Attribution of the extreme drought in eastern China in 2022 and its future risk
2024-01-09
(Press-News.org)
Eastern China was hit by an extreme drought in summer 2022 that caused severe economic and agricultural damage. The event has attracted a great deal of attention not only because of its severe intensity and huge social impacts, but also because it is yet another example within the hot topic of the influence of anthropogenic forcing induced warming on drought extremes and how they might change under different scenarios of continued warming in the future.
Recently, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters published a paper titled “Anthropogenic influence on the extreme drought in eastern China in 2022 and its future risk” by Professor Chen’s team from Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology. This research analyzed the anthropogenic impact on the occurrence probability of a “2022Drought-like event” and provided the projected changes of such an event under various future emission scenarios.
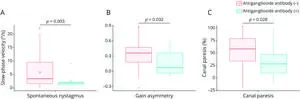
Based on DAMIP (Detection and Attribution Model Intercomparison Project) results, it was found that anthropogenic forcing increases the occurrence probability of a 2022Drought-like event by 56%. This change is probably associated with the change in the mean climate state over the eastern China region, including decreased moisture and weakened upward motion. Collectively, the anthropogenic forcing–induced changes in the mean state may stunt convective activity, providing a favorable condition for the formation of drought extremes.
“We further analyzed the responses of 2022Drought-like events to different warming scenarios, and found that, under a low-emissions scenario, the risk of such an event occurring declines dramatically, probably because of increased background moisture and enhanced upward motion. In sharp contrast, the high-emissions scenario simulations projected a 79% higher chance of a 2022Drought-like event happening than under present-day conditions, probably because of significantly enhanced background descending motion. The results indicate a nonlinear change in the occurrence of 2022Drought-like events in response to a warmer world”, explains Professor Chen.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—The success of scientific endeavors often depends on support from public research grants. Successful applicants increasingly describe their proposed research using promotional language ("hype"); however, it remains unclear whether they use hype in their subsequent research publications.
A research team led by the University of Tsukuba analyzed all published research abstracts of projects funded by the US National Institute of Health (NIH) from 1985 to 2020. The analysis covered 139 hype adjectives emphasizing significance ...
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—Although most natural spa waters primarily originate from atmospheric precipitation, such as rain and snow (known as meteoric water), the present study explored the unique qualities of certain spa waters. By analyzing the stable isotope compositions of hydrogen and oxygen in water molecules, researchers have identified distinct characteristics that indicate the presence of long-trapped lithospheric water. They traced the isotopic evolution of this water through sophisticated numerical modeling, and found that various types of water, including those found deep beneath the ...
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—Spices and other plant-derived products contain many active components, such as polyphenols and flavonoids. However, even the slightest variations in conditions can considerably affect the extraction efficiency of these active components, posing challenges in determining the exact quantity of active components in the extract solution.
In this study, researchers comprehensively measured the fluorescence emitted by polyphenols and flavonoids and analyzed the acquired data using machine learning methods. ...
2024-01-09
ORLANDO, Fla. (Jan. 9, 2024) — Injecting neuroblastoma tumors with Zika virus shrank or eliminated those tumors in studies with mice, suggesting that the virus could someday serve as an effective cancer therapy, according to a study led by Nemours Children’s Health researchers and published today in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Neuroblastoma is a rare childhood cancer that typically develops in the sympathetic nervous system or the adrenal glands. Only 700 to 800 cases are diagnosed each year in the United States, accounting for ...
2024-01-09
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 AM ET ON JANUARY 9, 2024
WASHINGTON (January 9, 2024) – Proceedings from an expert consensus roundtable that discussed the benefits of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in lower extremity revascularization procedures were released today in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (JSCAI), Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (JVIR), and Journal of Vascular Surgery - Vascular Insights.
The roundtable focused on the current challenges in diagnosing ...
2024-01-09
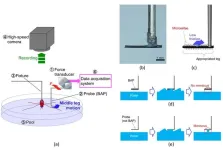
A research paper by scientists at the Ibaraki University analyzed the rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis.
The new research paper, published on Nov. 17 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, reported the rowing force of water striders obtained by direct and indirect measurements, and analyzed the maximum force arrival time and the middle leg angular velocity of the direct and indirect force measurements.
“Rowing force of the middle leg of a water ...
2024-01-09
Prof. Sun-Uk Lee of the Department of Neurology and Prof. Euyhyun Park of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology from Korea University’s Anam Hospital discovered a new mechanism of vestibular neuritis.
Vestibular neuritis is one of the common diseases causing acute dizziness. It is known to be caused by an inflammation in the vestibular nerve and inner ear, which is responsible for balance and body motion sensation.
Various mechanisms had been suggesting as the cause of vestibular neuritis, such as reactivation of latent herpes virus or peripheral blood circulation disorder in the ...
2024-01-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In an effort to make the internet more accessible for people with disabilities, researchers at The Ohio State University have begun developing an artificial intelligence agent that could complete complex tasks on any website using simple language commands.
In the three decades since it was first released into the public domain, the world wide web has become an incredibly intricate, dynamic system. Yet because internet function is now so integral to society’s well-being, its complexity also makes it considerably harder to navigate.
Today there ...
2024-01-09
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An international team of scientists led by Oregon State University researchers has used a novel 500-year dataset to frame a “restorative” pathway through which humanity can avoid the worst ecological and social outcomes of climate change.
In addition to charting a possible new course for society, the researchers say their “paradigm shifting” plan can support climate modeling and discussion by providing a set of actions that strongly emphasize social and economic justice as well ...
2024-01-09
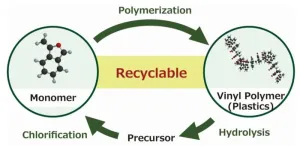
Chemical recycling of widely used vinyl polymers (VPs) is one of the key technologies required for realizing a sustainable society. In this regard, a team of researchers from Shinshu University have recently reported a new chemical process that facilitates the depolymerization of cyclic styrene-based VPs, resulting in the recovery of a monomer precursor. This highly efficient chemical recycling system can help with effective resource circulation and the development of new plastic recycling technologies.
Vinyl polymers (VPs) are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Attribution of the extreme drought in eastern China in 2022 and its future risk