(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.H. – An international team of researchers, including several from the University of New Hampshire, have completed the first DNA sequence of any strawberry plant, giving breeders much-needed tools to create tastier, healthier strawberries. Tom Davis, professor of biological sciences at UNH, and postdoctoral researcher Bo Liu were significant contributors to the genome sequence of the woodland strawberry, which was published last month in the journal Nature Genetics.
"We now have a resource for everybody who's interested in strawberry genetics. We can answer questions that before would have been impossible to address," says Davis, who has been working on the strawberry genome project since 2006 as part of the international Strawberry Genome Sequencing Consortium.
For instance, says Davis, breeders can now look at the DNA "fingerprint" of strawberry plants to more easily breed those with enhanced flavor, aroma, or antioxidant properties. Or they could breed more disease-resistant berries, decreasing the significant amount of spraying that cultivated strawberries currently need to thrive and thus enhancing the berry's healthful qualities.
Further, the woodland strawberry is a member of the Rosaceae family, which includes apples, peaches, cherries, raspberries, and almonds, all economically important and popular crops; researchers say the DNA sequence of the strawberry genome will inform the breeding of these other fruits. "We can now begin to understand how evolution works at the level of the genome on this family of plants we all enjoy," says Davis.
The genome sequencing effort, led by researchers at the University of Florida and Virginia Tech, found that the woodland strawberry -- Fragaria vesca – has 240 million base pairs of DNA (compared to 3 billion for humans), making it one of the smallest genomes of economically significant plants. The consortium focused first on sequencing the wild woodland strawberry because its cultivated cousins, all hybrids, are far more complex.
Building upon prior publications in which he described a one percent genomic sampling of a native New Hampshire wild strawberry, Davis played multiple roles in genome project planning, data interpretation, and manuscript preparation. Liu's unique contribution to this effort was to independently document the locations of specific sequences called ribosomal gene clusters on the chromosomes themselves, using an advanced microscopic technique known as fluorescent in situ hybridization.
INFORMATION:
The Nature Genetics paper, "The genome of the woodland strawberry," is available here: http://strawberrygenes.unh.edu/Published.740%5B1%5D.pdf. By fortuitous coincidence, the complete genomic sequence of another delectable plant species, Theobroma cacao (chocolate), was published in the same journal issue. More information on strawberry genome work at UNH is at strawberrygenes.unh.edu. The UNH component of this work was supported, in part, by the New Hampshire Agricultural Experiment Station and by a grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (National Research Initiative) Plant Genome program.
The University of New Hampshire, founded in 1866, is a world-class public research university with the feel of a New England liberal arts college. A land, sea, and space-grant university, UNH is the state's flagship public institution, enrolling 12,200 undergraduate and 2,300 graduate students.
First strawberry genome sequence promises better berries
2011-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights into sun's photosphere reported by NJIT researcher at Big Bear
2011-01-11
NJIT Distinguished Professor Philip R. Goode and the research team at Big Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO) have reported new insights into the small-scale dynamics of the Sun's photosphere. The observations were made during a period of historic inactivity on the Sun and reported in The Astrophysical Journal . http://iopscience.iop.org/2041-8205/714/1/L31 The high-resolution capabilities of BBSO's new 1.6-meter aperture solar telescope have made such work possible.
"The smallest scale photospheric magnetic field seems to come in isolated points in the dark intergranular ...
Body dysmorphic disorder patients who loathe appearance often get better, but it could take years
2011-01-11
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — In the longest-term study so far to track people with body dysmorphic disorder, a severe mental illness in which sufferers obsess over nonexistent or slight defects in their physical appearance, researchers at Brown University and Rhode Island Hospital found high rates of recovery, although recovery can take more than five years.
The results, based on following 15 sufferers of the disease over an eight-year span, appear in the current issue of the Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease.
"Compared to what we expected based on a prior ...
Debunking solar energy efficiency measurements
2011-01-11
In recent years, developers have been investigating light-harvesting thin film solar panels made from nanotechnology –– and promoting efficiency metrics to make the technology marketable. Now a Tel Aviv University researcher is providing new evidence to challenge recent "charge" measurements for increasing solar panel efficiency.
