(Press-News.org) Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) use various technologies to better characterize a rare form of leukemia on the molecular level
Tokyo, Japan – Leukemia is a common term used to refer to a form of blood cancer. However, there are different types of leukemia depending on the cell type involved. One unique form is myeloid/natural killer (NK) cell precursor acute leukemia (MNKPL). Because of its rarity, there is no consensus on the specific characteristics needed to clinically identify this disease. In a recent article published in Science Advances, a team led by researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) used various approaches to better assess the molecular profile and drug sensitivity characteristics of MNKPL.
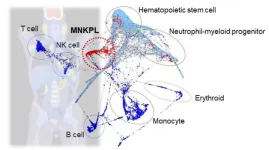
MNKPL was only first proposed as a leukemia subtype in 1997. Extramedullary involvement is one of the hallmarks of MNKPL. It is prevalent in East Asian countries. Although the immunological phenotype of MNKPL was explored previously, a full genetic characterization of this cancer type had not been performed. These details would help support more accurate diagnoses for patients, which would lead to more appropriate therapeutic decisions. Therefore, the TMDU group aimed to investigate MNKPL on a single-cell level.
“A single-cell exploration of MNKPL would not only help us better understand its clinical and genomic features, but also clarify the specific cellular origin of this disease,” says Dr. Akira Nishimura, lead author of the study.
The team first used what is known as a multiomics approach to investigate MNKPL patient samples. They used various sequencing technologies to determine if there were any relevant mutations in specific genes, look for expression differences in certain signaling pathways at the RNA level, and examine any unique DNA methylation patterns.
“Our results demonstrate that MNKPL has molecular qualities that are distinct from other similar cancers, such as acute myeloid leukemia, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and mixed-phenotype acute leukemia,” explains Dr. Masatoshi Takagi, senior author. “Specific hallmarks of MNKPL include activation of the NOTCH1 and RUNX3, as well as lower expression of the BCL11B.”
Further work at the single-cell level in MNKPL cells showed that NK cells and myeloid cells come from a common progenitor cell type.
The researchers also conducted in vitro drug sensitivity assays where they measured MNKPL cell responses to 79 individual anti-cancer drugs.
“We observed that MNKPL cells were highly sensitive to a drug called L-asparaginase, which has already shown clinical effectiveness for this disease,” says Dr. Nishimura. “Mechanistically, we found that this was from low expression of asparagine synthetase, a quality that was distinct from other similar types of leukemia.”
Overall, the robust and comprehensive analysis performed in this study provides crucial molecular details for characterizing MNKPL. This work will undoubtedly help clinicians more effectively diagnose MNKPL and choice of therapeutic option. Additionally, this work provides data that will assist with novel therapeutic target identification and drug development in this leukemia.
###
The article, “Myeloid/Natural Killer (NK) Cell Precursor Acute Leukemia as a Distinct Leukemia Type,” was published in Science Advances at DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adj4407.
END
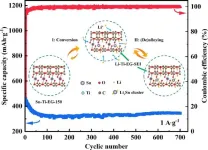
Battery capacity is one of the primary bottlenecks in efficient renewable energy storage and significant reductions in carbon emissions. As a battery anode that releases electrons in a lithium-ion battery (LIB), tin (Sn) and Sn-mixture alloys could theoretically store more energy at a higher density than more common carbon-based anodes. Pairing a Sn-Ti bimetal element with inexpensive ethylene glycol (Sn-Ti-EG) mitigated many of the challenges of using Sn as an anode material and produced an inexpensive LIB with excellent storage and performance characteristics.
Sn and Sn alloys, or mixture of another metal with Sn, could outperform other anode materials ...
Eastern China was hit by an extreme drought in summer 2022 that caused severe economic and agricultural damage. The event has attracted a great deal of attention not only because of its severe intensity and huge social impacts, but also because it is yet another example within the hot topic of the influence of anthropogenic forcing induced warming on drought extremes and how they might change under different scenarios of continued warming in the future.
Recently, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters published ...
Tsukuba, Japan—The success of scientific endeavors often depends on support from public research grants. Successful applicants increasingly describe their proposed research using promotional language ("hype"); however, it remains unclear whether they use hype in their subsequent research publications.
A research team led by the University of Tsukuba analyzed all published research abstracts of projects funded by the US National Institute of Health (NIH) from 1985 to 2020. The analysis covered 139 hype adjectives emphasizing significance ...
Tsukuba, Japan—Although most natural spa waters primarily originate from atmospheric precipitation, such as rain and snow (known as meteoric water), the present study explored the unique qualities of certain spa waters. By analyzing the stable isotope compositions of hydrogen and oxygen in water molecules, researchers have identified distinct characteristics that indicate the presence of long-trapped lithospheric water. They traced the isotopic evolution of this water through sophisticated numerical modeling, and found that various types of water, including those found deep beneath the ...
Tsukuba, Japan—Spices and other plant-derived products contain many active components, such as polyphenols and flavonoids. However, even the slightest variations in conditions can considerably affect the extraction efficiency of these active components, posing challenges in determining the exact quantity of active components in the extract solution.
In this study, researchers comprehensively measured the fluorescence emitted by polyphenols and flavonoids and analyzed the acquired data using machine learning methods. ...
ORLANDO, Fla. (Jan. 9, 2024) — Injecting neuroblastoma tumors with Zika virus shrank or eliminated those tumors in studies with mice, suggesting that the virus could someday serve as an effective cancer therapy, according to a study led by Nemours Children’s Health researchers and published today in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Neuroblastoma is a rare childhood cancer that typically develops in the sympathetic nervous system or the adrenal glands. Only 700 to 800 cases are diagnosed each year in the United States, accounting for ...
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 AM ET ON JANUARY 9, 2024
WASHINGTON (January 9, 2024) – Proceedings from an expert consensus roundtable that discussed the benefits of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in lower extremity revascularization procedures were released today in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (JSCAI), Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (JVIR), and Journal of Vascular Surgery - Vascular Insights.
The roundtable focused on the current challenges in diagnosing ...
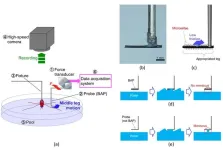
A research paper by scientists at the Ibaraki University analyzed the rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis.
The new research paper, published on Nov. 17 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, reported the rowing force of water striders obtained by direct and indirect measurements, and analyzed the maximum force arrival time and the middle leg angular velocity of the direct and indirect force measurements.
“Rowing force of the middle leg of a water ...
Prof. Sun-Uk Lee of the Department of Neurology and Prof. Euyhyun Park of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology from Korea University’s Anam Hospital discovered a new mechanism of vestibular neuritis.
Vestibular neuritis is one of the common diseases causing acute dizziness. It is known to be caused by an inflammation in the vestibular nerve and inner ear, which is responsible for balance and body motion sensation.
Various mechanisms had been suggesting as the cause of vestibular neuritis, such as reactivation of latent herpes virus or peripheral blood circulation disorder in the ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In an effort to make the internet more accessible for people with disabilities, researchers at The Ohio State University have begun developing an artificial intelligence agent that could complete complex tasks on any website using simple language commands.
In the three decades since it was first released into the public domain, the world wide web has become an incredibly intricate, dynamic system. Yet because internet function is now so integral to society’s well-being, its complexity also makes it considerably harder to navigate.
Today there ...