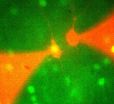
(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH—Carnegie Mellon University researchers have found that within the brain's neocortex lies a subnetwork of highly active neurons that behave much like people in social networks. Like Facebook, these neuronal networks have a small population of highly active members who give and receive more information than the majority of other members, says Alison Barth, associate professor of biological sciences at Carnegie Mellon and a member of the Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition (CNBC). By identifying these neurons, scientists will now be able to study them further and increase their understanding of the neocortex, which is thought to be the brain's center of higher learning.
Up to trillions of neurons make up the neocortex, the part of the cerebral cortex that is responsible for a number of important functions, including sensory perception, motor function, spatial reasoning, conscious thought and language. Although neuroscientists have been studying the neocortex for 40 years, technologies had only allowed them to look broadly at general areas of the brain, but not at the high-resolution of individual neurons. While they believed only a small proportion of neurons were doing most of the work in the neocortex, they couldn't see if this was indeed the case.
In the current study, published in the journal Neuron, the researchers used a specialized transgenic mouse model developed by Barth to overcome these challenges and clearly see which neocortical neurons were the most active. The model links green fluorescent protein (GFP) with the activity-dependent gene fos, causing the neuron to light up when it is activated. The researchers, including former Carnegie Mellon and CNBC postdoctoral student Lina Yassin, who is now at the Ludwig-Maximillians-Universtat Munich, took recordings from both fos-labeled and unlabeled neurons and found that the most active neurons were expressing the fos gene. The researchers were then able to isolate the active neurons using imaging techniques and take electrophysiological recordings from the neurons, allowing the researchers to begin to understand the mechanisms underlying the increased activity.
Barth and colleagues were able to see that the fos-expressing neurons weren't more active because they were intrinsically more excitable; in fact, the neurons seemed to be calmer or more suppressed than their neighboring, inactive neurons. What made them more active was their input.
According to Barth, it seems that this active network of neurons in the neocortex acts like a social network. There is a small, but significant, population of neurons that are more connected than other neurons. These neurons do most of the heavy lifting, giving and receiving more information than the rest of the neurons in their network.
"It's like Facebook. Most of your friends don't post much — if at all. But, there is a small percentage of your friends on Facebook who update their status and page often. Those people are more likely to be connected to more friends, so while they're sharing more information, they're also receiving more information from their expanded network, which includes other more active participants," Barth said.
The findings stand to have a dramatic impact on neuroscience. Now that researchers are able to identify and visualize these active cells they can begin to determine why they are more active and how stable the activity is. The Carnegie Mellon researchers plan to study these neurons to see what, if any, role these neurons play in learning.
The results also will help to further computational neuroscience, specifically in the area of sparse coding. In sparse coding, scientists hope to study how the brain recruits a small population of neurons to encode information. This research will for the first time allow for the study of the electrophysiological properties of strongly responsive but sparsely populated cells.
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, NeuroCure, the Deutsch Forschung Gemeinshaft, the Swiss-German Research Unit "Barrel Cortex Function" and the Max-Delbruck Center.
Other researchers on the study include: Brett Benedetti and Jing Wen of Carnegie Mellon; and Jean-Sebastien Jouhanneau and James Poulet of the Max-Delbruck Center for Molecular Medicine and Neuroscience Research Center of the Charite Universitatmedizin in Berlin.
doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.029
About Carnegie Mellon University: Carnegie Mellon (www.cmu.edu) is a private, internationally ranked research university with programs in areas ranging from science, technology and business, to public policy, the humanities and the fine arts. More than 11,000 students in the university's seven schools and colleges benefit from a small student-to-faculty ratio and an education characterized by its focus on creating and implementing solutions for real problems, interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation. A global university, Carnegie Mellon's main campus in the United States is in Pittsburgh, Pa. It has campuses in California's Silicon Valley and Qatar, and programs in Asia, Australia, Europe and Mexico. The university is in the midst of a $1 billion fundraising campaign, titled "Inspire Innovation: The Campaign for Carnegie Mellon University," which aims to build its endowment, support faculty, students and innovative research, and enhance the physical campus with equipment and facility improvements.
Carnegie Mellon researchers identify 'Facebook neurons'
Population of highly active neurons could provide insight into the neocortex
2011-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Outsourcing hurts consumers by softening competition among firms
2011-01-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. – Firms that outsource aspects of their business to a foreign country may profit by saving money, but the practice tends to soften the competition among industry rivals, exacting a hidden cost on consumers, says new research co-written by a University of Illinois business administration professor.
Yunchuan "Frank" Liu says outsourcing hurts society in two ways – it results in lost jobs for workers, and in consumers paying higher prices than they should for goods.
"Outsourcing is a topic that affects just about everyone, and the general consensus is that ...
