(Press-News.org)
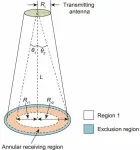
A team of researchers from Xidian University in China has achieved a new result in the field of microwave power transmission. Their study, published in Engineering, introduces an optimal design method for antenna aperture illumination with an annular collection area, with the goal of maximizing the power radiated on the collection area.
The research, led by Professor Baoyan Duan from Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Space Solar Power Station System, Xidian University, focused on formulating the aperture amplitude distribution using a unique set of series. As a result, they were able to simplify the optimal design problem to maximize the ratio of two real quadratic forms. Leveraging matrix theory, the team identified the solution to the optimization problem as determining the largest characteristic value and its associated characteristic vector.
In addressing security concerns, the researchers also integrated additional constraints to account for peak radiation levels outside the receiving area. To address this constrained optimization problem, they developed a hybrid grey wolf optimizer and Nelder–Mead simplex method. The effectiveness of this novel approach was confirmed through numerical experiments using continuous apertures. Furthermore, the optimized results were validated using discrete arrays of isotropic elements, along with patch arrays.
The newly proposed method offers several advantages in the field of microwave power transmission. “Our optimal design method enables the achievement of maximum beam collection efficiency (BCE) while satisfying security requirements,” explained the team. “This method allows for the design of continuous aperture distributions to maximize BCE, with or without extra constraints, and facilitates the easy design of array antennas of various sizes.”
The impact of this research extends beyond annular collection areas. The team emphasized, “Our method is not only applicable to annular collection areas but also extends to microwave power transmission applications with circular collection areas, as the circular collection area is a special case of an annular collection area.”
This breakthrough in optimal design methods for antenna aperture illumination holds significant potential for advancing microwave power transmission technologies. It has the capacity to optimize power radiated on collection areas, leading to more efficient and effective transmission of microwave power.
The research conducted by the team at Xidian University represents a promising development in the field. Their approach introduces new possibilities for enhancing the design and performance of microwave power transmission systems. As the demand for wireless power transfer continues to grow, advancements like these are crucial.
The paper “Optimal Design of Aperture Illuminations for Microwave Power Transmission with Annular Collection Areas,” authored by Xun Li, Baoyan Duan, Yiqun Zhang, Yongxin Guo. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.07.016. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on Twitter (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringPortfolio).
About Engineering:
Engineering (ISSN: 2095-8099 IF:12.8) is an international open-access journal that was launched by the Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE) in 2015. Its aims are to provide a high-level platform where cutting-edge advancements in engineering R&D, current major research outputs, and key achievements can be disseminated and shared; to report progress in engineering science, discuss hot topics, areas of interest, challenges, and prospects in engineering development, and consider human and environmental well-being and ethics in engineering; to encourage engineering breakthroughs and innovations that are of profound economic and social importance, enabling them to reach advanced international standards and to become a new productive force, and thereby changing the world, benefiting humanity, and creating a new future.
END
About The Study: Racial disparities in rates of general anesthesia continue to exist; however, the findings of this study including 35,000 patients who underwent cesarean delivery suggest that, for laboring patients who had labor epidural catheters in situ, no disparity by race or ethnicity existed. Future studies should address whether disparities in care that occur prior to neuraxial catheter placement are associated with higher rates of general anesthesia among patients from ethnic and racial minority groups.
Authors: Caroline Leigh Thomas, M.D., of ...
About The Study: In this study of 952,000 participants, women with perinatal depression were at an increased risk of suicidal behavior, particularly within the first year after diagnosis with persistent risk elevations throughout the 18 years of follow-up, highlighting the need for vigilant clinical monitoring of this vulnerable group.
Authors: Hang Yu, M.Sc., and Donghao Lu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.50897)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
WASHINGTON, Jan. 9, 2024 – Badminton traces its roots back more than a millennium, but the modern version of the racket game originated in the late 19th century in England. Today, it is the second most popular sport in the world behind soccer, with an estimated 220 million people who enjoy playing. For the last three decades, badminton has been a competitive Olympic sport, and with “bird” speeds topping 300 mph in “smash” shots, it certainly makes for exciting spectator sport.
Shuttlecocks, also known as birdies or birds, are ...
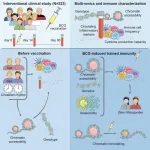
Humans are protected by two branches of the immune system. Innate immunity provides built-in defense against widespread characteristics of bacteria and viruses, while adaptive immunity memorizes individual pathogens that a person has already encountered. Vaccines teach the adaptive immune system about new pathogens without having to go through an actual infection. This has greatly contributed to human health, but requires a specific vaccine for each major pathogen.
Some vaccines not only teach the adaptive immune system ...
While mobile methadone units make a difference in expanding methadone use for patients with opioid addictions, they are likely to be most impactful in rural areas, according to new research.
The research was published today in Health Services Research and focused on the impact of adding new treatment services exclusively to rural Louisiana, where like in many other remote parts of the country, there are limited healthcare infrastructures and barriers to transportation. They compared this data to the impact of ...
The urgent need to meet global clean energy goals has world leaders searching for faster solutions. To meet that call, the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has teamed with Microsoft to use high-performance computing in the cloud and advanced artificial intelligence to accelerate scientific discovery on a scale not previously demonstrated. The initial focus of the partnership is chemistry and materials science—two scientific fields that underpin solutions to global energy challenges.
“The intersection of AI, cloud and high-performance computing, along with human scientists, we believe is key to accelerating the path to meaningful scientific ...
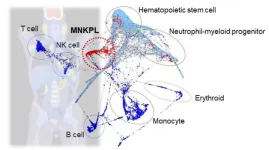
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) use various technologies to better characterize a rare form of leukemia on the molecular level
Tokyo, Japan – Leukemia is a common term used to refer to a form of blood cancer. However, there are different types of leukemia depending on the cell type involved. One unique form is myeloid/natural killer (NK) cell precursor acute leukemia (MNKPL). Because of its rarity, there is no consensus on the specific characteristics needed to clinically identify this disease. In a recent article ...
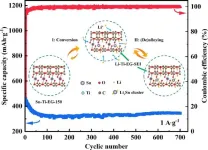
Battery capacity is one of the primary bottlenecks in efficient renewable energy storage and significant reductions in carbon emissions. As a battery anode that releases electrons in a lithium-ion battery (LIB), tin (Sn) and Sn-mixture alloys could theoretically store more energy at a higher density than more common carbon-based anodes. Pairing a Sn-Ti bimetal element with inexpensive ethylene glycol (Sn-Ti-EG) mitigated many of the challenges of using Sn as an anode material and produced an inexpensive LIB with excellent storage and performance characteristics.
Sn and Sn alloys, or mixture of another metal with Sn, could outperform other anode materials ...
Eastern China was hit by an extreme drought in summer 2022 that caused severe economic and agricultural damage. The event has attracted a great deal of attention not only because of its severe intensity and huge social impacts, but also because it is yet another example within the hot topic of the influence of anthropogenic forcing induced warming on drought extremes and how they might change under different scenarios of continued warming in the future.
Recently, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters published ...
Tsukuba, Japan—The success of scientific endeavors often depends on support from public research grants. Successful applicants increasingly describe their proposed research using promotional language ("hype"); however, it remains unclear whether they use hype in their subsequent research publications.
A research team led by the University of Tsukuba analyzed all published research abstracts of projects funded by the US National Institute of Health (NIH) from 1985 to 2020. The analysis covered 139 hype adjectives emphasizing significance ...