(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 AM ET ON JANUARY 9, 2024
WASHINGTON (January 9, 2024) – Proceedings from an expert consensus roundtable that discussed the benefits of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in lower extremity revascularization procedures were released today in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (JSCAI), Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (JVIR), and Journal of Vascular Surgery - Vascular Insights.
The roundtable focused on the current challenges in diagnosing and treating lower extremity revascularization, knowledge and data gaps, and the potential role of IVUS in addressing these challenges. Experts shared their insights and experiences from the fields of interventional cardiology, interventional radiology, and vascular surgery. The expert consensus meeting was convened by SCAI and co-sponsored by: American Vein and Lymphatic Society (AVLS), American Venous Forum (AVF), Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR), Society for Vascular Medicine (SVM), and Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS).
"Improvements in outcomes following peripheral vascular intervention have lagged compared to other endovascular treatments, such as percutaneous coronary intervention. Both clinical experience and evidence support the greater use of peripheral IVUS to reduce adverse events and extend the patency of our lower extremity revascularization procedures. By gathering experts from different specialties, we aimed to foster collaboration and exchange ideas to improve patient care for peripheral IVUS," said Eric A. Secemsky, MD, MSc, FSCAI, lead author of the proceedings document and Director of Vascular Intervention, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. "The roundtable provided a unique opportunity to identify knowledge gaps and discuss how IVUS can enhance our understanding and treatment of peripheral arterial and deep venous pathology."
Lower extremity revascularization is a critical procedure used to restore blood flow to the legs and feet in patients suffering from peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and deep venous pathology. It is estimated that millions of people worldwide are affected by these conditions, which can lead to severe pain, non-healing wounds, and even limb loss if left untreated. Although angiography is the dominant imaging modality in revascularization, it has inherent limitations. IVUS is a minimally invasive imaging technique that allows physicians to visualize the inside of blood vessels in real-time. It provides detailed information about the vessel wall, plaque composition, and blood flow characteristics, enabling more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
During the roundtable, participants highlighted the potential of IVUS in guiding revascularization procedures, such as angioplasty and stenting, to optimize outcomes for patients. They also emphasized the need for further research and evidence to support the integration of IVUS into routine clinical practice.
"The insights gained from this roundtable will help shape future research, training and clinical guidelines in the field of lower extremity revascularization," Secemsky said. "By leveraging the power of IVUS, we can improve our ability to diagnose and treat patients, ultimately leading to better outcomes and quality of life."
The roundtable concluded with a commitment to ongoing interdisciplinary collaboration and knowledge sharing among physicians. Participants agreed that treatment standards, formal training programs and global quality metrics remain needed to improve patient care.
The considerations and consensus views shared in “Intravascular Ultrasound Use in Peripheral Arterial and Deep Venous Interventions: Multidisciplinary Expert Opinion From SCAI/AVF/AVLS/SIR/SVM/SVS” represent the opinion of the consensus committee members.
The article will be available online at 10:00 a.m. ET on January 9 at the following sources:
Secemsky EA, Aronow HE, Kwolek CJ, et al. Intravascular ultrasound use in peripheral arterial and deep venous interventions: multidisciplinary expert opinion from SCAI/AVF/AVLS/SIR/ SVM/SVS. J Soc Cardiovasc Angiogr Interv. Published online January 9, 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.jscai.2023.101205.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscai.2023.101205
Secemsky, EA, Aronow HD, Kwolek, CJ, et al. Intravascular ultrasound use in peripheral arterial and deep venous interventions: multidisciplinary expert opinion from SCAI/AVF/AVLS/SIR/SVM/SVS. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2024. https://www.jvir.org/; published online January 9, 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2023.11.006
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2023.11.006
Secemsky, EA, Aronow HD, Kwolek, CJ, et al. Intravascular ultrasound use in peripheral arterial and deep venous interventions: multidisciplinary expert opinion from SCAI/AVF/AVLS/SIR/SVM/SVS. JVS-Vascular Insights. Published online January 9, 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsvi.2023.100033.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvsvi.2023.100033
END
Multidisciplinary panel advocates for increased adoption of Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) in peripheral vascular interventions
SCAI, SIR, and SVS jointly publish Proceedings from Multispecialty Peripheral IVUS Roundtable
2024-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
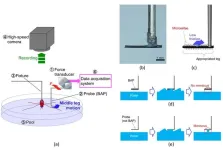
Analysis of rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis
2024-01-09
A research paper by scientists at the Ibaraki University analyzed the rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis.
The new research paper, published on Nov. 17 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, reported the rowing force of water striders obtained by direct and indirect measurements, and analyzed the maximum force arrival time and the middle leg angular velocity of the direct and indirect force measurements.
“Rowing force of the middle leg of a water ...
Discovering a new mechanism of vestibular neuritis
2024-01-09
Prof. Sun-Uk Lee of the Department of Neurology and Prof. Euyhyun Park of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology from Korea University’s Anam Hospital discovered a new mechanism of vestibular neuritis.
Vestibular neuritis is one of the common diseases causing acute dizziness. It is known to be caused by an inflammation in the vestibular nerve and inner ear, which is responsible for balance and body motion sensation.
Various mechanisms had been suggesting as the cause of vestibular neuritis, such as reactivation of latent herpes virus or peripheral blood circulation disorder in the ...
Researchers developing AI to make the internet more accessible
2024-01-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In an effort to make the internet more accessible for people with disabilities, researchers at The Ohio State University have begun developing an artificial intelligence agent that could complete complex tasks on any website using simple language commands.