Direct observation of carbon monoxide binding to metal-porphyrines
2011-01-11
The mechanism for binding oxygen to metalloporphyrins is a vital process for oxygen-breathing organisms. Understanding how small gas molecules are chemically bound to the metal complex is also important in catalysis or the implementation of chemical sensors. When investigating these binding mechanisms, scientists use porphyrin rings with a central cobalt or iron atom. They coat a copper or silver support surface with these substances.
An important characteristic of porphyrins is their conformational flexibility. Recent research has shown that each specific geometric configuration ...
Study finds nearly half of school social workers feel unequipped to handle cyberbullying
2011-01-11
Instances of cyber bullying continue to make news nearly every day, and while it's recognized as a problem among most school-aged children, a new study published this month in Children & Schools and coauthored by Temple University social work professor Jonathan Singer finds that nearly half of school social workers feel they are ill equipped to handle it.
"School social workers provide more crisis intervention services than any other school staff member – more than counselors, nurses, teachers, or psychologists," said Singer. "As a result, school social workers are a ...
'Liquid pistons' could drive new advances in camera lenses and drug delivery
2011-01-11
VIDEO:
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed liquid pistons, which can be used to precisely pump small volumes of liquid. Comprising the pistons are droplets of nanoparticle-infused ferrofluids, which can...
Click here for more information.
Troy, N.Y. – A few unassuming drops of liquid locked in a very precise game of "follow the leader" could one day be found in mobile phone cameras, medical imaging equipment, implantable drug delivery devices, ...
Embryonic stem cells help deliver 'good genes' in a model of inherited blood disorder
2011-01-11
Researchers at Nationwide Children's Hospital report a gene therapy strategy that improves the condition of a mouse model of an inherited blood disorder, Beta Thalassemia. The gene correction involves using unfertilized eggs from afflicted mice to produce a batch of embryonic stem cell lines. Some of these stem cell lines do not inherit the disease gene and can thus be used for transplantation-based treatments of the same mice. Findings could hold promise for a new treatment strategy for autosomal dominant diseases like certain forms of Beta Thalassemia, tuberous sclerosis ...
An earlier start on diagnosing breast, prostate cancers
2011-01-11
Using biological samples taken from patients and state-of-the-art biochemical techniques, a Florida State University researcher is working to identify a variety of "biomarkers" that might provide earlier warnings of the presence of breast and prostate cancers.
"Biomarkers are indicators of certain biological and pathological processes that are occurring, such as cancer," said Qing-Xiang "Amy" Sang, a professor in Florida State's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry. "Either the cancer cells themselves, or surrounding normal tissue for that matter, can produce specific ...
Protein thought to protect against oxidative stress also promotes clogging of arteries
2011-01-11
UCLA researchers have found that a protein that plays an important role in some antioxidant therapies may not be as effective due to additional mechanisms that cause it to promote atherosclerosis, or clogging of the arteries.
Published in the January issue of the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, the finding may give clues as to why some antioxidant therapies have not yielded more positive results.
The protein, called Nrf2, has been thought to be an important drug-therapy target for diseases such as cancer because it can induce chemopreventive ...
New species of flying reptile identified on B.C. coast
2011-01-11
Persistence paid off for a University of Alberta paleontology researcher, who after months of pondering the origins of a fossilized jaw bone, finally identified it as a new species of pterosaur, a flying reptile that lived 70 million years ago.
Victoria Arbour says she was stumped when the small piece of jaw bone was first pulled out of of a fossil storage cabinet in the U of A's paleontology department.
"It could have been from a dinosaur, a fish or a marine reptile," said Arbour. "
Arbour, a PhD student in paleontology, says the first clue to the fossil's identify ...
New glass tops steel in strength and toughness
2011-01-11
Glass stronger and tougher than steel? A new type of damage-tolerant metallic glass, demonstrating a strength and toughness beyond that of any known material, has been developed and tested by a collaboration of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab)and the California Institute of Technology. What's more, even better versions of this new glass may be on the way.
"These results mark the first use of a new strategy for metallic glass fabrication and we believe we can use it to make glass that will be even ...
How do you make lithium melt in the cold?
2011-01-11
Washington, D.C. — Sophisticated tools allow scientists to subject the basic elements of matter to conditions drastic enough to modify their behavior. By doing this, they can expand our understanding of matter. A research team including three Carnegie scientists was able to demonstrate surprising properties of the element lithium under intense pressure and low temperatures. Their results were published Jan. 9 on the Nature Physics website.
Lithium is the first metal in the periodic table and is the least dense solid element at room temperature. It is most commonly known ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
[Press-News.org] Carnegie Mellon researchers identify 'Facebook neurons'Population of highly active neurons could provide insight into the neocortex