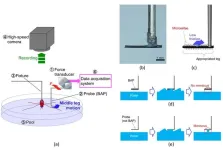
Analysis of rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis
2024-01-09
(Press-News.org)
A research paper by scientists at the Ibaraki University analyzed the rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis.
The new research paper, published on Nov. 17 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, reported the rowing force of water striders obtained by direct and indirect measurements, and analyzed the maximum force arrival time and the middle leg angular velocity of the direct and indirect force measurements.
“Rowing force of the middle leg of a water strider is one of the important factors affecting water repellency and applications in biomimetics, biomechanics and biology. However, many previous studies have been based on estimated leg rowing force and lack some credibility. Therefore, we tried to measure leg rowing force directly by a force transducer.” explained study author Dr. Keisuke Morishima, professor of Osaka University. In the direct measurement, water striders were set onto a sensor system and the rowing force of a middle leg of the set water striders was directly measured using a BAP, a kind of hook. In the indirect measurement, water striders were not fixed and the rowing force of locomoting water striders was evaluated by image analysis using a high-speed camera. “As a result, we determined the rowing force by the direct measurement to be 955 µN, while the rowing force by the indirect measurement was 488 µN.” said the author.
The microstructure of the water strider’s legs has been studied in developing semi-aquatic devices and robot. If more details about the rowing force are known, understanding will be deepened. “By determining and comparing the rowing forces which were measured by the direct and the indirect force measurements, we could discuss various properties of the water striders such as their water repellency, and we could also discuss applications to biomechanics and biology.” said Dr. Kaoru Uesugi.
The study authors proposed that measure leg rowing force directly by a force transducer. Additionally, in order to decrease the effect of a meniscus, a BAP was developed. By using the measurement method and system and the BAP, the rowing force by the direct measurement to be 955 µN, while the rowing force by the indirect measurement (image analysis) was 488 µN.
“There are a few studies which have dealt with direct and indirect force measurements. By comparing different types of force measurements, we successfully clarified the differences of these forces measured directly and indirectly.” said Dr. Kaoru Uesugi. Totally, the study can contribute to the fields of surface physics, biomechanics and biology, and inspiring innovation around it.
Authors of the paper include Kaoru Uesugi, Hiroyuki Mayama, Keisuke Morishima
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI [grant number 22K03805].
The paper, “Analysis of Rowing Force of the Water Strider Middle Leg by Direct Measurement Using a Bio-Appropriating Probe and by Indirect Measurement Using Image Analysis” was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Nov 17, 2023, at DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0061.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-09
Prof. Sun-Uk Lee of the Department of Neurology and Prof. Euyhyun Park of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology from Korea University’s Anam Hospital discovered a new mechanism of vestibular neuritis.
Vestibular neuritis is one of the common diseases causing acute dizziness. It is known to be caused by an inflammation in the vestibular nerve and inner ear, which is responsible for balance and body motion sensation.
Various mechanisms had been suggesting as the cause of vestibular neuritis, such as reactivation of latent herpes virus or peripheral blood circulation disorder in the ...
2024-01-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In an effort to make the internet more accessible for people with disabilities, researchers at The Ohio State University have begun developing an artificial intelligence agent that could complete complex tasks on any website using simple language commands.
In the three decades since it was first released into the public domain, the world wide web has become an incredibly intricate, dynamic system. Yet because internet function is now so integral to society’s well-being, its complexity also makes it considerably harder to navigate.
Today there ...
2024-01-09
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An international team of scientists led by Oregon State University researchers has used a novel 500-year dataset to frame a “restorative” pathway through which humanity can avoid the worst ecological and social outcomes of climate change.
In addition to charting a possible new course for society, the researchers say their “paradigm shifting” plan can support climate modeling and discussion by providing a set of actions that strongly emphasize social and economic justice as well ...
2024-01-09
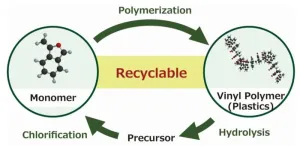
Chemical recycling of widely used vinyl polymers (VPs) is one of the key technologies required for realizing a sustainable society. In this regard, a team of researchers from Shinshu University have recently reported a new chemical process that facilitates the depolymerization of cyclic styrene-based VPs, resulting in the recovery of a monomer precursor. This highly efficient chemical recycling system can help with effective resource circulation and the development of new plastic recycling technologies.
Vinyl polymers (VPs) are ...
2024-01-09
The quantum Cheshire cat effect draws its name from the fictional Cheshire Cat in the Alice in Wonderland story. That cat was able to disappear, leaving only its grin behind. Similarly, in a 2013 paper, researchers claimed quantum particles are able to separate from their properties, with the properties travelling along paths the particle cannot. They named this the quantum Cheshire cat effect. Researchers since have claimed to extend this further, swapping disembodied properties between particles, disembodying multiple properties simultaneously, ...
2024-01-09
Complimentary press passes are now available for Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB). Join us March 23–26 in San Antonio to experience an engaging agenda showcasing the newest developments and current trends in the field.
As the flagship meeting for one of the largest molecular life science organizations in the world, #DiscoverBMB brings together researchers in academia and industry from across the globe.
Explore captivating science stories and connect with leading experts during the scientific symposia, which will encompass 12 themes. Topics include:
Exciting ...
2024-01-09
Children and adults with rare, deadly genetic diseases have fresh hope for curative therapies, thanks to a new collaboration between the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI) and Danaher Corporation, a global life sciences and diagnostics innovator.
The new Danaher-IGI Beacon for CRISPR Cures center will use genome editing to address potentially hundreds of diseases, including rare genetic disorders that have no cure. The goal is to ensure treatments can be developed and brought to patients ...
2024-01-09
DALLAS, Jan. 9, 2024 — A physician-scientist from Massachusetts researching whether chemicals naturally occurring in foods could help treat heart disease, a genetics expert from Pennsylvania exploring the molecular mechanisms of lipid metabolism and cardiovascular diseases and a California-based professor of cardiovascular medicine studying how vaping impacts the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms are the most recent American Heart Association Merit Award recipients. Over the next five years, each researcher will receive a total of $1 million in funding from the Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health and research, ...
2024-01-09
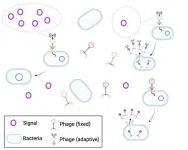
Phages, the viruses that infect bacteria, will pay a high growth-rate cost to access environmental information that can help them choose which lifecycle to pursue, according to a study. Yigal Meir and colleagues developed a model of a bacteria-phage system to investigate how much the viruses should be willing to invest to acquire information about their local environment. A temperate phage, once inside a bacterium, can choose one of two life cycles. In the lytic cycle, the phage turns the bacterium ...
2024-01-09
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Researchers from Binghamton University, State University of New York are unraveling the workings of Group B Strep (GBS) infections in pregnant women, which could someday lead to a vaccine.
One in five pregnant women carry Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Strep or GBS) in the vaginal tract, which is typically harmless — except when it isn’t.
The bacterial infection poses serious and even fatal consequences for newborns, including pneumonia, sepsis and meningitis, which can have long-term effects on the child’s cognitive function.
Researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Analysis of rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis