(Press-News.org) Plastic litter is a growing problem around the world, and new research shows that the bottom of Lake Tahoe is no exception. In one of the first studies to utilize scuba divers to collect litter from a lakebed, 673 plastic items were counted from just a small fraction of the lake.
In the study, published in the November issue of the journal Applied Spectroscopy, researchers from DRI and the UC Davis Tahoe Environmental Research Center teamed up with the nonprofit Clean Up the Lake to take a close look at the litter. First, scientists broke it down into categories based on use (such as food containers and water bottles), followed by the chemical composition of the plastic. The knowledge gained can help scientists better understand the source of large pieces of litter in the lake, as well as whether they’re a significant source of microplastics as larger pieces break down and degrade. Previous research found that the waters of Lake Tahoe contain high levels of microplastics, defined as plastics smaller than a pencil eraser.
“There’s very little work on submerged plastic litter in lakes,” said Monica Arienzo, Ph.D., associate research professor of hydrology at DRI and one of the study’s lead authors. “And I think that’s a real issue, because when we think about how plastics may be moving in freshwater systems, there’s a good chance that they’ll end up in a lake.”
To collect the litter, research divers swam transects along the lakebed near Lake Tahoe Nevada State Park and Zephyr Cove, covering 9.3 kilometers. They found an average of 83 pieces of plastic litter per kilometer, with the lakebed near Hidden Beach and South Sand Harbor showing significantly more (140 items/km and 124 items/km, respectively). No stretches of the lakebed surveyed were free of plastic litter.
The most common plastic litter categories were food containers, bottles, plastic bags, and toys, along with many items that couldn’t be categorized.
“There’s a lot of education we can do, as well as continuing to work on reducing the use of those plastics,” Arienzo says. “Because we have to start thinking about turning that plastic pipe off.”
Arienzo and co-author Julia Davidson, then an undergraduate student working in Arienzo’s lab, also identified the types of plastic that made up 516 of the litter samples. Using an instrument that uses infrared light to fingerprint and identify the material, they found that the six most common plastics were polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene, polyester/polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyamide. Collecting this information can contribute to Arienzo’s ongoing microplastics research in the region, helping to identify the sources of the small plastic fragments.
“When we study microplastics, we only have the chemical information, or the plastic type,” Davidson says. “We don’t know where it came from—a plastic bag, toy, or otherwise— because it’s just a tiny piece of plastic. But now we can use this litter data to point to the dominant types of plastics and compare them to microplastic data.”
The study can help inform efforts by Tahoe-area communities to address plastic litter, such as South Lake Tahoe’s 2022 ban on single-use plastic bottles and Truckee’s ban on single-use food containers. The research also highlights ways that scientists can work with nonprofits to collect data that can address local environmental concerns.
“I think one of the things that's really cool about this project is the collaboration between DRI, Clean Up the Lake, and UC Davis at Tahoe,” Arienzo says. “It demonstrates the power of bringing together a nonprofit that really wants to clean up Tahoe, while collecting data in the process that can help answer scientific questions.”
###
More information: The full study, Polymer Characterization of Submerged Plastic Litter from Lake Tahoe, is available from Applied Spectroscopy at https://doi.org/10.1177/00037028231201174
Study authors include: Julia Davidson (DRI), Monica Arienzo (DRI), Zoe Harrold (Clear Horizons Consulting), Colin West (Clean Up the Lake), Erick R. Bandala (DRI), Sadye Easler (Clean Up the Lake), Katie Senft (UC Davis Tahoe Environmental Research Center)
###
About DRI
The Desert Research Institute (DRI) is a recognized world leader in basic and applied environmental research. Committed to scientific excellence and integrity, DRI faculty, students who work alongside them, and staff have developed scientific knowledge and innovative technologies in research projects around the globe. Since 1959, DRI’s research has advanced scientific knowledge on topics ranging from humans’ impact on the environment to the environment’s impact on humans. DRI’s impactful science and inspiring solutions support Nevada’s diverse economy, provide science-based educational opportunities, and inform policymakers, business leaders, and community members. With campuses in Las Vegas and Reno, DRI serves as the non-profit research arm of the Nevada System of Higher Education. For more information, please visit www.dri.edu.
About Clean Up The Lake
Clean Up The Lake is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to activate local communities to take action to protect their environment both above and below the surface, starting in Lake Tahoe. The organization has completed its flagship project of a 72 mile SCUBA cleanup of Lake Tahoe's entire circumference in 2022 and has gone on to clean up over 69,000 pounds of litter in the Sierra region, primarily from beneath the surface of Alpine Lakes. The non profit has expanded from submerged litter cleanups to include aquatic invasive species surveillance and education, collaborations to bring litter-art sculptures and stewardship messaging to communities they work in and also a variety of youth programs for our future generations. To learn more about the organization or to donate, please visit cleanupthelake.org.
Media Contacts:
DRI
Elyse DeFranco
Science Writer
elyse.defranco@dri.edu
Clean Up The Lake:
Colin West
+1 (530) 562 7131
colin@cleanupthelake.org
END
First dive survey of Lake Tahoe’s lakebed finds high amounts of plastic and other litter
Scientists teamed up with nonprofit Clean Up the Lake to collect and analyze litter found on the bottom of Lake Tahoe
2024-01-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study on extremely preterm infants provides important healthcare knowledge
2024-01-03
Infants born extremely prematurely need to get enrichment as an addition to breast milk. But does it make any difference whether the enrichment is made from breast milk or cow’s milk when it comes to the risk of severe complications in children? This has been investigated by a large clinical study led from Linköping, Sweden.