Offering a less expensive, smaller solution than traditional panels, Prof. Eran Rabani of Tel Aviv University's School of Chemistry at the Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty of Exact Sciences puts a lid on some current hype that promises to ...
Study identifies new genetic signatures of breast cancer drug resistance
2011-01-11
A new study conducted by Josh LaBaer's research team in the Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University has pinpointed more than 30 breast cancer gene targets ---including several novel genes---that are involved in drug resistance to a leading chemotherapy treatment.
The results of the study may one day aid in the treatment of the one in ten U.S. women who will develop breast cancer, by empowering physicians with a more personalized approach to therapy as well as a new tool for the early screening of those that may ultimately become resistant to chemotherapy.
Drugs ...
Study estimates land available for biofuel crops
2011-01-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Using detailed land analysis, Illinois researchers have found that biofuel crops cultivated on available land could produce up to half of the world's current fuel consumption – without affecting food crops or pastureland.
Published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology, the study led by civil and environmental engineering professor Ximing Cai identified land around the globe available to produce grass crops for biofuels, with minimal impact on agriculture or the environment.
Many studies on biofuel crop viability focus on biomass yield, ...
Miscanthus has a fighting chance against weeds
2011-01-11
University of Illinois research reports that several herbicides used on corn also have good selectivity to Miscanthus x giganteus (Giant Miscanthus), a potential bioenergy feedstock.
"No herbicides are currently labeled for use in Giant Miscanthus grown for biomass," said Eric Anderson, an instructor of bioenergy for the Center of Advanced BioEnergy Research at the University of Illinois. "Our research shows that several herbicides used on corn are also safe on this rhizomatous grass."
M. x giganteus is sterile and predominantly grown by vegetative propagation, or planting ...
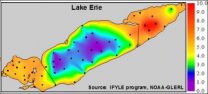
Lake Erie hypoxic zone doesn't affect all fish the same, study finds
2011-01-11
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Large hypoxic zones low in oxygen long have been thought to have negative influences on aquatic life, but a Purdue University study shows that while these so-called dead zones have an adverse affect, not all species are impacted equally.
Tomas Höök, an assistant professor of forestry and natural resources, and former Purdue postdoctoral researcher Kristen Arend used output from a model to estimate how much dissolved oxygen was present in Lake Erie's hypoxic zone each day from 1987 to 2005. That information was compared with biological ...
Being poor can suppress children's genetic potentials
2011-01-11
AUSTIN, Texas — Growing up poor can suppress a child's genetic potential to excel cognitively even before the age of 2, according to research from psychologists at The University of Texas at Austin.
Half of the gains that wealthier children show on tests of mental ability between 10 months and 2 years of age can be attributed to their genes, the study finds. But children from poorer families, who already lag behind their peers by that age, show almost no improvements that are driven by their genetic makeup.
The study of 750 sets of twins by Assistant Professor Elliot ...
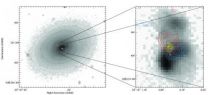
Possible missing link between young and old galaxies
2011-01-11
University of California, Berkeley, astronomers may have found the missing link between gas-filled, star-forming galaxies and older, gas-depleted galaxies typically characterized as "red and dead."
In a poster to be presented this week at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Seattle, UC Berkeley astronomers report that a long-known "early-type" galaxy, NGC 1266, is expelling molecular gas, mostly hydrogen, from its core.
Astronomers have long recognized the distinction between early-type red and dead galaxies, thought to be largely devoid of gas and dust and ...
Oxygen-free early oceans likely delayed rise of life on planet
2011-01-11
RIVERSIDE, Calif. – Geologists at the University of California, Riverside have found chemical evidence in 2.6-billion-year-old rocks that indicates that Earth's ancient oceans were oxygen-free and, surprisingly, contained abundant hydrogen sulfide in some areas.
"We are the first to show that ample hydrogen sulfide in the ocean was possible this early in Earth's history," said Timothy Lyons, a professor of biogeochemistry and the senior investigator in the study, which appears in the February issue of Geology. "This surprising finding adds to growing evidence showing ...