In the three decades since it was first released into the public domain, the world wide web has become an incredibly intricate, dynamic system. Yet because internet function is now so integral to society’s well-being, its complexity also makes it considerably harder to navigate.
Today there ...
Scientists outline a bold solution to climate change, biodiversity loss, social injustice
2024-01-09
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An international team of scientists led by Oregon State University researchers has used a novel 500-year dataset to frame a “restorative” pathway through which humanity can avoid the worst ecological and social outcomes of climate change.
In addition to charting a possible new course for society, the researchers say their “paradigm shifting” plan can support climate modeling and discussion by providing a set of actions that strongly emphasize social and economic justice as well ...
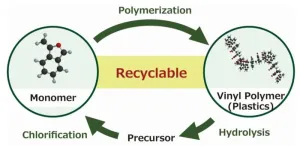
Novel chemical recycling system for vinyl polymers of cyclic styrene derivatives
2024-01-09
Chemical recycling of widely used vinyl polymers (VPs) is one of the key technologies required for realizing a sustainable society. In this regard, a team of researchers from Shinshu University have recently reported a new chemical process that facilitates the depolymerization of cyclic styrene-based VPs, resulting in the recovery of a monomer precursor. This highly efficient chemical recycling system can help with effective resource circulation and the development of new plastic recycling technologies.
Vinyl polymers (VPs) are ...
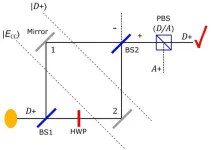
Quantum particles can’t separate from their properties, after all
2024-01-09
The quantum Cheshire cat effect draws its name from the fictional Cheshire Cat in the Alice in Wonderland story. That cat was able to disappear, leaving only its grin behind. Similarly, in a 2013 paper, researchers claimed quantum particles are able to separate from their properties, with the properties travelling along paths the particle cannot. They named this the quantum Cheshire cat effect. Researchers since have claimed to extend this further, swapping disembodied properties between particles, disembodying multiple properties simultaneously, ...
Press passes now available for Discover BMB to be held March 23–26
2024-01-09
Complimentary press passes are now available for Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB). Join us March 23–26 in San Antonio to experience an engaging agenda showcasing the newest developments and current trends in the field.
As the flagship meeting for one of the largest molecular life science organizations in the world, #DiscoverBMB brings together researchers in academia and industry from across the globe.
Explore captivating science stories and connect with leading experts during the scientific symposia, which will encompass 12 themes. Topics include:
Exciting ...
New CRISPR Center brings hope for rare and deadly genetic diseases
2024-01-09
Children and adults with rare, deadly genetic diseases have fresh hope for curative therapies, thanks to a new collaboration between the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI) and Danaher Corporation, a global life sciences and diagnostics innovator.
The new Danaher-IGI Beacon for CRISPR Cures center will use genome editing to address potentially hundreds of diseases, including rare genetic disorders that have no cure. The goal is to ensure treatments can be developed and brought to patients ...
Three researchers awarded $1 million each to study new heart disease treatments, causes
2024-01-09
DALLAS, Jan. 9, 2024 — A physician-scientist from Massachusetts researching whether chemicals naturally occurring in foods could help treat heart disease, a genetics expert from Pennsylvania exploring the molecular mechanisms of lipid metabolism and cardiovascular diseases and a California-based professor of cardiovascular medicine studying how vaping impacts the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms are the most recent American Heart Association Merit Award recipients. Over the next five years, each researcher will receive a total of $1 million in funding from the Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health and research, ...
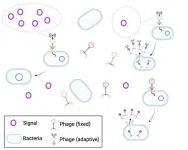
The value of information gathering for phages
2024-01-09
Phages, the viruses that infect bacteria, will pay a high growth-rate cost to access environmental information that can help them choose which lifecycle to pursue, according to a study. Yigal Meir and colleagues developed a model of a bacteria-phage system to investigate how much the viruses should be willing to invest to acquire information about their local environment. A temperate phage, once inside a bacterium, can choose one of two life cycles. In the lytic cycle, the phage turns the bacterium ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
Flagging claims about cancer treatment on social media as potentially false might help reduce spreading of misinformation, per online experiment with 1,051 US adults
Yawns in healthy fetuses might indicate mild distress
Conservation agriculture, including no-dig, crop-rotation and mulching methods, reduces water runoff and soil loss and boosts crop yield by as much as 122%, in Ethiopian trial
Tropical flowers are blooming weeks later than they used to through climate change
Risk of whale entanglement in fishing gear tied to size of cool-water habitat
Climate change could fragment habitat for monarch butterflies, disrupting mass migration
Neurosurgeons are really good at removing brain tumors, and they’re about to get even better
Almost 1-in-3 American adolescents has diabetes or prediabetes, with waist-to-height ratio the strongest independent predictor of prediabetes/diabetes, reveals survey of 1,998 adolescents (10-19 years
Researchers sharpen understanding of how the body responds to energy demands from exercise
New “lock-and-key” chemistry
Benzodiazepine use declines across the U.S., led by reductions in older adults
How recycled sewage could make the moon or Mars suitable for growing crops
Don’t Panic: ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’ has begun
A robust new telecom qubit in silicon
Vertebrate paleontology has a numbers problem. Computer vision can help
Reinforced enzyme expression drives high production of durable lactate-based polyester
In Rett syndrome, leaky brain blood vessels traced to microRNA
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
[Press-News.org] Multidisciplinary panel advocates for increased adoption of Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) in peripheral vascular interventionsSCAI, SIR, and SVS jointly publish Proceedings from Multispecialty Peripheral IVUS Roundtable