Infants born extremely prematurely, between weeks 22 and 27 of pregnancy, are among the most vulnerable patients in healthcare. The risk of serious complications is very high. Almost one in four extremely premature babies die before the age of one.
There is strong research support for giving breast ...
New research shows “Juvenile T. rex” fossils are a distinct species of small tyrannosaur
2024-01-03
A new analysis of fossils believed to be juveniles of T. rex now shows they were adults of a small tyrannosaur, with narrower jaws, longer legs, and bigger arms than T. rex. The species, Nanotyrannus lancensis, was first named decades ago but later reinterpreted as a young T. rex.
The first skull of Nanotyrannus was found in Montana in 1942, but for decades, paleontologists have gone back and forth on whether it was a separate species, or simply a juvenile of the much larger T. rex.
Dr Nick Longrich, from the Milner Centre for Evolution at the University ...
Using electricity, scientists find promising new method of boosting chemical reactions
2024-01-02
As the world moves away from gas towards electricity as a greener power source, the to-do list goes beyond cars. The vast global manufacturing network that makes everything from our batteries to our fertilizers needs to flip the switch, too.
A study from UChicago chemists found a way to use electricity to boost a type of chemical reaction often used in synthesizing new candidates for pharmaceutical drugs.
Published Jan. 2 in Nature Catalysis, the research is an advance in the field of electrochemistry and shows a path forward to designing ...
Combine mindfulness with exercise for mental health boost in 2024 – study
2024-01-02
For people looking to start 2024 with a new routine to feel fitter and happier, a new study from the University of Bath suggests that combining mindfulness with exercise could be your key to success.
A study, published in the academic journal Mental Health and Physical Activity, suggests that life changes which combine both physical activity and mindfulness are most effective at lifting mood and improving health and wellbeing.
Both physical activity and mindfulness practice have well established psychological benefits. However, ...
New AI tool brings precision pathology for cancer and beyond into quicker, sharper focus
2024-01-02
A new artificial intelligence tool that interprets medical images with unprecedented clarity does so in a way that could allow time-strapped clinicians to dedicate their attention to critical aspects of disease diagnosis and image interpretation.
The tool, called iStar (Inferring Super-Resolution Tissue Architecture), was developed by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, who believe they can help clinicians diagnose and better treat cancers that might otherwise go undetected. The imaging technique provides both highly detailed views of individual cells and a broader look of the ...
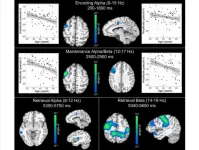
Age-related alterations in the oscillatory dynamics serving verbal working memory processing
2024-01-02
“[...] we discuss the implications of these novel findings on our understanding of how healthy aging affects verbal working memory processing.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 2, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 24, entitled, “Age-related alterations in the oscillatory dynamics serving verbal working memory processing.”
Working memory (WM) is a foundational cognitive function involving the temporary storage of information. Unfortunately, WM ...
Is oxygen the cosmic key to alien technology?
2024-01-02
In the quest to understand the potential for life beyond Earth, researchers are widening their search to encompass not only biological markers, but also technological ones. While astrobiologists have long recognized the importance of oxygen for life as we know it, oxygen could also be a key to unlocking advanced technology on a planetary scale.
In a new study published in Nature Astronomy, Adam Frank, the Helen F. and Fred H. Gowen Professor of Physics and Astronomy at the University ...
How tomato plants use their roots to ration water during drought
2024-01-02
Plants have to be flexible to survive environmental changes, and the adaptive methods they deploy must often be as changeable as the shifts in climate and condition to which they adapt. To cope with drought, plant roots produce a water-repellent polymer called suberin that blocks water from flowing up towards the leaves, where it would quickly evaporate. Without suberin, the resulting water loss would be like leaving the tap running.
In some plants, suberin is produced by endodermal cells that line the vessels inside the roots. But in others, like tomatoes, suberin is produced in exodermal cells that sit just below ...
Targeted household cleaning can reduce toxic chemicals post-wildfire, Portland State research shows
2024-01-02
After the last embers of a campfire dim, the musky smell of smoke remains. Whiffs of that distinct smokey smell may serve as a pleasant reminder of the evening prior, but in the wake of a wildfire, that smell comes with ongoing health risks.
Wildfire smoke is certainly more pervasive than a small campfire, and the remnants can linger for days, weeks and months inside homes and businesses. New research from Portland State’s Elliott Gall, associate professor in Mechanical and Materials Engineering, examined how long harmful chemicals found in wildfire smoke can persist and the ...
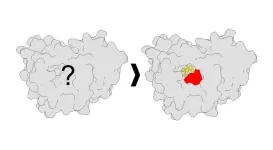
New method illuminates druggable sites on proteins
2024-01-02
LA JOLLA, CA—Identifying new ways to target proteins involved in human diseases is a priority for many researchers around the world. However, discovering how to alter the function of these proteins can be difficult, especially in live cells. Now, scientists from Scripps Research have developed a new method to examine how proteins interact with drug-like small molecules in human cells—revealing critical information about how to potentially target them therapeutically.
The strategy, published in Nature Chemical Biology on January 2, 2024, uses a combination of chemistry and analytical techniques to reveal the specific places where proteins and small molecules bind ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] First dive survey of Lake Tahoe’s lakebed finds high amounts of plastic and other litterScientists teamed up with nonprofit Clean Up the Lake to collect and analyze litter found on the bottom of Lake Tahoe