(Press-News.org) Persistence paid off for a University of Alberta paleontology researcher, who after months of pondering the origins of a fossilized jaw bone, finally identified it as a new species of pterosaur, a flying reptile that lived 70 million years ago.
Victoria Arbour says she was stumped when the small piece of jaw bone was first pulled out of of a fossil storage cabinet in the U of A's paleontology department.
"It could have been from a dinosaur, a fish or a marine reptile," said Arbour. "
Arbour, a PhD student in paleontology, says the first clue to the fossil's identify came after she compared it to known species of pterosaurs, "I found a previously published paper describing the teeth of a previously discovered pterosaur and ours was very close," said Arbour.
"The teeth of our fossil were small and set close together," said Arbour. "They reminded me of piranha teeth, designed for pecking away at meat." That led Arbour to believe her new species, named Gwawinapterus beardi was a scavenger of the late Cretaceous. "It had a wing span of about 3 metres and patrolled the sky and set down to feed on the leftover kills made by predator dinosaurs of the time such as Albertosaurus."
The fossil is not only a new species it's the first pterosaur of any kind to be found in British Columbia. It was found on Hornby Island, off the coast of Vancouver Island
However, Arbour says the place where the fossil was located has little to do with the actual area where the living pterosaur, was actually flying around 70 million years ago.
"In the late Cretaceous period, the B.C. coastal islands were about 2,500 kilometres to the south and part of what is now mainland, California," said Arbour.
Arbour's research was published in the Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences.
INFORMATION: END
Glass stronger and tougher than steel? A new type of damage-tolerant metallic glass, demonstrating a strength and toughness beyond that of any known material, has been developed and tested by a collaboration of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab)and the California Institute of Technology. What's more, even better versions of this new glass may be on the way.
"These results mark the first use of a new strategy for metallic glass fabrication and we believe we can use it to make glass that will be even ...
Washington, D.C. — Sophisticated tools allow scientists to subject the basic elements of matter to conditions drastic enough to modify their behavior. By doing this, they can expand our understanding of matter. A research team including three Carnegie scientists was able to demonstrate surprising properties of the element lithium under intense pressure and low temperatures. Their results were published Jan. 9 on the Nature Physics website.
Lithium is the first metal in the periodic table and is the least dense solid element at room temperature. It is most commonly known ...
DURHAM, N.H. – An international team of researchers, including several from the University of New Hampshire, have completed the first DNA sequence of any strawberry plant, giving breeders much-needed tools to create tastier, healthier strawberries. Tom Davis, professor of biological sciences at UNH, and postdoctoral researcher Bo Liu were significant contributors to the genome sequence of the woodland strawberry, which was published last month in the journal Nature Genetics.
"We now have a resource for everybody who's interested in strawberry genetics. We can answer questions ...
NJIT Distinguished Professor Philip R. Goode and the research team at Big Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO) have reported new insights into the small-scale dynamics of the Sun's photosphere. The observations were made during a period of historic inactivity on the Sun and reported in The Astrophysical Journal . http://iopscience.iop.org/2041-8205/714/1/L31 The high-resolution capabilities of BBSO's new 1.6-meter aperture solar telescope have made such work possible.
"The smallest scale photospheric magnetic field seems to come in isolated points in the dark intergranular ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — In the longest-term study so far to track people with body dysmorphic disorder, a severe mental illness in which sufferers obsess over nonexistent or slight defects in their physical appearance, researchers at Brown University and Rhode Island Hospital found high rates of recovery, although recovery can take more than five years.
The results, based on following 15 sufferers of the disease over an eight-year span, appear in the current issue of the Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease.
"Compared to what we expected based on a prior ...
In recent years, developers have been investigating light-harvesting thin film solar panels made from nanotechnology –– and promoting efficiency metrics to make the technology marketable. Now a Tel Aviv University researcher is providing new evidence to challenge recent "charge" measurements for increasing solar panel efficiency.
Offering a less expensive, smaller solution than traditional panels, Prof. Eran Rabani of Tel Aviv University's School of Chemistry at the Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty of Exact Sciences puts a lid on some current hype that promises to ...
A new study conducted by Josh LaBaer's research team in the Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University has pinpointed more than 30 breast cancer gene targets ---including several novel genes---that are involved in drug resistance to a leading chemotherapy treatment.
The results of the study may one day aid in the treatment of the one in ten U.S. women who will develop breast cancer, by empowering physicians with a more personalized approach to therapy as well as a new tool for the early screening of those that may ultimately become resistant to chemotherapy.
Drugs ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Using detailed land analysis, Illinois researchers have found that biofuel crops cultivated on available land could produce up to half of the world's current fuel consumption – without affecting food crops or pastureland.
Published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology, the study led by civil and environmental engineering professor Ximing Cai identified land around the globe available to produce grass crops for biofuels, with minimal impact on agriculture or the environment.
Many studies on biofuel crop viability focus on biomass yield, ...
University of Illinois research reports that several herbicides used on corn also have good selectivity to Miscanthus x giganteus (Giant Miscanthus), a potential bioenergy feedstock.
"No herbicides are currently labeled for use in Giant Miscanthus grown for biomass," said Eric Anderson, an instructor of bioenergy for the Center of Advanced BioEnergy Research at the University of Illinois. "Our research shows that several herbicides used on corn are also safe on this rhizomatous grass."
M. x giganteus is sterile and predominantly grown by vegetative propagation, or planting ...
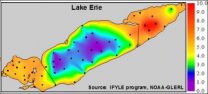
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Large hypoxic zones low in oxygen long have been thought to have negative influences on aquatic life, but a Purdue University study shows that while these so-called dead zones have an adverse affect, not all species are impacted equally.
Tomas Höök, an assistant professor of forestry and natural resources, and former Purdue postdoctoral researcher Kristen Arend used output from a model to estimate how much dissolved oxygen was present in Lake Erie's hypoxic zone each day from 1987 to 2005. That information was compared with biological ...