(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Jan. 9, 2024 – Badminton traces its roots back more than a millennium, but the modern version of the racket game originated in the late 19th century in England. Today, it is the second most popular sport in the world behind soccer, with an estimated 220 million people who enjoy playing. For the last three decades, badminton has been a competitive Olympic sport, and with “bird” speeds topping 300 mph in “smash” shots, it certainly makes for exciting spectator sport.
Shuttlecocks, also known as birdies or birds, are traditionally made from duck feathers, but nylon shuttlecocks have become more widely used because of their superior durability. Their flight behavior, however, is far different from that of traditional feather birdies.
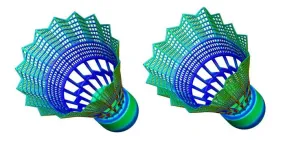
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, a trio of scientists in India explored the aerodynamic performance of nylon shuttlecocks at various flight speeds. Through computational analyses based on two-way fluid-structure interactions, the team coupled equations governing air flow with equations determining skirt deformation of a shuttlecock in flight.
“We studied the flow by examining aerodynamic forces on the shuttlecock as well as its deformations at each flight speed,” said author Sanjay Mittal. “The pressure on the skirt causes it to deform inwards and this deformation increases with speed.”
The team identified four distinct regimes of deformation. At speeds less than 40 meters per second (89 mph), the skirt maintains circularity despite cross-sectional deformation; at higher speeds, it buckles and deforms into a square before it then vibrates radially. Eventually, it undergoes a low frequency wavelike circumferential deformation.
“The cross-sectional area of the shuttlecock decreases with speed, which lowers the air flow rate through the shuttlecock,” said Mittal. “The vortex structures that form inside the shuttlecock weaken when it deforms. As a result of these effects, the deformed shuttlecock offers a much lower air resistance compared to its rigid counterpart.”
The study’s computational results confirm experimental measurements, explaining the phenomenology of why a duck feather shuttlecock does not deform as much as a nylon shuttlecock – and why the flight of each at high speed is quite different. From the perspective of a player on the receiving end of a smash shot, the nylon shuttlecock, which travels faster, is harder to return.
Ultimately, the research may represent a new arc in the history of the beloved sport.
“Our study opens up the possibility for improved designs that make the nylon shuttlecock structurally stiffer so that it more closely mimics the aerodynamic performance of feather shuttlecocks,” said Mittal. “This could be a game-changer, literally.”
###
The article “Computational analysis of the fluid-structure interactions of a synthetic badminton shuttlecock” is authored by Darshankumar Zala, Harish Dechiraju, and Sanjay Mittal. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on Jan. 9, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0182411). After that date, it can be accessed at http://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0182411.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
END
Rallying for a better badminton birdie
Study examines aerodynamic performance of nylon shuttlecocks
2024-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vaccine boosts innate immunity in people with dormant immune cells
2024-01-09
Humans are protected by two branches of the immune system. Innate immunity provides built-in defense against widespread characteristics of bacteria and viruses, while adaptive immunity memorizes individual pathogens that a person has already encountered. Vaccines teach the adaptive immune system about new pathogens without having to go through an actual infection. This has greatly contributed to human health, but requires a specific vaccine for each major pathogen.
Some vaccines not only teach the adaptive immune system ...
New research shows mobile methadone units are most impactful in rural areas
2024-01-09
While mobile methadone units make a difference in expanding methadone use for patients with opioid addictions, they are likely to be most impactful in rural areas, according to new research.
The research was published today in Health Services Research and focused on the impact of adding new treatment services exclusively to rural Louisiana, where like in many other remote parts of the country, there are limited healthcare infrastructures and barriers to transportation. They compared this data to the impact of ...
PNNL kicks off multi-year energy storage, scientific discovery collaboration with Microsoft
2024-01-09
The urgent need to meet global clean energy goals has world leaders searching for faster solutions. To meet that call, the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has teamed with Microsoft to use high-performance computing in the cloud and advanced artificial intelligence to accelerate scientific discovery on a scale not previously demonstrated. The initial focus of the partnership is chemistry and materials science—two scientific fields that underpin solutions to global energy challenges.
