological activities. While several methods are available for synthesizing these compounds, most of them involve high temperature and pressure conditions, or the use of precious ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Continuous glucose monitoringTissue-integrated sensitive glucose nanosenor using inactive glucose oxidase enzyme