“The intersection of AI, cloud and high-performance computing, along with human scientists, we believe is key to accelerating the path to meaningful scientific ...
The hidden identity of leukemia
2024-01-09
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) use various technologies to better characterize a rare form of leukemia on the molecular level
Tokyo, Japan – Leukemia is a common term used to refer to a form of blood cancer. However, there are different types of leukemia depending on the cell type involved. One unique form is myeloid/natural killer (NK) cell precursor acute leukemia (MNKPL). Because of its rarity, there is no consensus on the specific characteristics needed to clinically identify this disease. In a recent article ...
Unique framework of tin bimetal organic compound facilitates stable lithium-ion storage
2024-01-09
Battery capacity is one of the primary bottlenecks in efficient renewable energy storage and significant reductions in carbon emissions. As a battery anode that releases electrons in a lithium-ion battery (LIB), tin (Sn) and Sn-mixture alloys could theoretically store more energy at a higher density than more common carbon-based anodes. Pairing a Sn-Ti bimetal element with inexpensive ethylene glycol (Sn-Ti-EG) mitigated many of the challenges of using Sn as an anode material and produced an inexpensive LIB with excellent storage and performance characteristics.
Sn and Sn alloys, or mixture of another metal with Sn, could outperform other anode materials ...
Attribution of the extreme drought in eastern China in 2022 and its future risk
2024-01-09
Eastern China was hit by an extreme drought in summer 2022 that caused severe economic and agricultural damage. The event has attracted a great deal of attention not only because of its severe intensity and huge social impacts, but also because it is yet another example within the hot topic of the influence of anthropogenic forcing induced warming on drought extremes and how they might change under different scenarios of continued warming in the future.
Recently, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters published ...
Increasing levels of "hype" language in grant applications and publications
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—The success of scientific endeavors often depends on support from public research grants. Successful applicants increasingly describe their proposed research using promotional language ("hype"); however, it remains unclear whether they use hype in their subsequent research publications.
A research team led by the University of Tsukuba analyzed all published research abstracts of projects funded by the US National Institute of Health (NIH) from 1985 to 2020. The analysis covered 139 hype adjectives emphasizing significance ...
Is spa water a fossil of water? Uncover the real ultra-deep water cycles
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—Although most natural spa waters primarily originate from atmospheric precipitation, such as rain and snow (known as meteoric water), the present study explored the unique qualities of certain spa waters. By analyzing the stable isotope compositions of hydrogen and oxygen in water molecules, researchers have identified distinct characteristics that indicate the presence of long-trapped lithospheric water. They traced the isotopic evolution of this water through sophisticated numerical modeling, and found that various types of water, including those found deep beneath the ...
Light measurement enables estimation of the chemical attributes of spice extracts
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—Spices and other plant-derived products contain many active components, such as polyphenols and flavonoids. However, even the slightest variations in conditions can considerably affect the extraction efficiency of these active components, posing challenges in determining the exact quantity of active components in the extract solution.
In this study, researchers comprehensively measured the fluorescence emitted by polyphenols and flavonoids and analyzed the acquired data using machine learning methods. ...
Nemours Children’s Health researchers find Zika virus is effective when used to treat a type of childhood cancer in mice
2024-01-09
ORLANDO, Fla. (Jan. 9, 2024) — Injecting neuroblastoma tumors with Zika virus shrank or eliminated those tumors in studies with mice, suggesting that the virus could someday serve as an effective cancer therapy, according to a study led by Nemours Children’s Health researchers and published today in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Neuroblastoma is a rare childhood cancer that typically develops in the sympathetic nervous system or the adrenal glands. Only 700 to 800 cases are diagnosed each year in the United States, accounting for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] Rallying for a better badminton birdieStudy examines aerodynamic performance of nylon shuttlecocks